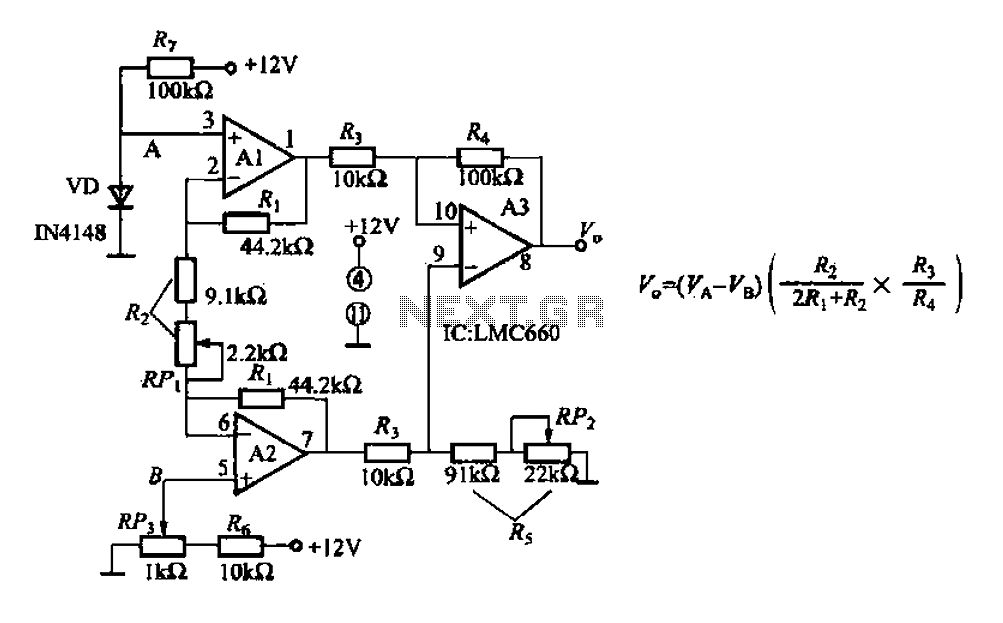
Unity-Gain Noninverting Amplifier Circuit
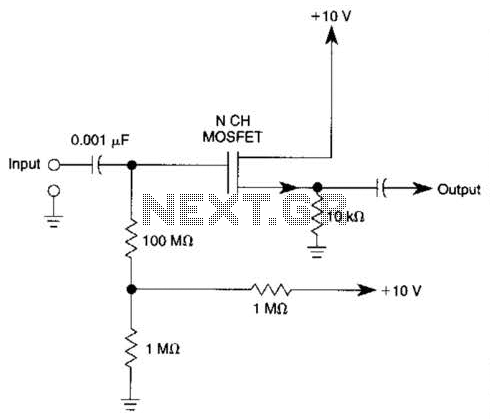
Biasing methods for an N-channel MOSFET to form a unity-gain noninverting amplifier or source-follower.
The N-channel MOSFET can be utilized in various configurations, with one common application being the unity-gain noninverting amplifier, also known as a source-follower. In this configuration, the MOSFET operates in the saturation region, where it can effectively buffer an input signal while maintaining the same voltage level at the output.
To achieve the desired biasing for the MOSFET, several methods can be employed. One common approach is to use a resistor divider network connected to the gate terminal of the MOSFET. This network establishes a stable DC voltage that sets the operating point of the device. The gate voltage must be sufficiently above the source voltage to ensure that the MOSFET remains in the saturation region throughout the input signal's range.
Another method involves using a current source to provide a constant biasing current to the MOSFET's source terminal. This arrangement helps stabilize the operating point against variations in temperature and device parameters, enhancing performance consistency.
The output of the source-follower configuration is taken from the source terminal of the MOSFET, which closely follows the input voltage while providing high input impedance and low output impedance. This characteristic makes the source-follower ideal for impedance matching applications, where it can drive loads without significant voltage drop.
In summary, employing biasing methods for an N-channel MOSFET in a unity-gain noninverting amplifier configuration allows for effective signal buffering with high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications. Biasing methods for an N-channel MOSFET to form a unity-gain noninverting amplifier or source-follower.
The N-channel MOSFET can be utilized in various configurations, with one common application being the unity-gain noninverting amplifier, also known as a source-follower. In this configuration, the MOSFET operates in the saturation region, where it can effectively buffer an input signal while maintaining the same voltage level at the output.
To achieve the desired biasing for the MOSFET, several methods can be employed. One common approach is to use a resistor divider network connected to the gate terminal of the MOSFET. This network establishes a stable DC voltage that sets the operating point of the device. The gate voltage must be sufficiently above the source voltage to ensure that the MOSFET remains in the saturation region throughout the input signal's range.
Another method involves using a current source to provide a constant biasing current to the MOSFET's source terminal. This arrangement helps stabilize the operating point against variations in temperature and device parameters, enhancing performance consistency.
The output of the source-follower configuration is taken from the source terminal of the MOSFET, which closely follows the input voltage while providing high input impedance and low output impedance. This characteristic makes the source-follower ideal for impedance matching applications, where it can drive loads without significant voltage drop.
In summary, employing biasing methods for an N-channel MOSFET in a unity-gain noninverting amplifier configuration allows for effective signal buffering with high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications. Biasing methods for an N-channel MOSFET to form a unity-gain noninverting amplifier or source-follower.