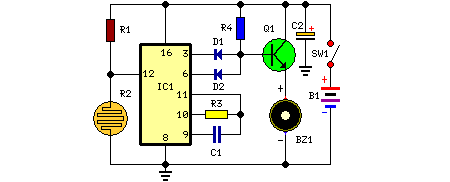
Two Flashing LEDs Circuit
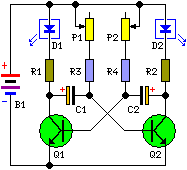
This circuit diagram illustrates a setup for two flashing LEDs designed for various applications, including model construction and recreational uses. It features adjustable flashing speeds controlled by two potentiometers. The circuit comprises a combination of active and passive components. It is straightforward to construct, making it an ideal project for beginners. The assembly can be performed on a general-purpose PCB or a veroboard. The complete schematic and image of this project are provided below.
The circuit operates by utilizing two LEDs that flash alternately at varying speeds, which can be adjusted according to user preference. The core components include two potentiometers, which serve as variable resistors to modify the timing intervals for the flashing LEDs. The active components typically include a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output is then used to drive the LEDs.
Passive components such as resistors and capacitors are also integrated into the circuit to set the frequency of the flashing and to ensure the LEDs operate within their specified current limits. The resistors limit the current flowing through the LEDs, while the capacitors help to stabilize the timing circuit and determine the flashing rate alongside the potentiometers.
For assembly, the components can be laid out on a veroboard or a general-purpose PCB, allowing for flexibility in design. Proper attention should be given to the orientation of the LEDs, as they are polarized components. The schematic diagram typically includes the connections between the timer IC, the LEDs, the potentiometers, and the power supply, ensuring clarity in the assembly process.
This circuit not only serves as an excellent introduction to basic electronics for beginners but also provides practical experience in soldering and layout design. Its versatility allows for adaptation in various projects, making it a valuable addition to any electronics toolkit.Here is the circuit diagram of Two Flashing LED`s for different applications (such as model construction), and recreational. Having adjustable flashing speed with two potentiometers. It is the collection of a few active and passive components. This circuit is very easy to built ( a good idea for beginners ) and can be build on a general purpose pcb or on a veroboard.
The complete picture and schematic of this project is shown below.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing two LEDs that flash alternately at varying speeds, which can be adjusted according to user preference. The core components include two potentiometers, which serve as variable resistors to modify the timing intervals for the flashing LEDs. The active components typically include a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output is then used to drive the LEDs.
Passive components such as resistors and capacitors are also integrated into the circuit to set the frequency of the flashing and to ensure the LEDs operate within their specified current limits. The resistors limit the current flowing through the LEDs, while the capacitors help to stabilize the timing circuit and determine the flashing rate alongside the potentiometers.
For assembly, the components can be laid out on a veroboard or a general-purpose PCB, allowing for flexibility in design. Proper attention should be given to the orientation of the LEDs, as they are polarized components. The schematic diagram typically includes the connections between the timer IC, the LEDs, the potentiometers, and the power supply, ensuring clarity in the assembly process.
This circuit not only serves as an excellent introduction to basic electronics for beginners but also provides practical experience in soldering and layout design. Its versatility allows for adaptation in various projects, making it a valuable addition to any electronics toolkit.Here is the circuit diagram of Two Flashing LED`s for different applications (such as model construction), and recreational. Having adjustable flashing speed with two potentiometers. It is the collection of a few active and passive components. This circuit is very easy to built ( a good idea for beginners ) and can be build on a general purpose pcb or on a veroboard.
The complete picture and schematic of this project is shown below.. 🔗 External reference