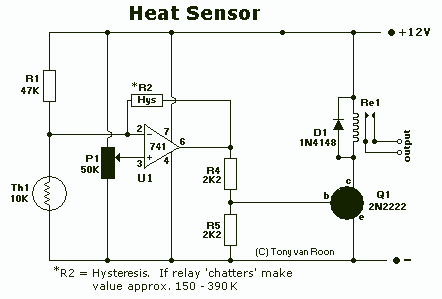
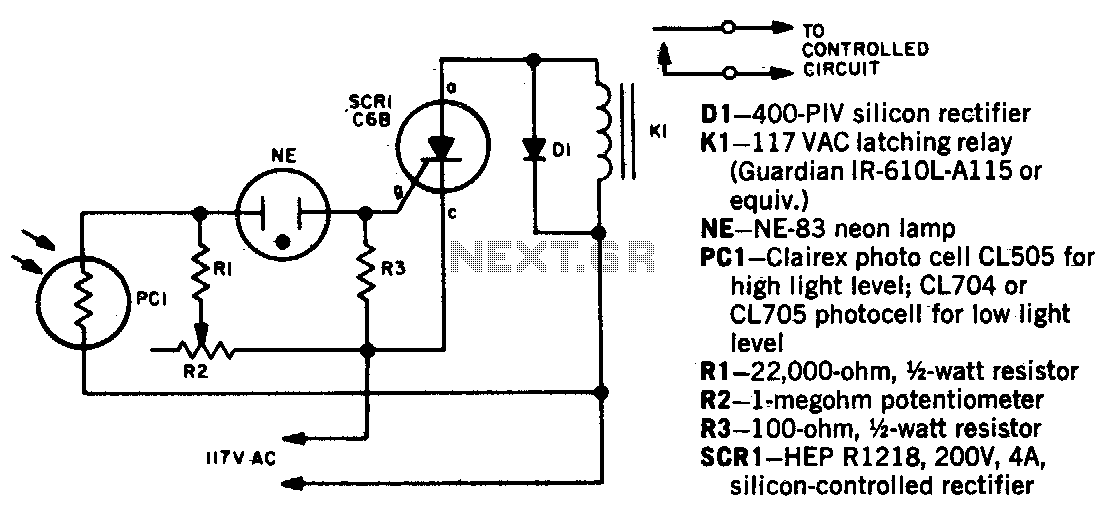
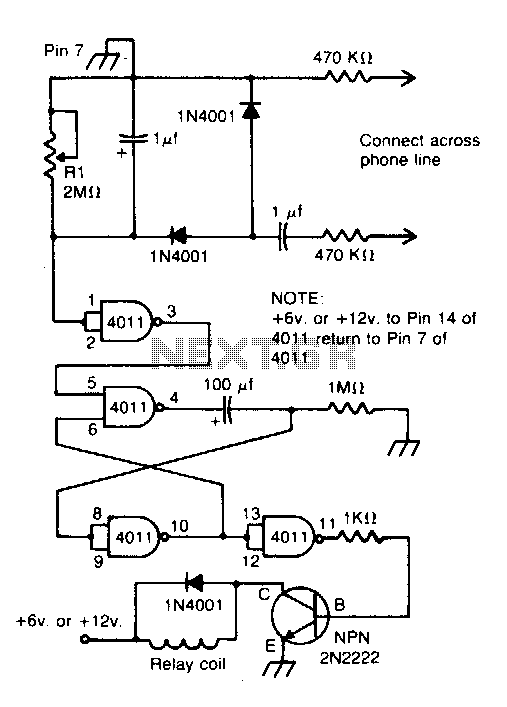
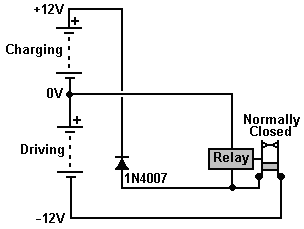
Tone-actuated relay
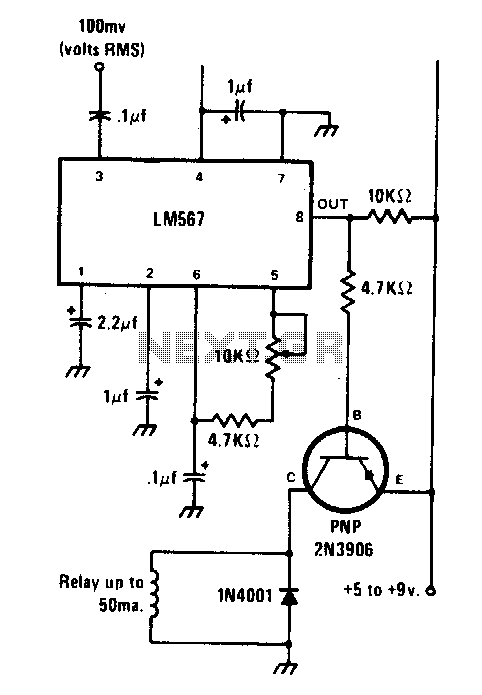
The circuit is designed using the LM567 tone decoder integrated circuit (IC), which operates with an input signal of approximately 100 millivolts at its designated frequency. The frequency can be adjusted using a 10 kΩ variable resistor, allowing it to range between 700 Hz and 1500 Hz. When a tone matching the set frequency is detected, the output of the LM567 transitions to a low state, which activates a relay via a 2N3906 PNP transistor.
The circuit fundamentally utilizes the LM567 tone decoder, which is particularly effective for applications requiring tone detection. The LM567 operates by comparing the frequency of an incoming audio signal with a reference frequency set by the variable resistor. The adjustment of this resistor allows for fine-tuning of the detection range, providing versatility in applications where different frequencies may need to be monitored.
When the input tone matches the adjusted frequency, the LM567's output goes low, signaling that a valid tone has been detected. This output is connected to the base of the 2N3906 PNP transistor, which acts as a switch to control the relay. The relay can be utilized to activate or deactivate larger loads, making this circuit suitable for various control applications.
The 2N3906 transistor is chosen for its capability to handle the current required to energize the relay. It is important to ensure that the relay's coil voltage and current ratings are compatible with the transistor's specifications to prevent damage. Additionally, a flyback diode may be included across the relay coil to protect the transistor from voltage spikes generated when the relay is de-energized.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective tone detection system, leveraging the capabilities of the LM567 and the switching properties of the 2N3906 transistor to control external devices based on audio frequency inputs.The circuit is built around the LM567 tone decoder IC that requires about 100 millivolts at its operating frequency. The frequency is set by a 10 K variable resistor and can be between 700 and 1500 He When a tone at the set frequency is present, the 567"s output goes low to energize a relay through a 2N3906 PNP transistor.
The circuit fundamentally utilizes the LM567 tone decoder, which is particularly effective for applications requiring tone detection. The LM567 operates by comparing the frequency of an incoming audio signal with a reference frequency set by the variable resistor. The adjustment of this resistor allows for fine-tuning of the detection range, providing versatility in applications where different frequencies may need to be monitored.
When the input tone matches the adjusted frequency, the LM567's output goes low, signaling that a valid tone has been detected. This output is connected to the base of the 2N3906 PNP transistor, which acts as a switch to control the relay. The relay can be utilized to activate or deactivate larger loads, making this circuit suitable for various control applications.
The 2N3906 transistor is chosen for its capability to handle the current required to energize the relay. It is important to ensure that the relay's coil voltage and current ratings are compatible with the transistor's specifications to prevent damage. Additionally, a flyback diode may be included across the relay coil to protect the transistor from voltage spikes generated when the relay is de-energized.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective tone detection system, leveraging the capabilities of the LM567 and the switching properties of the 2N3906 transistor to control external devices based on audio frequency inputs.The circuit is built around the LM567 tone decoder IC that requires about 100 millivolts at its operating frequency. The frequency is set by a 10 K variable resistor and can be between 700 and 1500 He When a tone at the set frequency is present, the 567"s output goes low to energize a relay through a 2N3906 PNP transistor.