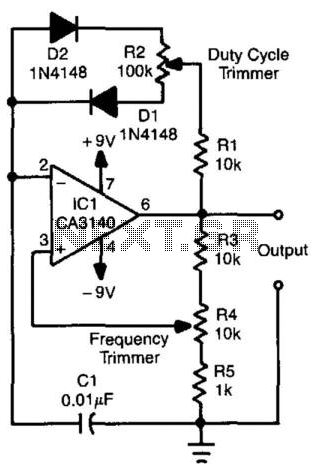
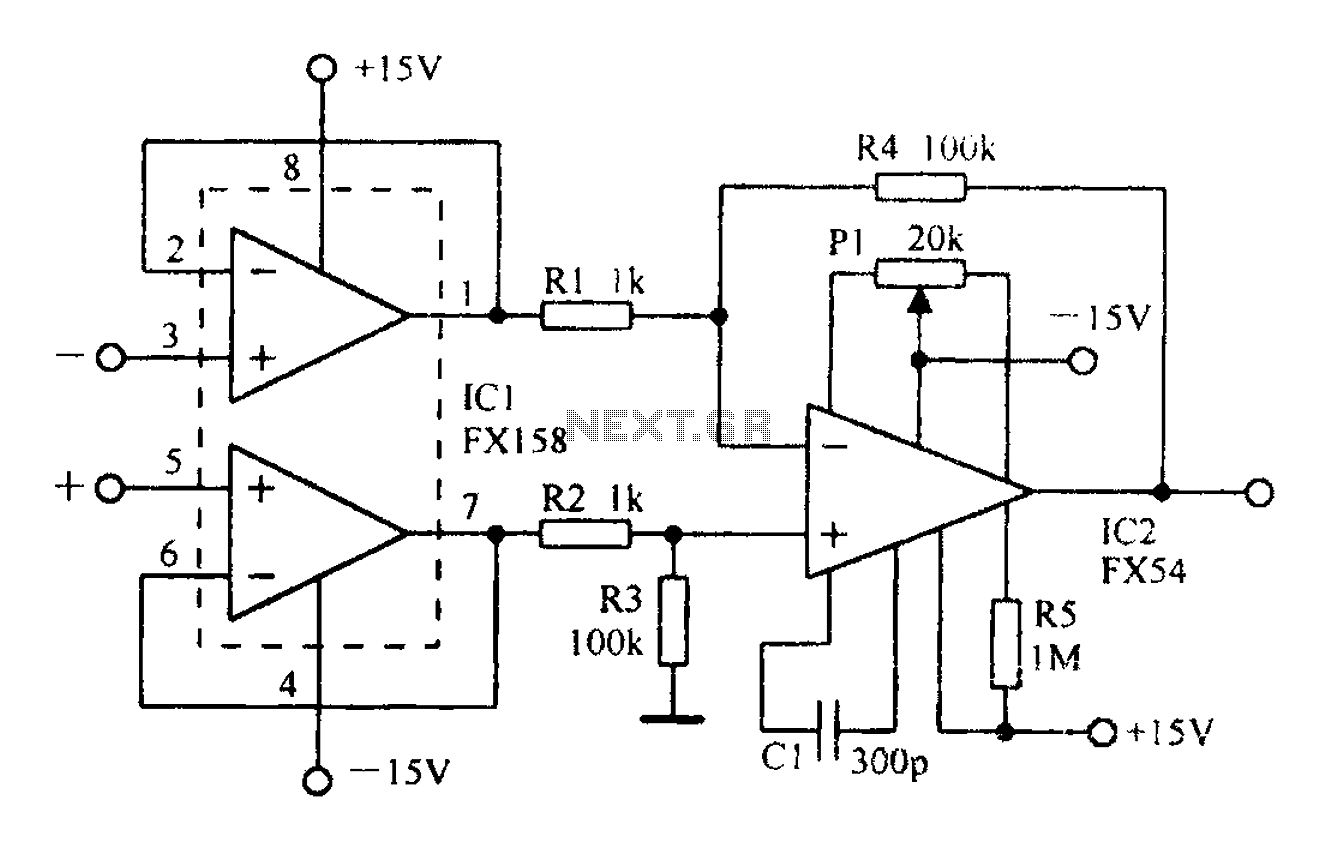
Tone generator circuit
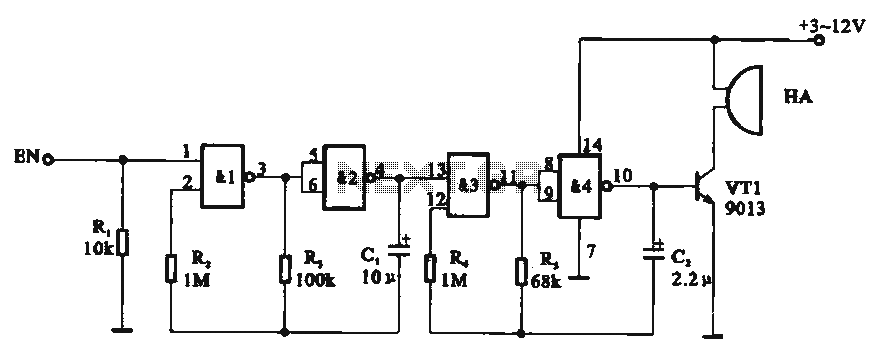
Tone generator circuit. The tone generator circuit utilizes a quad 2-input NAND gate integrated circuit, specifically the CD4011. NAND gates 1 and 2, along with NAND gates 3 and 4, form two gating multivibrator oscillators. The oscillation period of the first multivibrator is 2 seconds, while the second has an oscillation period of 330 milliseconds. The latter is controlled by the output of the former, and the first multivibrator can also be controlled by the potential at the EN control terminal. When there is no control voltage at the EN pin, the circuit stops oscillating, resulting in no sound output. Conversely, when a positive control voltage is applied to the EN pin, the circuit activates, allowing the two multivibrators to function. As a result, the output from NAND gate 4 produces a series of positive pulses, generating an intermittent square wave that drives a buzzer, producing a "drip, drip, clear" crisp tone.
The tone generator circuit is designed around the CD4011 quad 2-input NAND gate integrated circuit. This IC contains four independent NAND gates, which can be configured to create multivibrator circuits. In this specific application, two of the NAND gates are configured as astable multivibrators, producing square wave outputs at different frequencies. The first multivibrator, formed by NAND gates 1 and 2, has a longer period of 2 seconds, while the second multivibrator, formed by NAND gates 3 and 4, oscillates at a much higher frequency of 330 milliseconds.
The output of the first multivibrator serves as a control signal for the second multivibrator. This cascading configuration allows for the modulation of the second oscillator based on the state of the first. The control terminal, labeled EN, plays a critical role in the circuit's operation. When the EN pin is not supplied with a control voltage, the circuit remains inactive, halting any oscillation and producing no sound. However, when a positive voltage is applied to the EN pin, it enables the first multivibrator, which in turn activates the second multivibrator.
The output from the fourth NAND gate generates a series of positive pulses that correspond to the oscillation of the second multivibrator. These pulses are then used to drive an audio output device, such as a buzzer. The resulting sound is characterized by a series of intermittent tones, described as "drip, drip, clear," which can be utilized in various applications requiring sound generation, such as alarms, timers, or notification systems. This design effectively demonstrates the versatility and functionality of NAND gates in creating sound-generating circuits.Tone generator circuit Tone generator circuit shown in FIG. Circuit uses a quad 2-input NAND gate integrated circuit CD4011. NAND gate NAND gate 1,2 and 3,4 form two gating multivibrator oscillation period of the former 2s, the latter oscillation period of 330 ms, and the latter controlled by the output of the former, while the former also by control terminal EN potential control. When the EN pin no control voltage, circuit stop vibration HA no sound issue; when EN end when there is a positive control voltage start-up circuit, the role of the two multivibrators, so the output of NAND gate 4 @ pin output every three positive pulse for a group of intermittent square wave, driven by vri buzzer (Xiangqi) HA issued a "drip, drip, clear" crisp tone.
The tone generator circuit is designed around the CD4011 quad 2-input NAND gate integrated circuit. This IC contains four independent NAND gates, which can be configured to create multivibrator circuits. In this specific application, two of the NAND gates are configured as astable multivibrators, producing square wave outputs at different frequencies. The first multivibrator, formed by NAND gates 1 and 2, has a longer period of 2 seconds, while the second multivibrator, formed by NAND gates 3 and 4, oscillates at a much higher frequency of 330 milliseconds.
The output of the first multivibrator serves as a control signal for the second multivibrator. This cascading configuration allows for the modulation of the second oscillator based on the state of the first. The control terminal, labeled EN, plays a critical role in the circuit's operation. When the EN pin is not supplied with a control voltage, the circuit remains inactive, halting any oscillation and producing no sound. However, when a positive voltage is applied to the EN pin, it enables the first multivibrator, which in turn activates the second multivibrator.
The output from the fourth NAND gate generates a series of positive pulses that correspond to the oscillation of the second multivibrator. These pulses are then used to drive an audio output device, such as a buzzer. The resulting sound is characterized by a series of intermittent tones, described as "drip, drip, clear," which can be utilized in various applications requiring sound generation, such as alarms, timers, or notification systems. This design effectively demonstrates the versatility and functionality of NAND gates in creating sound-generating circuits.Tone generator circuit Tone generator circuit shown in FIG. Circuit uses a quad 2-input NAND gate integrated circuit CD4011. NAND gate NAND gate 1,2 and 3,4 form two gating multivibrator oscillation period of the former 2s, the latter oscillation period of 330 ms, and the latter controlled by the output of the former, while the former also by control terminal EN potential control. When the EN pin no control voltage, circuit stop vibration HA no sound issue; when EN end when there is a positive control voltage start-up circuit, the role of the two multivibrators, so the output of NAND gate 4 @ pin output every three positive pulse for a group of intermittent square wave, driven by vri buzzer (Xiangqi) HA issued a "drip, drip, clear" crisp tone.