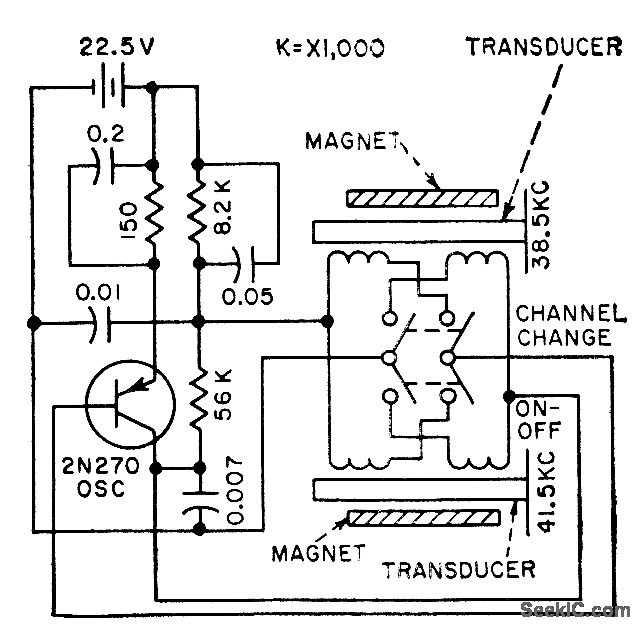
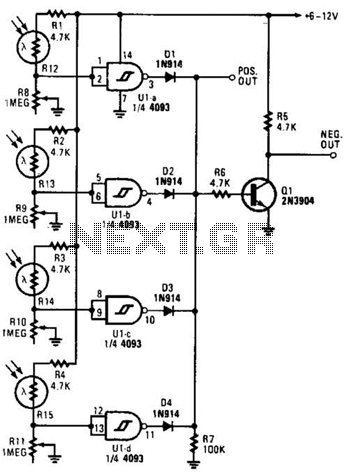
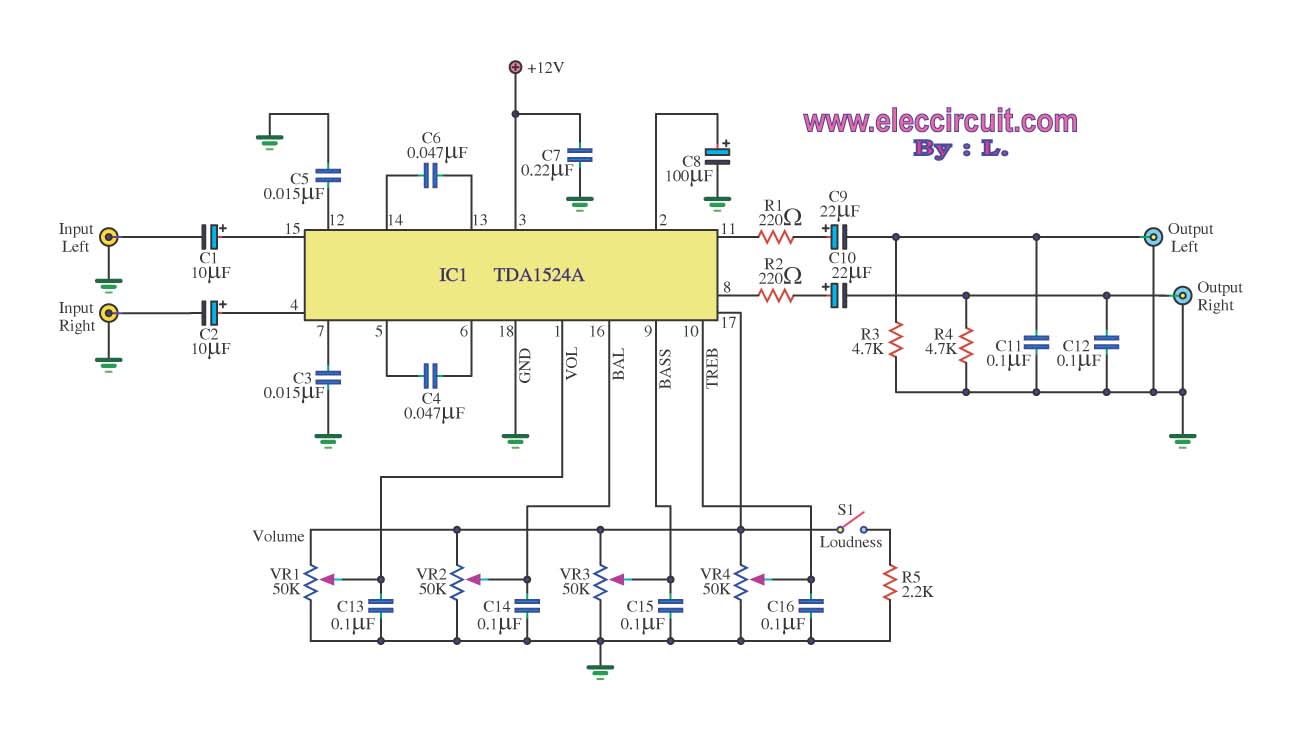
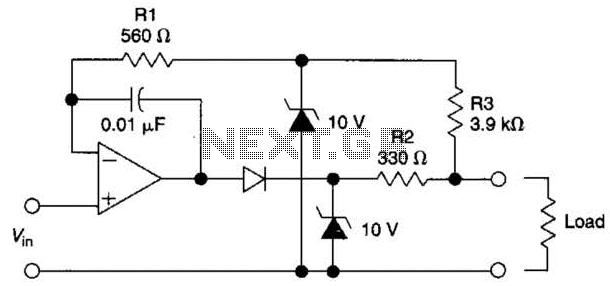
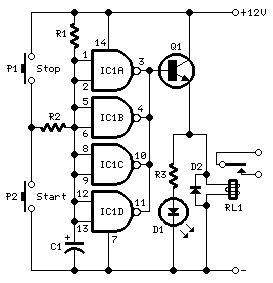
Time to start reversing relay control circuit
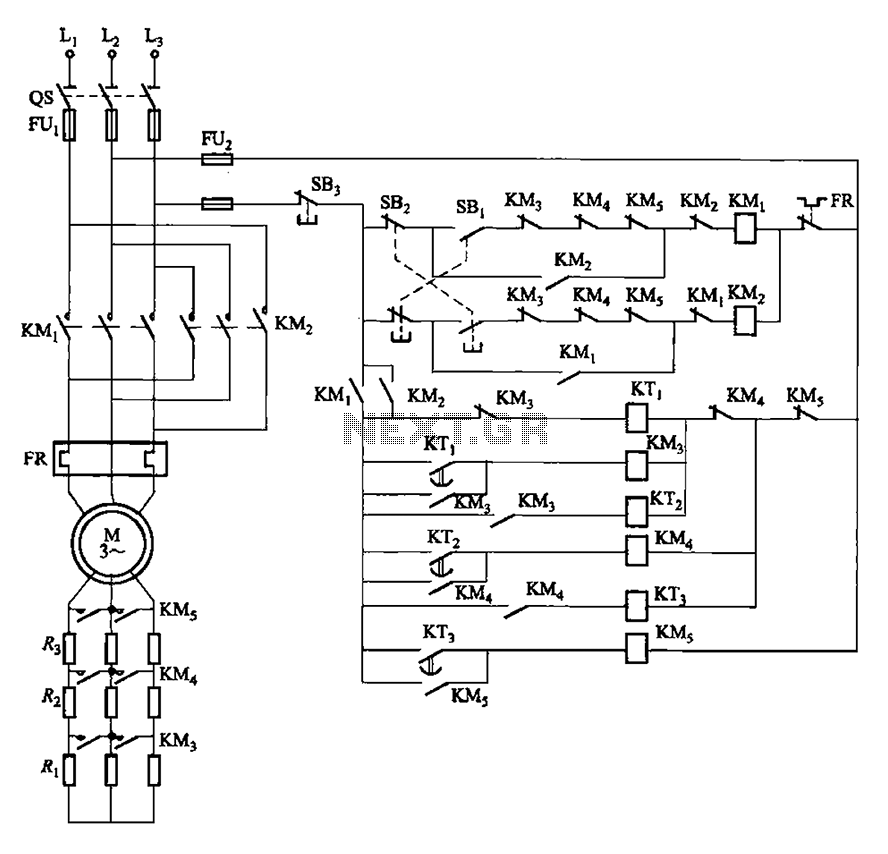
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-162 includes several components: SBi serves as the forward start button, SBz functions as the reverse start button, and SB3 is designated as the stop button. The resistance levels for the start switches are managed by time relay KTi to KTa.
The circuit design incorporates three primary push-button switches: SBi, SBz, and SB3, each serving distinct functions in the operation of the system. SBi, the forward start button, initiates the forward motion of the connected load, while SBz, the reverse start button, allows for reverse operation. SB3, the stop button, halts all operations when pressed.
The time relay units, KTi and KTa, play a critical role in controlling the resistance levels associated with the start buttons. These relays are responsible for timing operations, ensuring that the resistance values are adjusted based on the required operational time intervals. This feature allows for precise control over the speed and direction of the system, enhancing performance and safety.
The configuration of the circuit ensures that pressing the start buttons activates the corresponding relay, which then modifies the resistance in the circuit. This modification influences the current flow to the motor or load, dictating its operational behavior. The design may also incorporate additional safety features, such as interlocks or emergency stop mechanisms, to prevent accidental activation or ensure safe operation during maintenance.
Overall, the circuit is designed for efficient control of a motorized system, allowing for both forward and reverse motion with the ability to stop on demand. The integration of time relays adds a layer of complexity that enhances functionality and adaptability in various applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-162. in graph. SBi is forward the start button, SBz to reverse the start button, SB3 for the stop button. Start switching resistance levels are contro lled by time relay KTi ~ KTa.
The circuit design incorporates three primary push-button switches: SBi, SBz, and SB3, each serving distinct functions in the operation of the system. SBi, the forward start button, initiates the forward motion of the connected load, while SBz, the reverse start button, allows for reverse operation. SB3, the stop button, halts all operations when pressed.
The time relay units, KTi and KTa, play a critical role in controlling the resistance levels associated with the start buttons. These relays are responsible for timing operations, ensuring that the resistance values are adjusted based on the required operational time intervals. This feature allows for precise control over the speed and direction of the system, enhancing performance and safety.
The configuration of the circuit ensures that pressing the start buttons activates the corresponding relay, which then modifies the resistance in the circuit. This modification influences the current flow to the motor or load, dictating its operational behavior. The design may also incorporate additional safety features, such as interlocks or emergency stop mechanisms, to prevent accidental activation or ensure safe operation during maintenance.
Overall, the circuit is designed for efficient control of a motorized system, allowing for both forward and reverse motion with the ability to stop on demand. The integration of time relays adds a layer of complexity that enhances functionality and adaptability in various applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-162. in graph. SBi is forward the start button, SBz to reverse the start button, SB3 for the stop button. Start switching resistance levels are contro lled by time relay KTi ~ KTa.