Transistor Tester
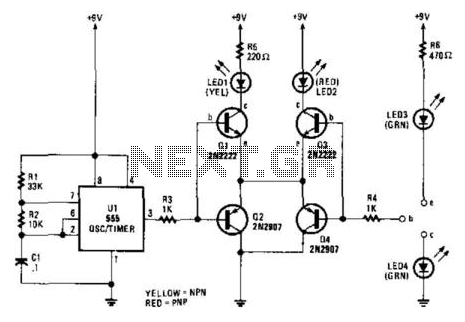
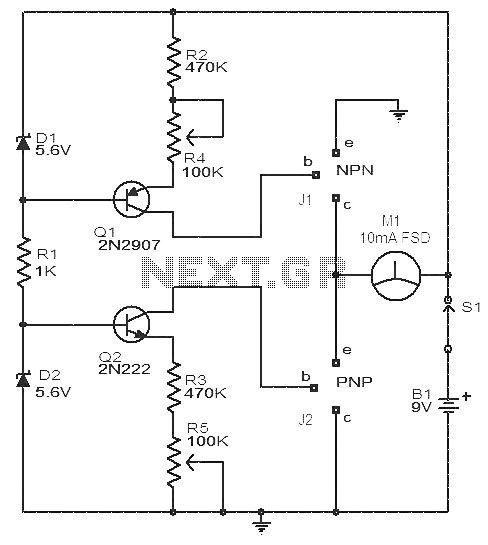
A 555 timer drives Q1 through Q4 with a square wave. LED1 and LED2 illuminate when an NPN or PNP transistor, respectively, is connected to the test terminals. If LED3 and LED4 light up equally as LED1 and LED2, the transistor is functional. If LED3 and LED4 are brighter than LED1 or LED2, the transistor is shorted.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. This square wave is used to drive a series of transistors, specifically Q1 through Q4, which serve as switching elements in the circuit. The operation of the 555 timer is critical as it sets the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal, influencing the behavior of the connected transistors.
LED1 and LED2 are indicators that provide visual feedback on the operation of the transistors. When an NPN or PNP transistor is connected to the test terminals, the corresponding LED will illuminate, indicating that the transistor is functioning correctly. The presence of LED1 signifies that the NPN transistor is conducting, while LED2 indicates that the PNP transistor is operational.
Additionally, LED3 and LED4 serve as diagnostic tools for assessing the condition of the transistors. If these LEDs illuminate with the same brightness as LED1 and LED2, it confirms that the tested transistor is functional and correctly biased. However, if LED3 and LED4 exhibit a brightness that surpasses that of LED1 and LED2, it indicates a short circuit condition in the transistor, suggesting that it has failed and is no longer performing its intended function.
The circuit design emphasizes the importance of clear visual indicators for troubleshooting and verifying the integrity of transistor operation. Proper biasing and connection of the transistors are essential for accurate results, and the use of LEDs provides an immediate visual representation of the circuit's status. This schematic can be used in various applications, including educational demonstrations and practical testing of transistor functionality. A 555 timer drives Ql through Q4 with a square wave. LED1 and LED2 light when an npn or pnp transistor respectively, are connected to the text terminals. If LED3 and LED4 light equally as LED1 and LED2, the transistor is functional. If LED3 and LED4 are brighter than LED1 or LED2, the transistor is shorted.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. This square wave is used to drive a series of transistors, specifically Q1 through Q4, which serve as switching elements in the circuit. The operation of the 555 timer is critical as it sets the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal, influencing the behavior of the connected transistors.
LED1 and LED2 are indicators that provide visual feedback on the operation of the transistors. When an NPN or PNP transistor is connected to the test terminals, the corresponding LED will illuminate, indicating that the transistor is functioning correctly. The presence of LED1 signifies that the NPN transistor is conducting, while LED2 indicates that the PNP transistor is operational.
Additionally, LED3 and LED4 serve as diagnostic tools for assessing the condition of the transistors. If these LEDs illuminate with the same brightness as LED1 and LED2, it confirms that the tested transistor is functional and correctly biased. However, if LED3 and LED4 exhibit a brightness that surpasses that of LED1 and LED2, it indicates a short circuit condition in the transistor, suggesting that it has failed and is no longer performing its intended function.
The circuit design emphasizes the importance of clear visual indicators for troubleshooting and verifying the integrity of transistor operation. Proper biasing and connection of the transistors are essential for accurate results, and the use of LEDs provides an immediate visual representation of the circuit's status. This schematic can be used in various applications, including educational demonstrations and practical testing of transistor functionality. A 555 timer drives Ql through Q4 with a square wave. LED1 and LED2 light when an npn or pnp transistor respectively, are connected to the text terminals. If LED3 and LED4 light equally as LED1 and LED2, the transistor is functional. If LED3 and LED4 are brighter than LED1 or LED2, the transistor is shorted.