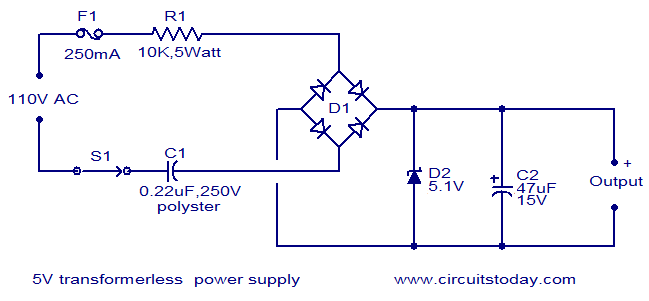
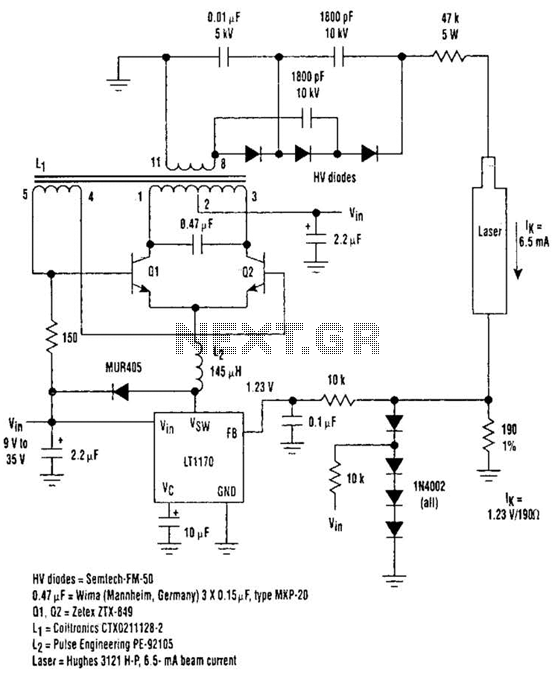
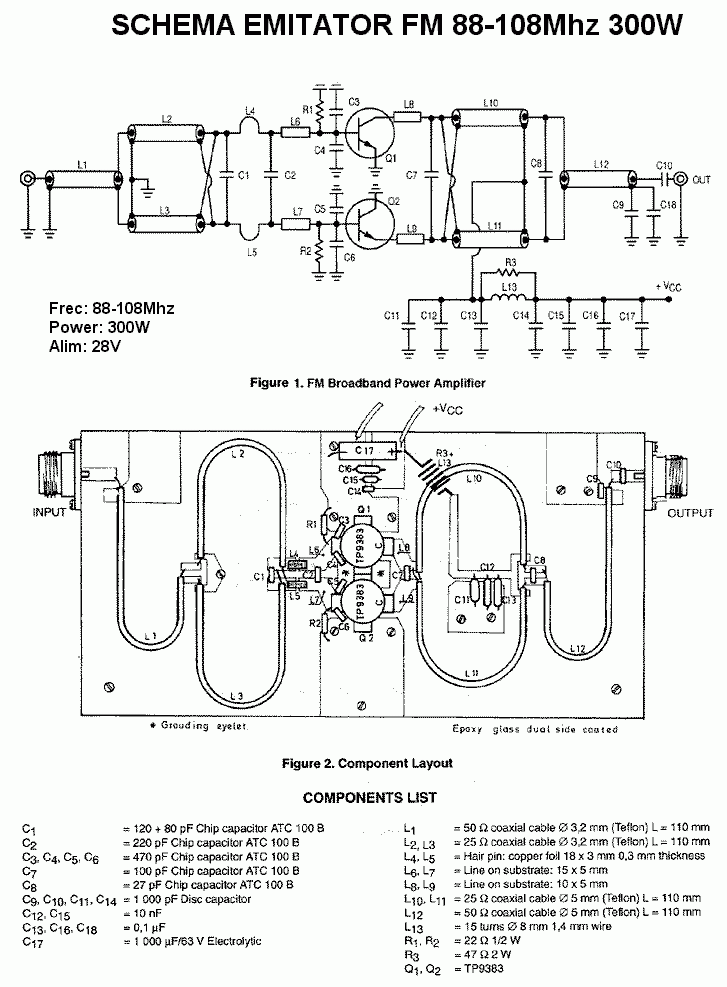
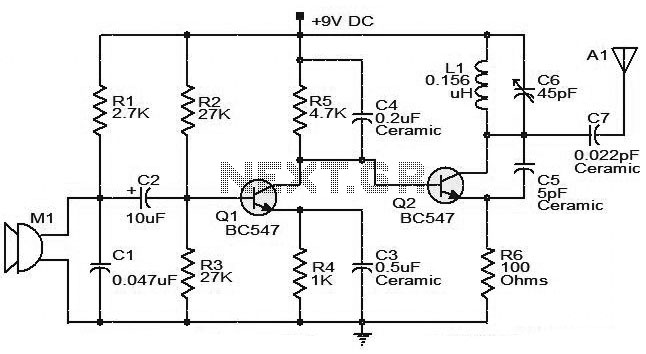
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): BasicCircuit
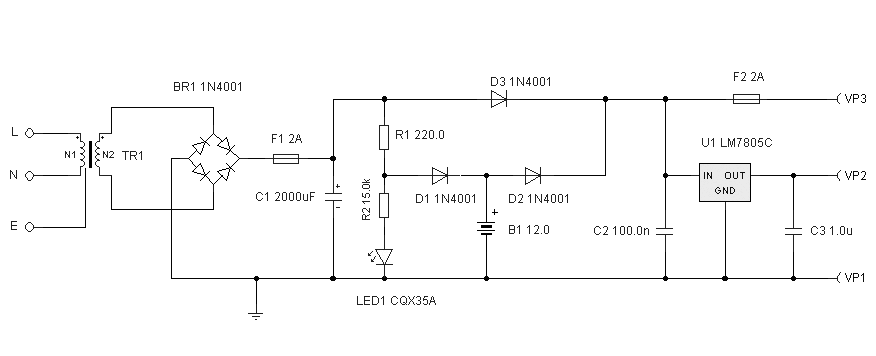
The circuit illustrated relates to a standard industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), demonstrating how the batteries assume control during an electrical outage.
The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) circuit typically consists of several key components that ensure a reliable power supply during interruptions. The core of the UPS is its battery system, which is responsible for providing backup power when the main electrical source fails.
In the circuit, the battery is connected to an inverter, which converts the stored DC power from the batteries into AC power, suitable for powering connected loads. The inverter is equipped with control circuitry that monitors the input voltage from the mains supply. When a power failure is detected, the control circuitry automatically switches the load from the mains supply to the inverter output.
Additionally, the UPS circuit includes a rectifier, which converts AC power from the mains into DC power to charge the batteries during normal operation. This ensures that the batteries remain charged and ready to provide power during an outage. A battery management system (BMS) may also be incorporated to monitor the health and state of charge of the batteries, preventing overcharging or deep discharging, which can reduce battery lifespan.
Protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are typically included to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. An indicator circuit may also be part of the design, providing visual or audible alerts to indicate the status of the UPS, such as when it is operating on battery power or when the batteries require maintenance.
Overall, the design of a UPS circuit is critical for maintaining continuous power supply in industrial settings, ensuring that sensitive equipment remains operational during electrical disturbances.The circuit drawn pertains to a regular industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), which shows how the batteries take control during an outage in elec.. 🔗 External reference
The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) circuit typically consists of several key components that ensure a reliable power supply during interruptions. The core of the UPS is its battery system, which is responsible for providing backup power when the main electrical source fails.
In the circuit, the battery is connected to an inverter, which converts the stored DC power from the batteries into AC power, suitable for powering connected loads. The inverter is equipped with control circuitry that monitors the input voltage from the mains supply. When a power failure is detected, the control circuitry automatically switches the load from the mains supply to the inverter output.
Additionally, the UPS circuit includes a rectifier, which converts AC power from the mains into DC power to charge the batteries during normal operation. This ensures that the batteries remain charged and ready to provide power during an outage. A battery management system (BMS) may also be incorporated to monitor the health and state of charge of the batteries, preventing overcharging or deep discharging, which can reduce battery lifespan.
Protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are typically included to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. An indicator circuit may also be part of the design, providing visual or audible alerts to indicate the status of the UPS, such as when it is operating on battery power or when the batteries require maintenance.
Overall, the design of a UPS circuit is critical for maintaining continuous power supply in industrial settings, ensuring that sensitive equipment remains operational during electrical disturbances.The circuit drawn pertains to a regular industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), which shows how the batteries take control during an outage in elec.. 🔗 External reference