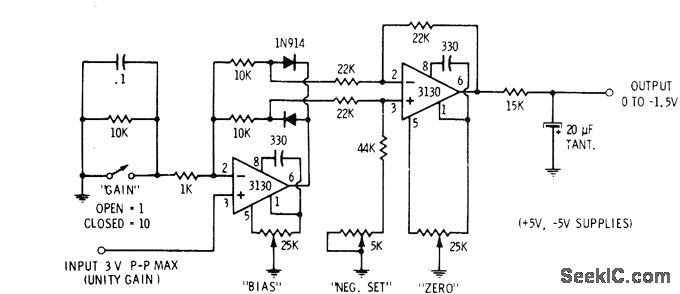
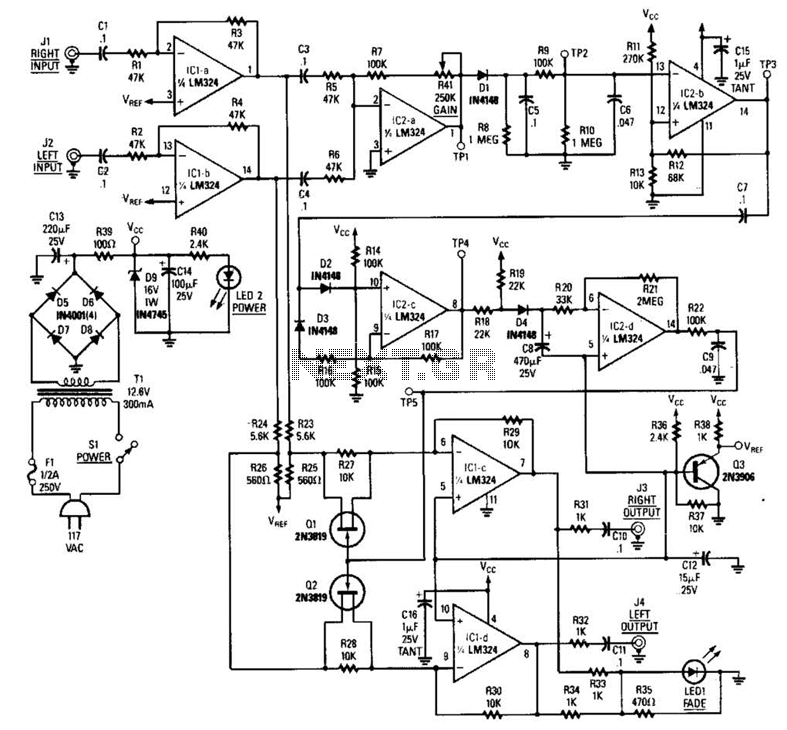
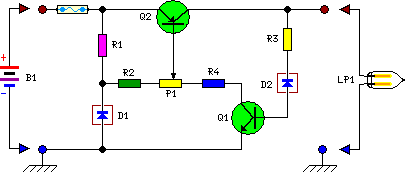
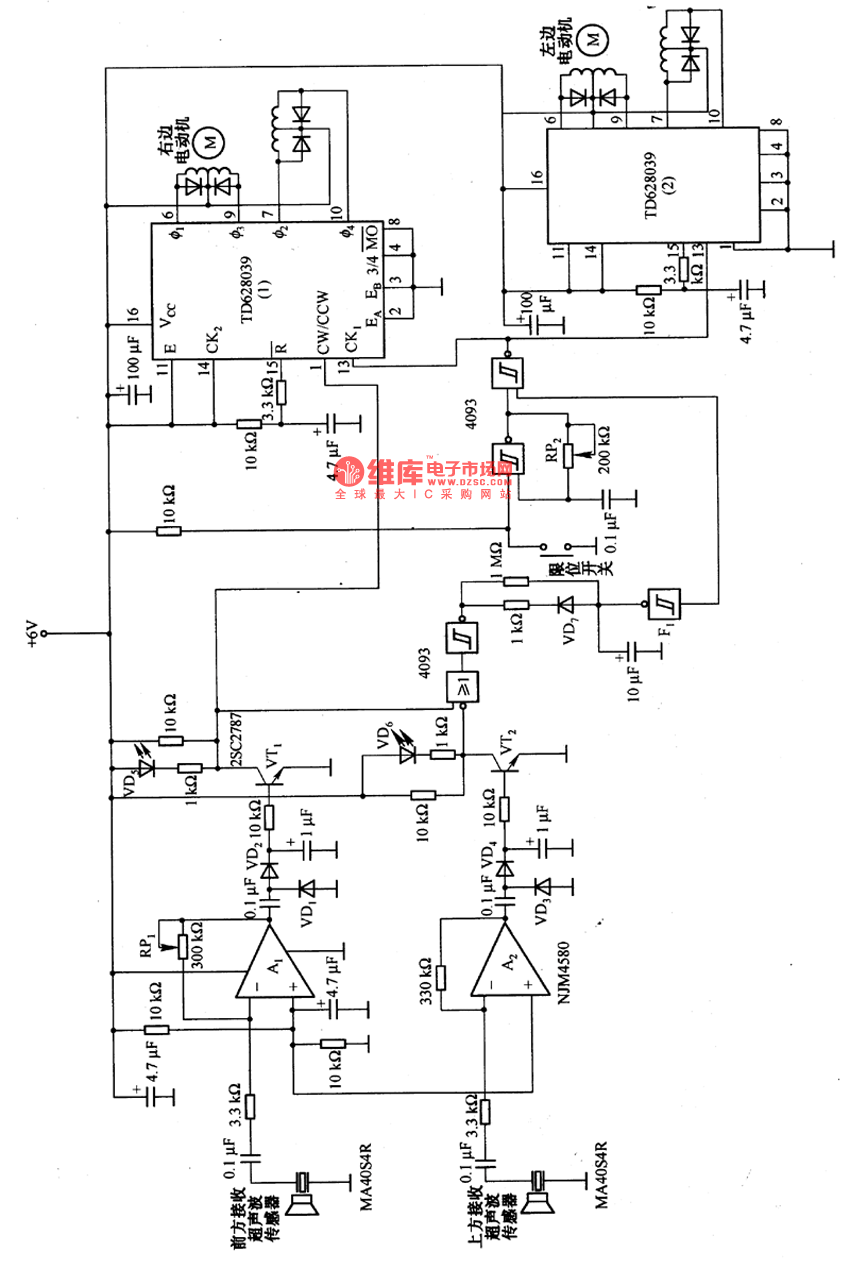
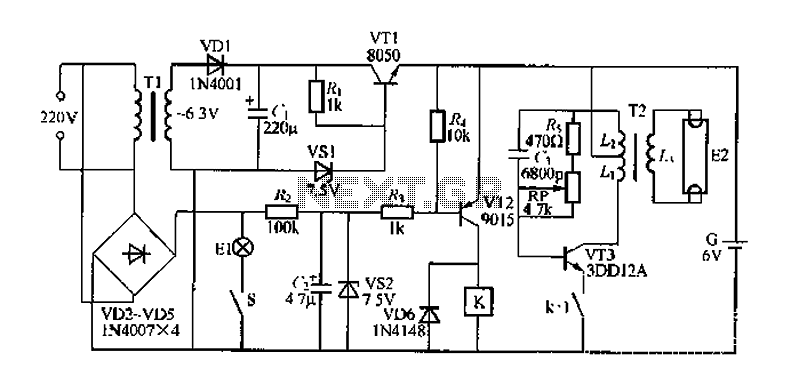
Thyristor - linking arm rectifier module three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit
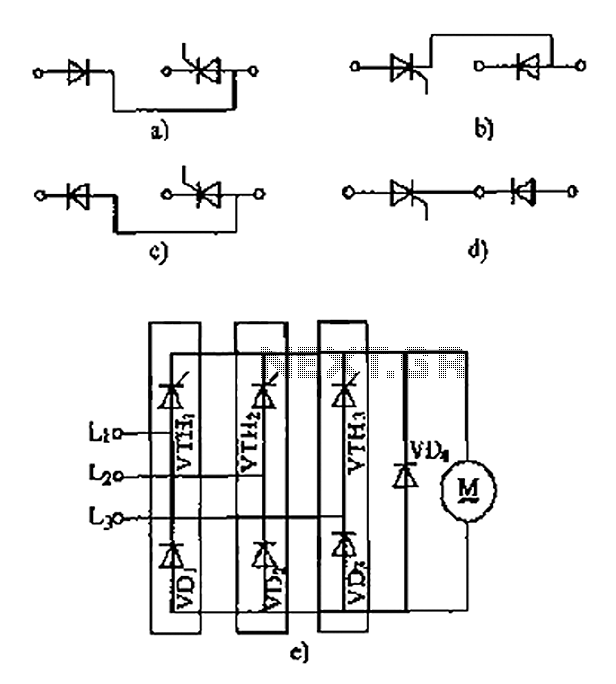
The thyristor linking arm rectifier module is a three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit. The thyristor-rectifier module linking arm consists of a thyristor and a rectifier diode connected in series or parallel, designed to fulfill specific requirements in power circuits. The commonly used linked arm module is illustrated in the accompanying figure.
The three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit utilizes a combination of thyristors and diodes to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In this configuration, two thyristors are used for the positive half-cycle of the input AC waveform, while two diodes handle the negative half-cycle. This arrangement allows for controlled rectification, enabling the adjustment of output voltage by varying the firing angle of the thyristors.
In a typical application, the thyristor linking arm module can be employed in industrial power supplies, motor drives, and other systems requiring efficient power conversion. The thyristors are triggered by a control circuit, which determines the timing of the conduction phase, thereby regulating the amount of power delivered to the load. The rectifier diodes provide a path for current during the negative cycle, ensuring continuous operation and reducing ripple in the output DC voltage.
The linking arm design facilitates modularity, allowing for easy integration into various power systems. The series or parallel configuration of the thyristors and diodes can be adapted based on the specific voltage and current requirements of the application. This flexibility makes the thyristor linking arm rectifier module a versatile choice for engineers and designers working on power electronics projects.
In summary, the thyristor linking arm rectifier module is an essential component in modern power electronics, providing an effective means of controlling and converting electrical energy for a wide range of applications. As shown thyristors - linking arm rectifier module three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit. Thyristor - rectifier module linking arm is made of a thyristor and a r ectifier diode in series or in parallel through the building blocks to meet the needs of some of the power circuit, the common-linked arm module as shown in FIG.
The three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit utilizes a combination of thyristors and diodes to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In this configuration, two thyristors are used for the positive half-cycle of the input AC waveform, while two diodes handle the negative half-cycle. This arrangement allows for controlled rectification, enabling the adjustment of output voltage by varying the firing angle of the thyristors.
In a typical application, the thyristor linking arm module can be employed in industrial power supplies, motor drives, and other systems requiring efficient power conversion. The thyristors are triggered by a control circuit, which determines the timing of the conduction phase, thereby regulating the amount of power delivered to the load. The rectifier diodes provide a path for current during the negative cycle, ensuring continuous operation and reducing ripple in the output DC voltage.
The linking arm design facilitates modularity, allowing for easy integration into various power systems. The series or parallel configuration of the thyristors and diodes can be adapted based on the specific voltage and current requirements of the application. This flexibility makes the thyristor linking arm rectifier module a versatile choice for engineers and designers working on power electronics projects.
In summary, the thyristor linking arm rectifier module is an essential component in modern power electronics, providing an effective means of controlling and converting electrical energy for a wide range of applications. As shown thyristors - linking arm rectifier module three-phase half-controlled bridge rectifier circuit. Thyristor - rectifier module linking arm is made of a thyristor and a r ectifier diode in series or in parallel through the building blocks to meet the needs of some of the power circuit, the common-linked arm module as shown in FIG.