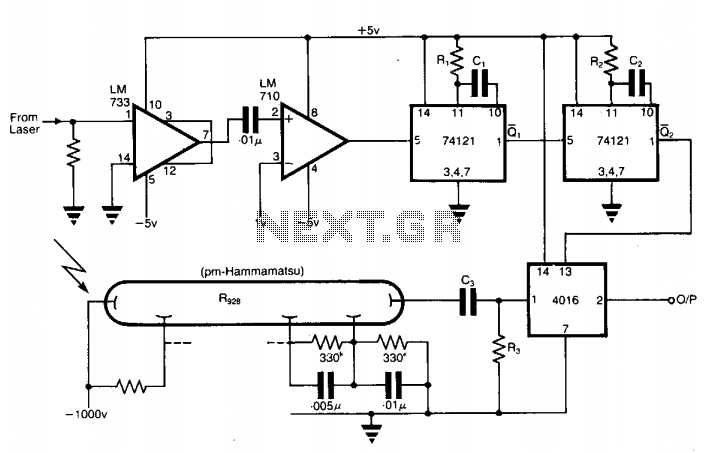
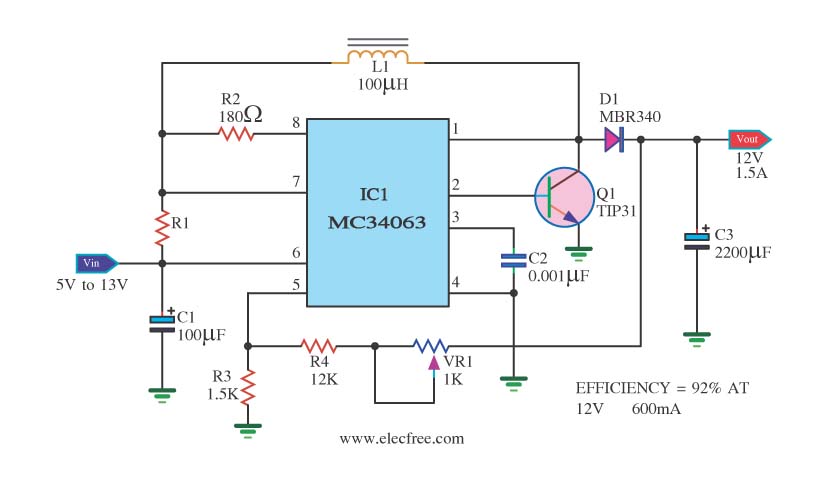
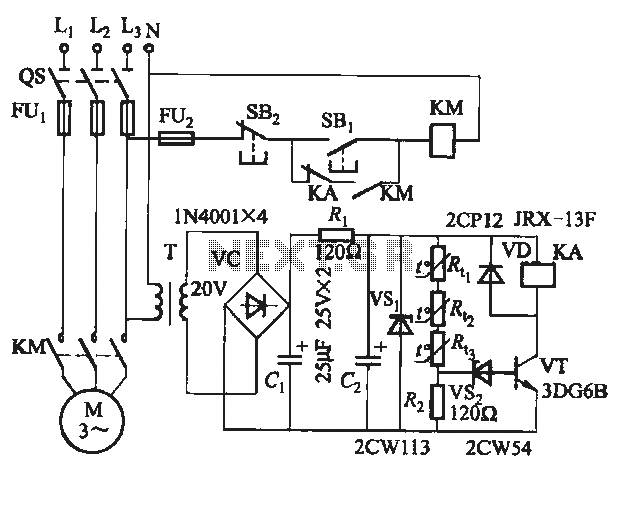
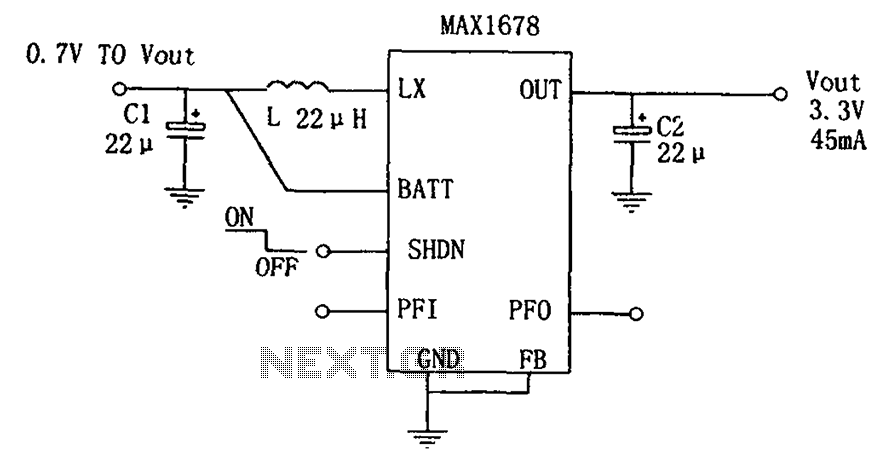
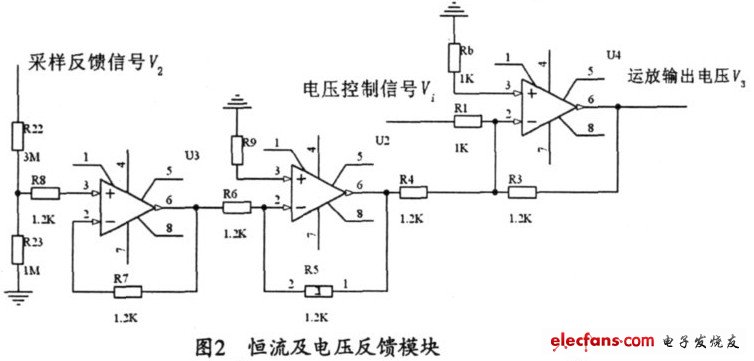
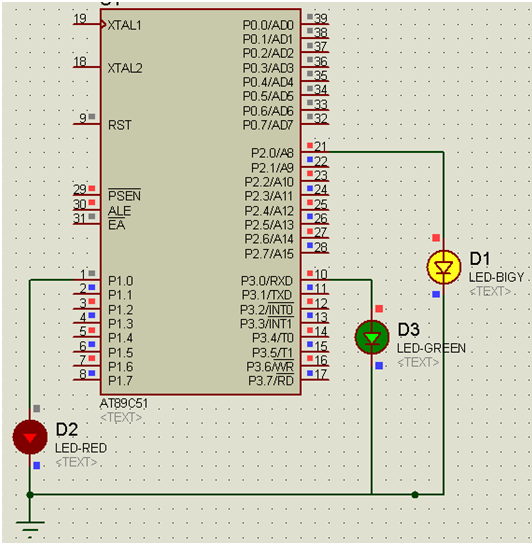
Three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connection and the output voltage waveform
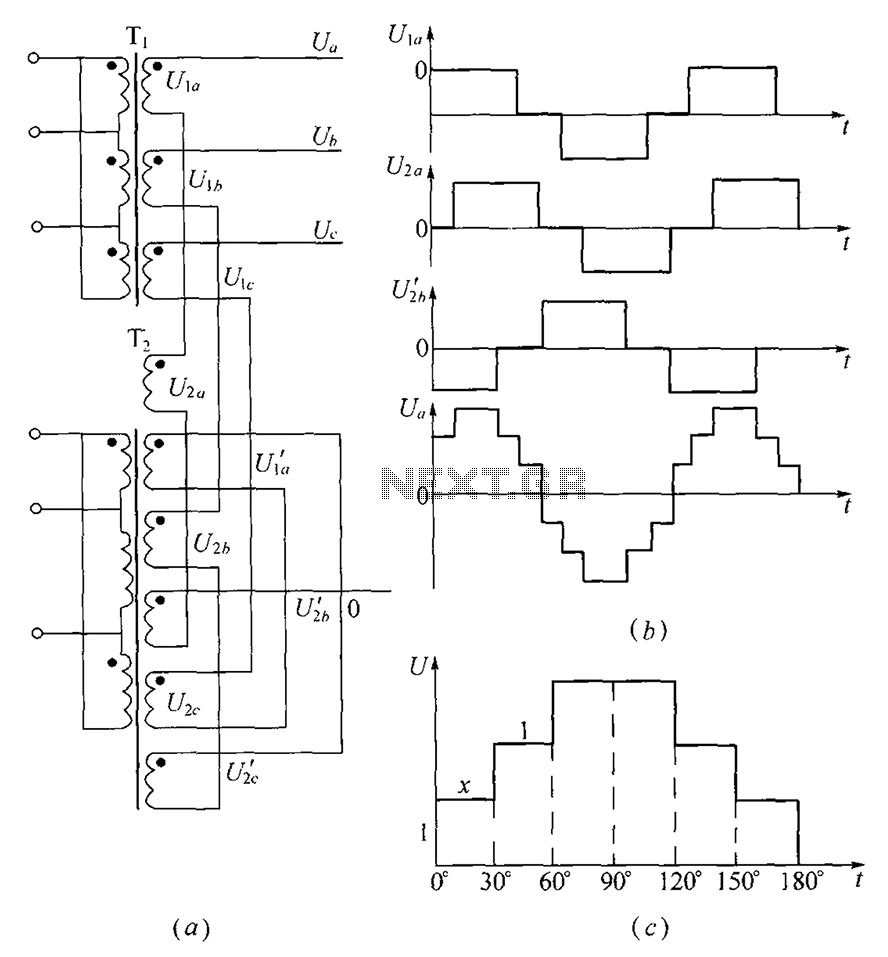
As shown, (a) for the three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connections; (b) in the figure, its output waveform.
The three-phase step wave inverter is designed to convert direct current (DC) into a three-phase alternating current (AC) output. This inverter utilizes transformer winding connections to achieve the desired output characteristics. The transformer plays a crucial role in stepping up or stepping down the voltage levels as required by the application.
In the schematic, the winding connections of the transformer are organized to facilitate the generation of a step wave output. Each phase of the inverter is connected to its respective winding, ensuring that the output is balanced and symmetrical, which is essential for the efficient operation of three-phase systems. The output waveform produced by the inverter is characterized by its step-like appearance, which is indicative of the switching mechanism employed in the inverter design.
The output waveform can be analyzed for its fundamental frequency and harmonic content, which are critical for determining the quality of the power delivered to the load. Proper filtering and modulation techniques may be applied to reduce any unwanted harmonics and improve the overall performance of the inverter.
In summary, the three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connections are integral to achieving a reliable and efficient AC output, while the output waveform reflects the inverter's operational characteristics and performance. As shown, (a) for the three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connections; (b) in FIG its output waveform.
The three-phase step wave inverter is designed to convert direct current (DC) into a three-phase alternating current (AC) output. This inverter utilizes transformer winding connections to achieve the desired output characteristics. The transformer plays a crucial role in stepping up or stepping down the voltage levels as required by the application.
In the schematic, the winding connections of the transformer are organized to facilitate the generation of a step wave output. Each phase of the inverter is connected to its respective winding, ensuring that the output is balanced and symmetrical, which is essential for the efficient operation of three-phase systems. The output waveform produced by the inverter is characterized by its step-like appearance, which is indicative of the switching mechanism employed in the inverter design.
The output waveform can be analyzed for its fundamental frequency and harmonic content, which are critical for determining the quality of the power delivered to the load. Proper filtering and modulation techniques may be applied to reduce any unwanted harmonics and improve the overall performance of the inverter.
In summary, the three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connections are integral to achieving a reliable and efficient AC output, while the output waveform reflects the inverter's operational characteristics and performance. As shown, (a) for the three-phase step wave inverter output transformer winding connections; (b) in FIG its output waveform.