Transistor sorter-tester

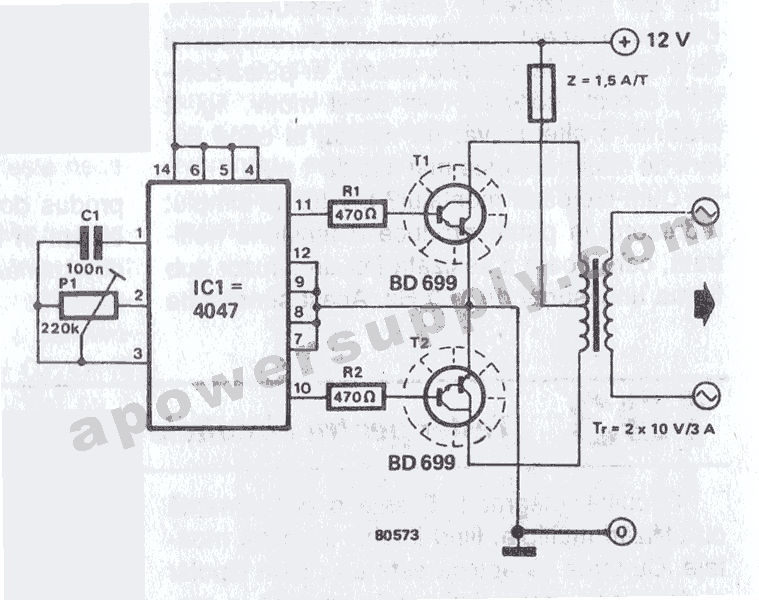
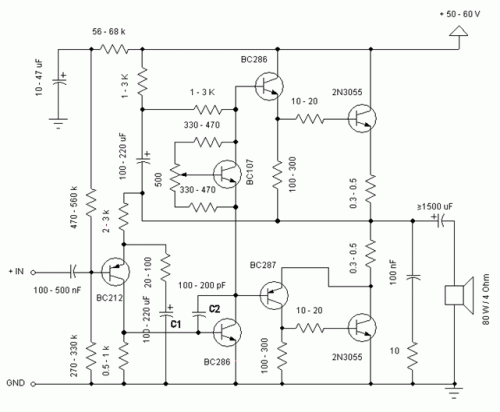
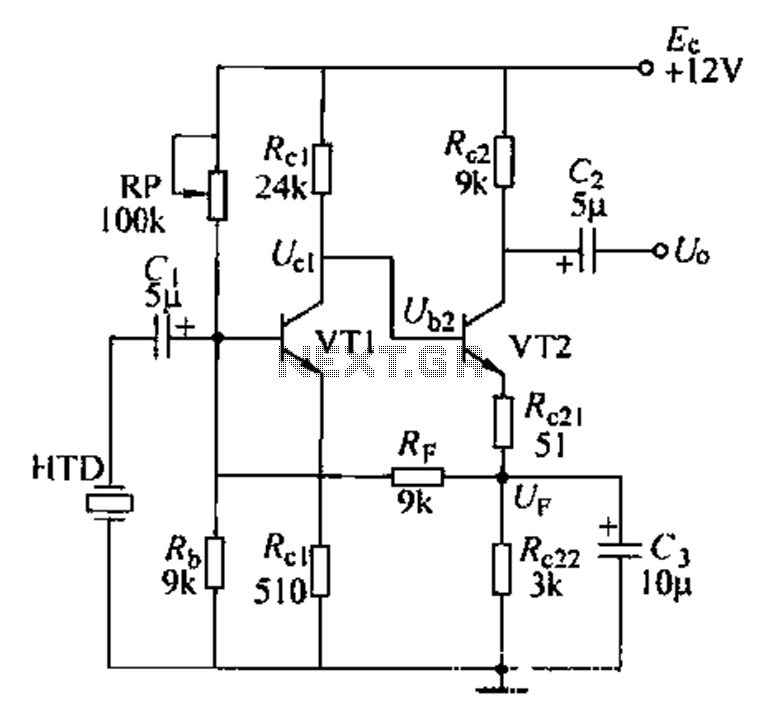
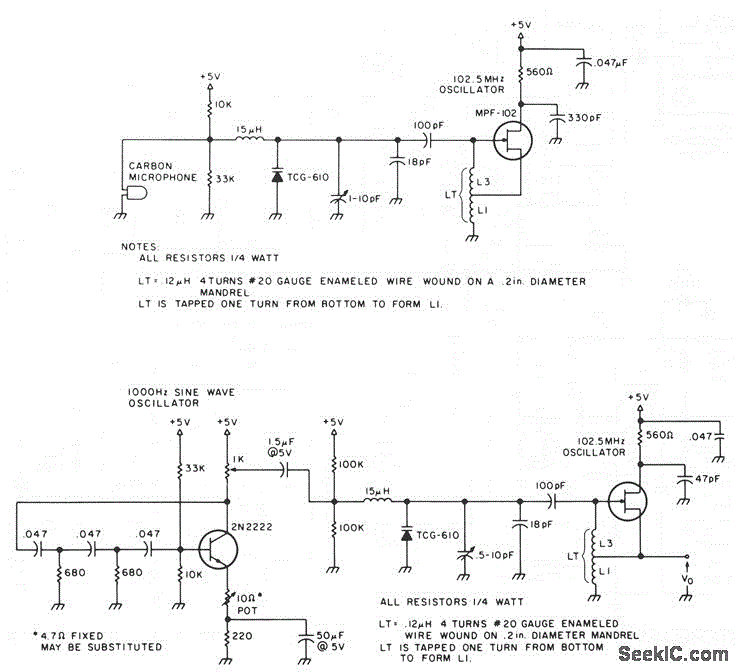
This tester checks the polarity of transistors (PNP or NPN). An audible signal indicates the gain. Additionally, the tester can function as a GO/NO GO tester for matching unmarked devices.
The transistor tester is designed to evaluate the polarity and gain of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), which are essential components in various electronic circuits. The primary function of this device is to discern whether a transistor is of the PNP or NPN type. This is achieved through a simple interface that connects the transistor leads to the tester.
Upon connection, the tester applies a small voltage to the transistor and measures the resultant current flow. If the transistor is functioning correctly, an audible signal will be emitted, indicating that the transistor is operational and providing information about its gain, which is crucial for understanding its performance in a circuit.
Furthermore, this tester can serve as a GO/NO GO device. This feature is particularly useful for matching unmarked transistors, which may not have clear labeling for their type or specifications. By providing a straightforward pass/fail indication, the tester simplifies the process of identifying suitable replacements or matching components in circuit design and repair.
The design of the tester typically includes a visual display or LED indicators alongside the audible signal, enhancing usability. The circuit may incorporate a microcontroller or dedicated IC to process the input signals from the transistor and generate the necessary outputs. This ensures accurate readings and reliable performance, making the tester an invaluable tool for electronics engineers and hobbyists alike.This tester checks transistor for polarity (PNP or NPN). An audible signal will give an indication of gain Tester can also be used as a GO/NO GO tester to match unmarked devices.
The transistor tester is designed to evaluate the polarity and gain of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), which are essential components in various electronic circuits. The primary function of this device is to discern whether a transistor is of the PNP or NPN type. This is achieved through a simple interface that connects the transistor leads to the tester.
Upon connection, the tester applies a small voltage to the transistor and measures the resultant current flow. If the transistor is functioning correctly, an audible signal will be emitted, indicating that the transistor is operational and providing information about its gain, which is crucial for understanding its performance in a circuit.
Furthermore, this tester can serve as a GO/NO GO device. This feature is particularly useful for matching unmarked transistors, which may not have clear labeling for their type or specifications. By providing a straightforward pass/fail indication, the tester simplifies the process of identifying suitable replacements or matching components in circuit design and repair.
The design of the tester typically includes a visual display or LED indicators alongside the audible signal, enhancing usability. The circuit may incorporate a microcontroller or dedicated IC to process the input signals from the transistor and generate the necessary outputs. This ensures accurate readings and reliable performance, making the tester an invaluable tool for electronics engineers and hobbyists alike.This tester checks transistor for polarity (PNP or NPN). An audible signal will give an indication of gain Tester can also be used as a GO/NO GO tester to match unmarked devices.