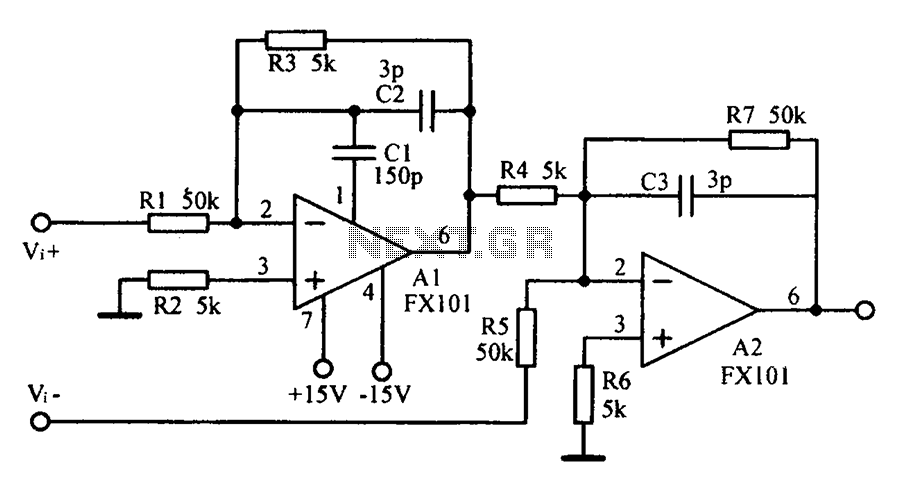
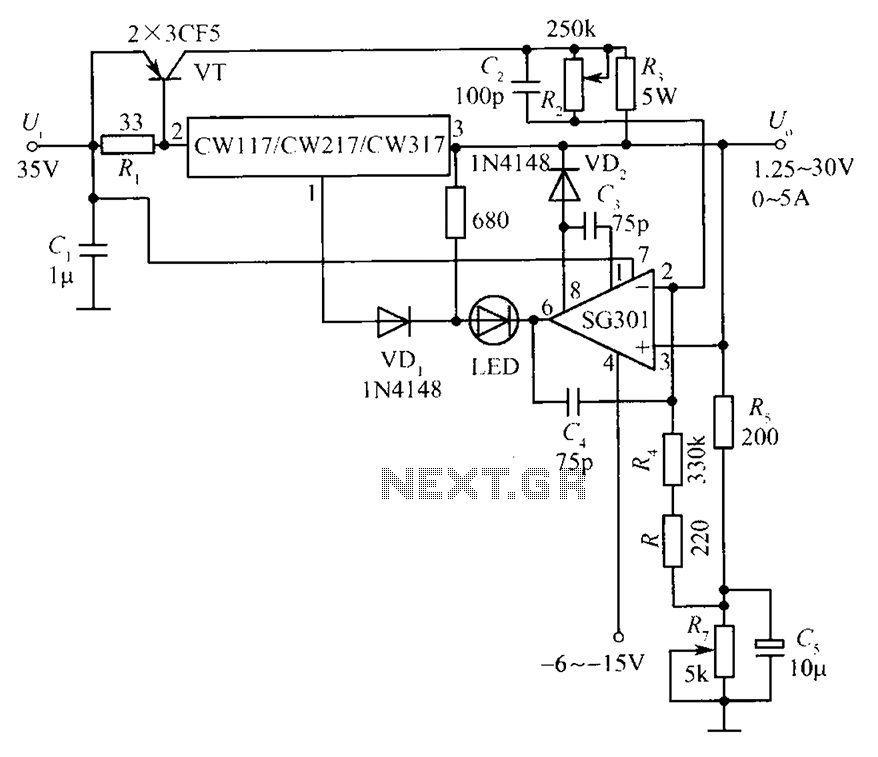
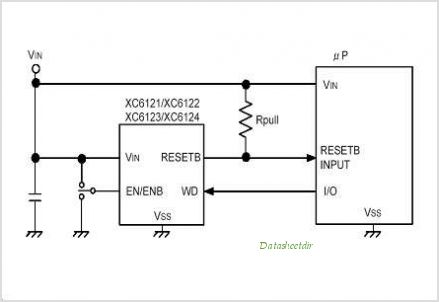
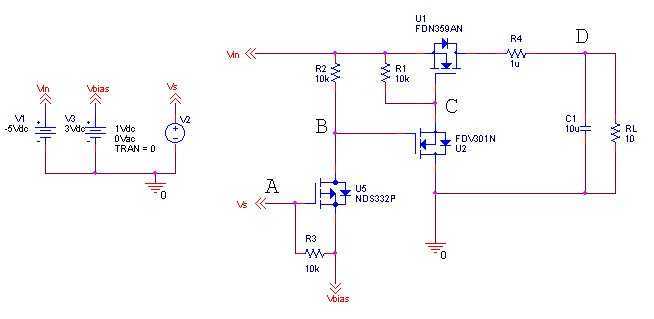
Varactor The Core of Voltage Controlled LC Tuner
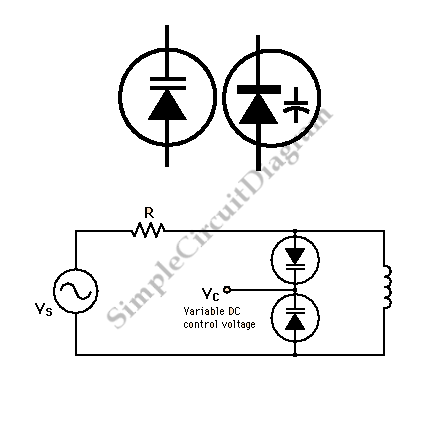
In a hybrid system, an analog system with digital control, voltage-controlled components are crucial as they can be interfaced with a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) from the digital system.
In hybrid systems, the integration of analog and digital components allows for enhanced functionality and versatility in various applications. The voltage-controlled elements serve as a bridge between the digital and analog domains, enabling precise control over analog signals. The DAC plays a pivotal role in this setup by converting digital signals into corresponding analog voltages, which can then be used to control various analog devices, such as motors, sensors, and amplifiers.
The design of such a hybrid system typically involves several key components: the digital control unit, the DAC, and the analog subsystems. The digital control unit, often implemented using microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs), generates the digital signals based on the desired output or control parameters. These digital signals are then fed into the DAC, which converts them into analog voltages. The output voltage of the DAC can be adjusted based on the input digital values, allowing for fine-tuned control over the connected analog devices.
Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be incorporated to monitor the performance of the analog components. Sensors can be used to provide real-time data to the digital control unit, enabling dynamic adjustments to the output voltage as needed. This feedback loop enhances the system's responsiveness and accuracy, making it suitable for applications such as robotics, automated control systems, and audio processing.
Overall, the combination of analog systems with digital control through voltage-controlled components and DACs is fundamental in creating efficient, high-performance hybrid systems that meet the demands of modern electronic applications.In hybrid system, analog system with digital control, a voltage controlled things is very important since it can be interfaced by DAC from digital system. For.. 🔗 External reference
In hybrid systems, the integration of analog and digital components allows for enhanced functionality and versatility in various applications. The voltage-controlled elements serve as a bridge between the digital and analog domains, enabling precise control over analog signals. The DAC plays a pivotal role in this setup by converting digital signals into corresponding analog voltages, which can then be used to control various analog devices, such as motors, sensors, and amplifiers.
The design of such a hybrid system typically involves several key components: the digital control unit, the DAC, and the analog subsystems. The digital control unit, often implemented using microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs), generates the digital signals based on the desired output or control parameters. These digital signals are then fed into the DAC, which converts them into analog voltages. The output voltage of the DAC can be adjusted based on the input digital values, allowing for fine-tuned control over the connected analog devices.
Additionally, feedback mechanisms may be incorporated to monitor the performance of the analog components. Sensors can be used to provide real-time data to the digital control unit, enabling dynamic adjustments to the output voltage as needed. This feedback loop enhances the system's responsiveness and accuracy, making it suitable for applications such as robotics, automated control systems, and audio processing.
Overall, the combination of analog systems with digital control through voltage-controlled components and DACs is fundamental in creating efficient, high-performance hybrid systems that meet the demands of modern electronic applications.In hybrid system, analog system with digital control, a voltage controlled things is very important since it can be interfaced by DAC from digital system. For.. 🔗 External reference