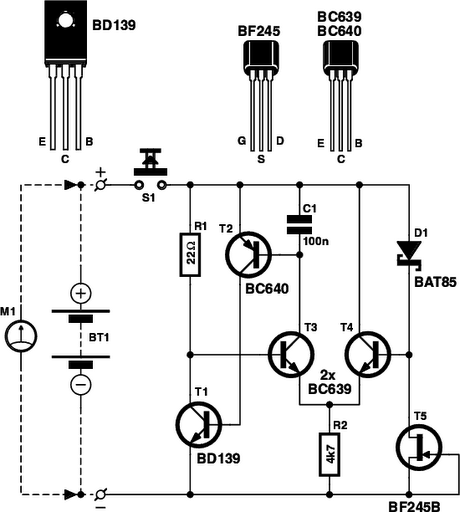
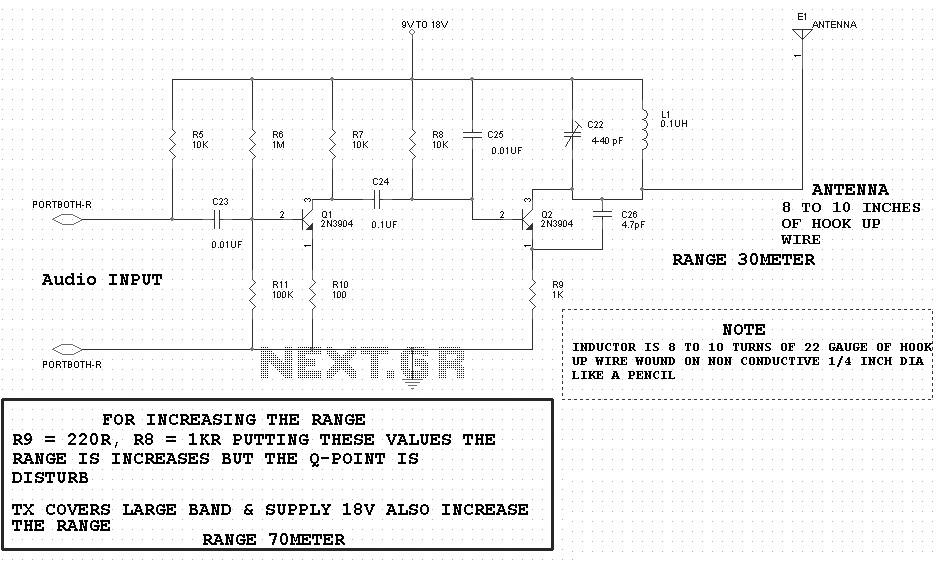
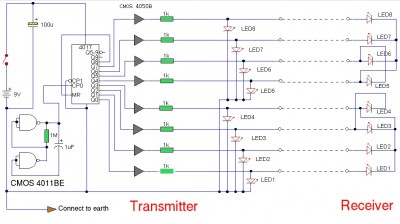
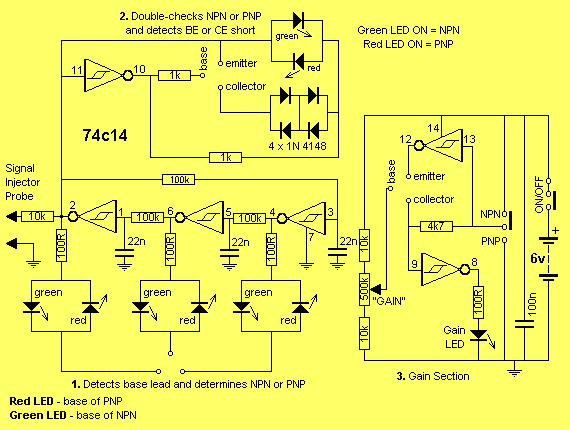
Ttl logic tester
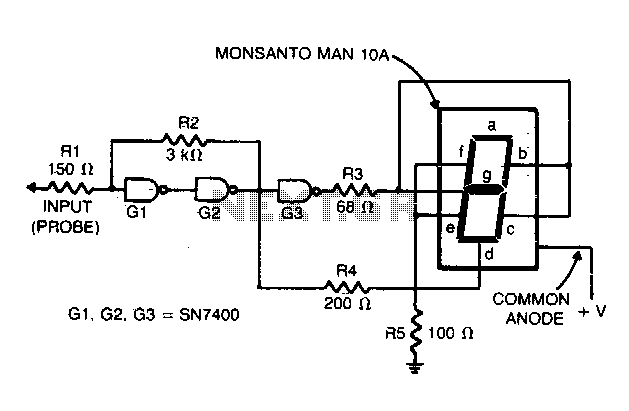
Gates G1 and G2, along with resistors R1 and R2, create a straightforward voltage monitor with a trip point set at 1 volt. Gate G3 functions as an inverter. The display section of the tester features a common anode alphanumeric LED accompanied by current-limiting resistors. This configuration indicates whether the input voltage exceeds or falls short of 1.4 V, displaying an 'H' for high logic level or an 'L' for low logic level accordingly.
The circuit utilizes two logic gates, G1 and G2, to monitor the input voltage. Resistors R1 and R2 are configured to establish a voltage divider that determines the trip point at which the circuit will respond. When the input voltage crosses the threshold of 1 volt, the output from these gates will change state, effectively signaling the inverter gate G3. The inverter then alters the signal, ensuring that a high input voltage results in a low output and vice versa.
The output of gate G3 is connected to a common anode alphanumeric LED, which is designed to visually indicate the logic level. The current-limiting resistors are essential to prevent excessive current from flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from damage and ensuring proper functioning.
When the input voltage is above 1.4 V, the circuit outputs a high signal, illuminating the LED to display 'H'. Conversely, if the input voltage drops below this threshold, the output becomes low, and the LED displays 'L'. This simple yet effective voltage monitoring circuit is suitable for various applications where voltage levels need to be visually indicated, making it a valuable tool in electronic diagnostics and testing.Gates Gl and G2 together with resistors Rl and R2 form a simple voltage monitor that has a trip point of 1 volts. Gate G3 is simply an inverter. The display section of the tester consists of a common anode alphanumeric LED and current-limiting resistors
It indicates whether the input voltage is above or below 1,4 V, and displays a H or a L (for high or low logic-level) respectively.
The circuit utilizes two logic gates, G1 and G2, to monitor the input voltage. Resistors R1 and R2 are configured to establish a voltage divider that determines the trip point at which the circuit will respond. When the input voltage crosses the threshold of 1 volt, the output from these gates will change state, effectively signaling the inverter gate G3. The inverter then alters the signal, ensuring that a high input voltage results in a low output and vice versa.
The output of gate G3 is connected to a common anode alphanumeric LED, which is designed to visually indicate the logic level. The current-limiting resistors are essential to prevent excessive current from flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from damage and ensuring proper functioning.
When the input voltage is above 1.4 V, the circuit outputs a high signal, illuminating the LED to display 'H'. Conversely, if the input voltage drops below this threshold, the output becomes low, and the LED displays 'L'. This simple yet effective voltage monitoring circuit is suitable for various applications where voltage levels need to be visually indicated, making it a valuable tool in electronic diagnostics and testing.Gates Gl and G2 together with resistors Rl and R2 form a simple voltage monitor that has a trip point of 1 volts. Gate G3 is simply an inverter. The display section of the tester consists of a common anode alphanumeric LED and current-limiting resistors
It indicates whether the input voltage is above or below 1,4 V, and displays a H or a L (for high or low logic-level) respectively.