Thermostat Circuits
Affordable, straightforward, and precise thermostat circuits with instructions.
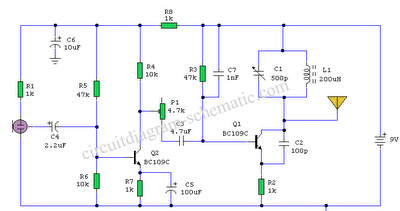
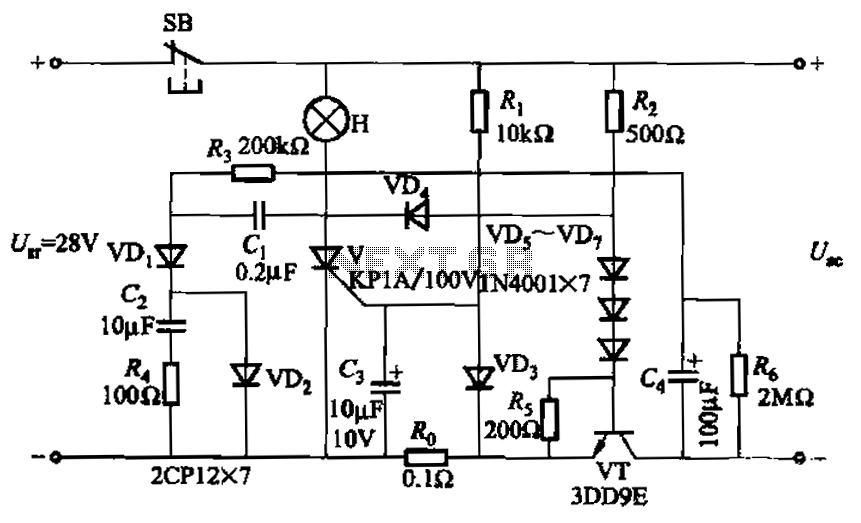
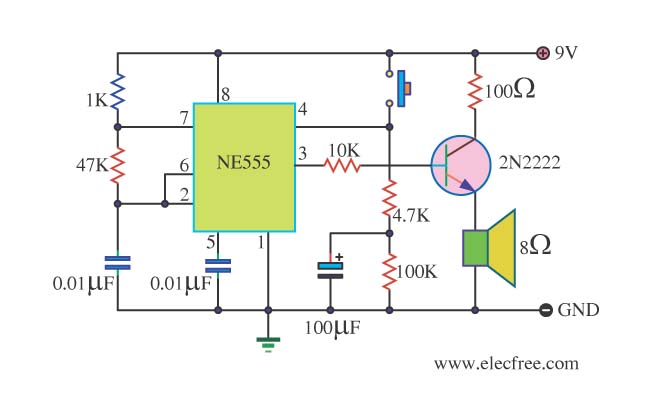
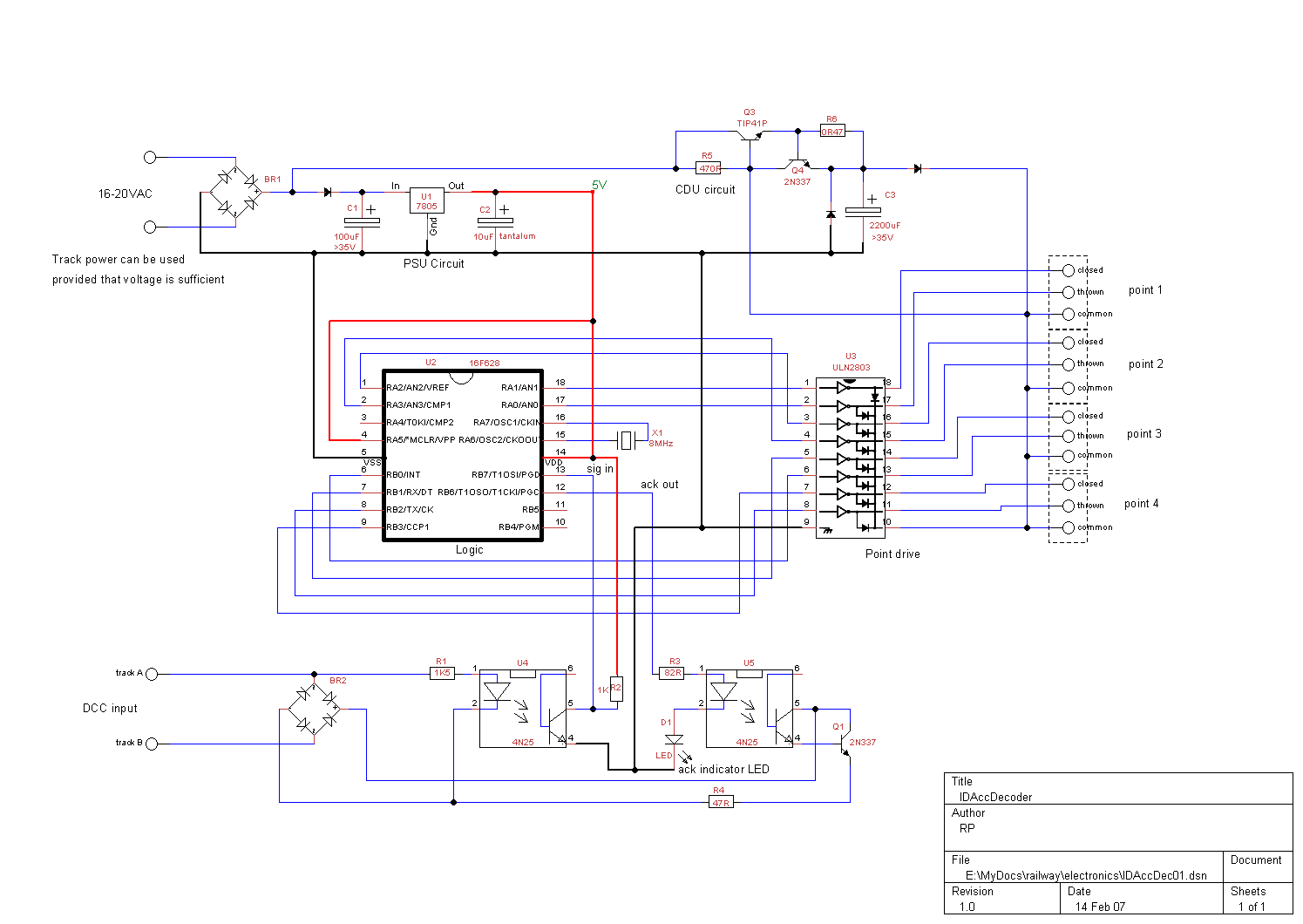
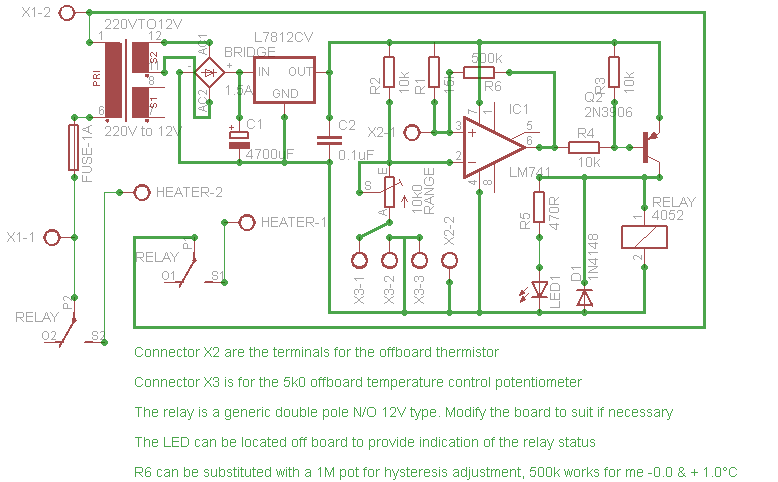
The thermostat circuit is designed to provide a cost-effective and reliable solution for temperature control applications. It typically utilizes a temperature sensor, such as a thermistor or a thermocouple, to monitor the ambient temperature. The output from the temperature sensor is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the measured temperature against a predetermined setpoint.
When the measured temperature deviates from the setpoint, the comparator activates a control mechanism, which can be a relay or a solid-state switch, to either engage or disengage a heating or cooling element. This feedback loop ensures that the temperature is maintained within a specified range, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort.
The simplicity of the circuit design allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it suitable for both hobbyists and professionals. Additionally, the use of low-cost components ensures that the overall expense remains minimal while still achieving high accuracy in temperature regulation.
For implementation, a basic schematic would include the following components: a power supply, a temperature sensor, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, a relay or transistor for controlling the load, and passive components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the circuit. Proper calibration of the temperature sensor and the comparator is essential for optimal performance, ensuring that the thermostat responds accurately to changes in temperature.
This type of thermostat circuit can be applied in various settings, including home heating systems, refrigeration units, and industrial temperature control systems, providing versatility and reliability in temperature management.Cheap, simple, and accurate thermostat circuits with instructions.. 🔗 External reference
The thermostat circuit is designed to provide a cost-effective and reliable solution for temperature control applications. It typically utilizes a temperature sensor, such as a thermistor or a thermocouple, to monitor the ambient temperature. The output from the temperature sensor is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the measured temperature against a predetermined setpoint.
When the measured temperature deviates from the setpoint, the comparator activates a control mechanism, which can be a relay or a solid-state switch, to either engage or disengage a heating or cooling element. This feedback loop ensures that the temperature is maintained within a specified range, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort.
The simplicity of the circuit design allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it suitable for both hobbyists and professionals. Additionally, the use of low-cost components ensures that the overall expense remains minimal while still achieving high accuracy in temperature regulation.
For implementation, a basic schematic would include the following components: a power supply, a temperature sensor, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, a relay or transistor for controlling the load, and passive components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the circuit. Proper calibration of the temperature sensor and the comparator is essential for optimal performance, ensuring that the thermostat responds accurately to changes in temperature.
This type of thermostat circuit can be applied in various settings, including home heating systems, refrigeration units, and industrial temperature control systems, providing versatility and reliability in temperature management.Cheap, simple, and accurate thermostat circuits with instructions.. 🔗 External reference