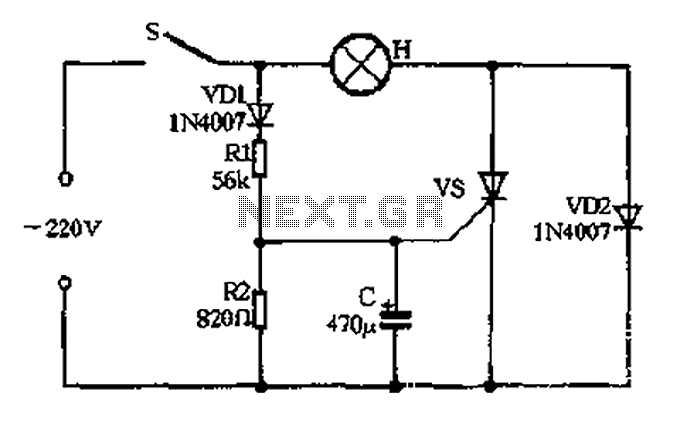
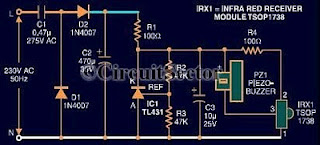
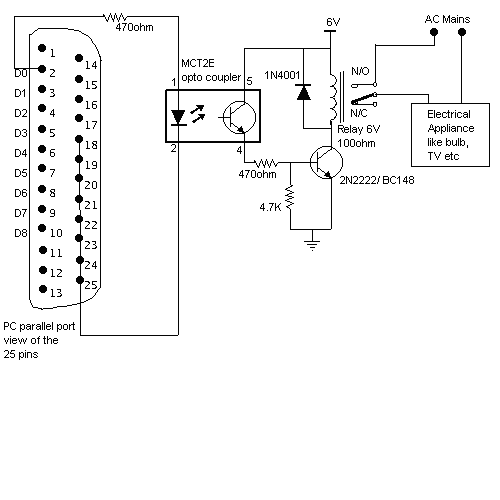
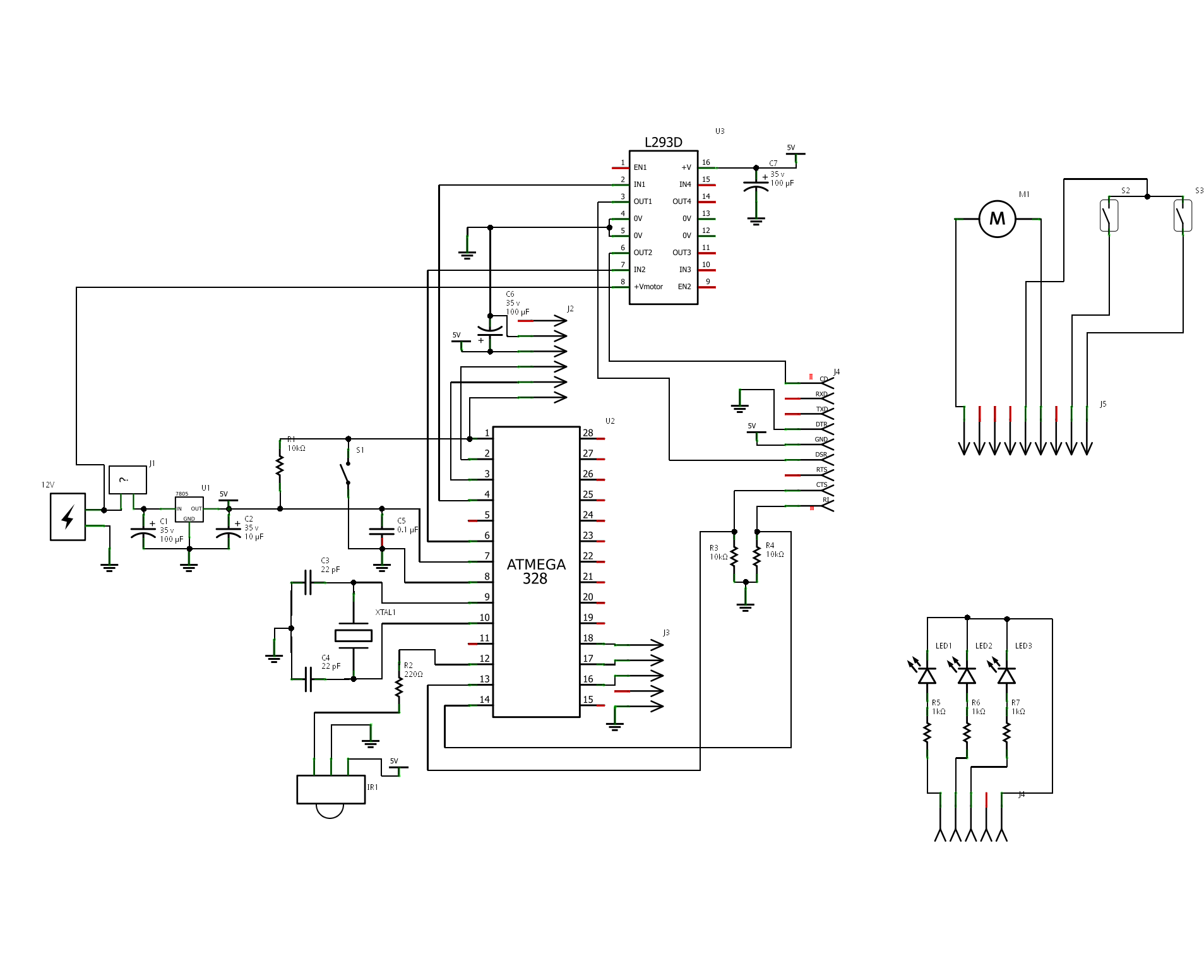
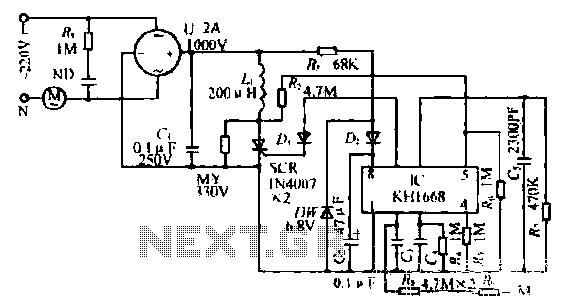
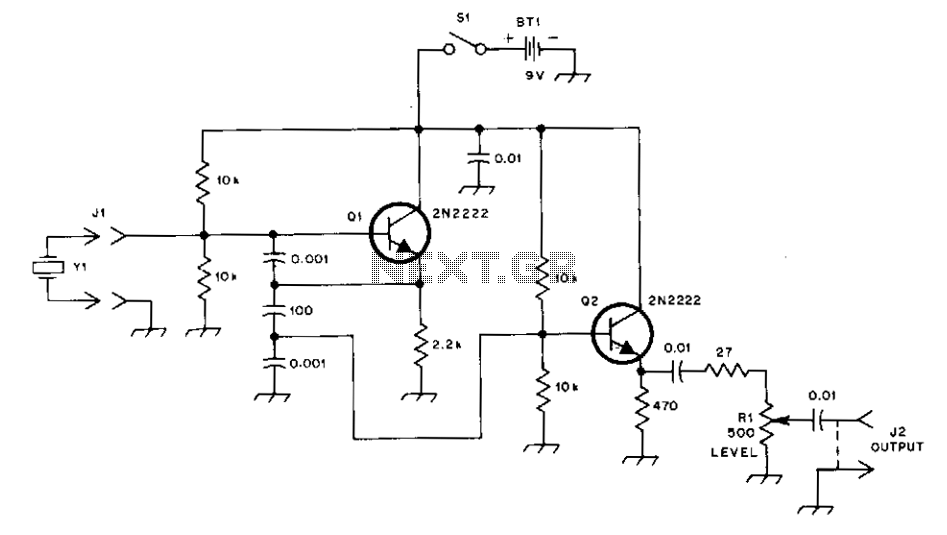
Tone Control
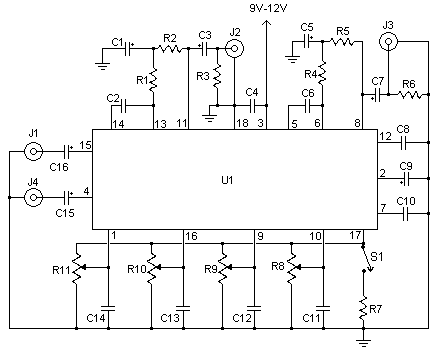
This simple tone control can be used in many audio applications. It can be added to amplifiers, used as a standalone control module, or even built into new and exciting instruments. Its one IC construction makes it a very compact circuit, as only a few support components are required. Plus, it does not use a dual power supply. This means that the circuit will run from 9V to 15V (although the bass will be a little weak at 9V). The circuit is by Robert Barg and originally appeared in the Think Tank column of the May 1998 issue of Popular Electronics.
The tone control circuit described is a versatile audio processing tool that enhances the listening experience by allowing users to adjust bass, midrange, and treble frequencies. The circuit typically employs a single integrated circuit (IC), which integrates the necessary functions for tone adjustment, thus simplifying the design and reducing the footprint of the overall circuit.
The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of 9V to 15V. It is important to note that while the circuit can function at the lower end of this voltage range, performance may be diminished, particularly in the bass response, which may not be as pronounced at 9V. This characteristic should be considered when designing applications that require robust low-frequency response.
The design is modular, allowing it to be incorporated into various audio systems, whether as an add-on to existing amplifiers or as a standalone unit. The simplicity of the circuit, requiring only a few additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and potentiometers for control, makes it an ideal choice for both hobbyists and professionals looking to implement tone control in their audio projects.
The original design by Robert Barg, featured in the May 1998 issue of Popular Electronics, emphasizes practicality and efficiency. The compact nature of the circuit not only saves space but also minimizes the complexity associated with wiring and assembly, making it suitable for integration into custom audio instruments or devices.
In summary, this tone control circuit stands out for its compact design, ease of use, and adaptability across a range of audio applications, providing users with the ability to tailor sound characteristics to their preferences without extensive modifications to existing equipment.This simple tone control can be used in may audio applications. It can be added to amplifers, used as a stand alone control module, or even built into new and exciting instruments. It`s one IC construction makes it a very compact circuit, as only a few support components are required.
Plus, it does not use a dual power supply. This means that the circuit will run from 9V to 15V (although the bass will be a little weak at 9V). The circuit is by Robert Barg and originally appeared in the Think Tank column of the May 1998 issue of Popular Electronics.. 🔗 External reference
The tone control circuit described is a versatile audio processing tool that enhances the listening experience by allowing users to adjust bass, midrange, and treble frequencies. The circuit typically employs a single integrated circuit (IC), which integrates the necessary functions for tone adjustment, thus simplifying the design and reducing the footprint of the overall circuit.
The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of 9V to 15V. It is important to note that while the circuit can function at the lower end of this voltage range, performance may be diminished, particularly in the bass response, which may not be as pronounced at 9V. This characteristic should be considered when designing applications that require robust low-frequency response.
The design is modular, allowing it to be incorporated into various audio systems, whether as an add-on to existing amplifiers or as a standalone unit. The simplicity of the circuit, requiring only a few additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and potentiometers for control, makes it an ideal choice for both hobbyists and professionals looking to implement tone control in their audio projects.
The original design by Robert Barg, featured in the May 1998 issue of Popular Electronics, emphasizes practicality and efficiency. The compact nature of the circuit not only saves space but also minimizes the complexity associated with wiring and assembly, making it suitable for integration into custom audio instruments or devices.
In summary, this tone control circuit stands out for its compact design, ease of use, and adaptability across a range of audio applications, providing users with the ability to tailor sound characteristics to their preferences without extensive modifications to existing equipment.This simple tone control can be used in may audio applications. It can be added to amplifers, used as a stand alone control module, or even built into new and exciting instruments. It`s one IC construction makes it a very compact circuit, as only a few support components are required.
Plus, it does not use a dual power supply. This means that the circuit will run from 9V to 15V (although the bass will be a little weak at 9V). The circuit is by Robert Barg and originally appeared in the Think Tank column of the May 1998 issue of Popular Electronics.. 🔗 External reference