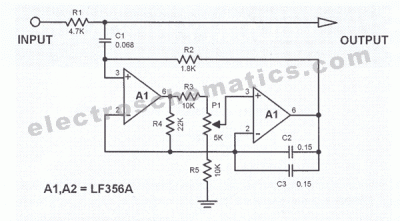
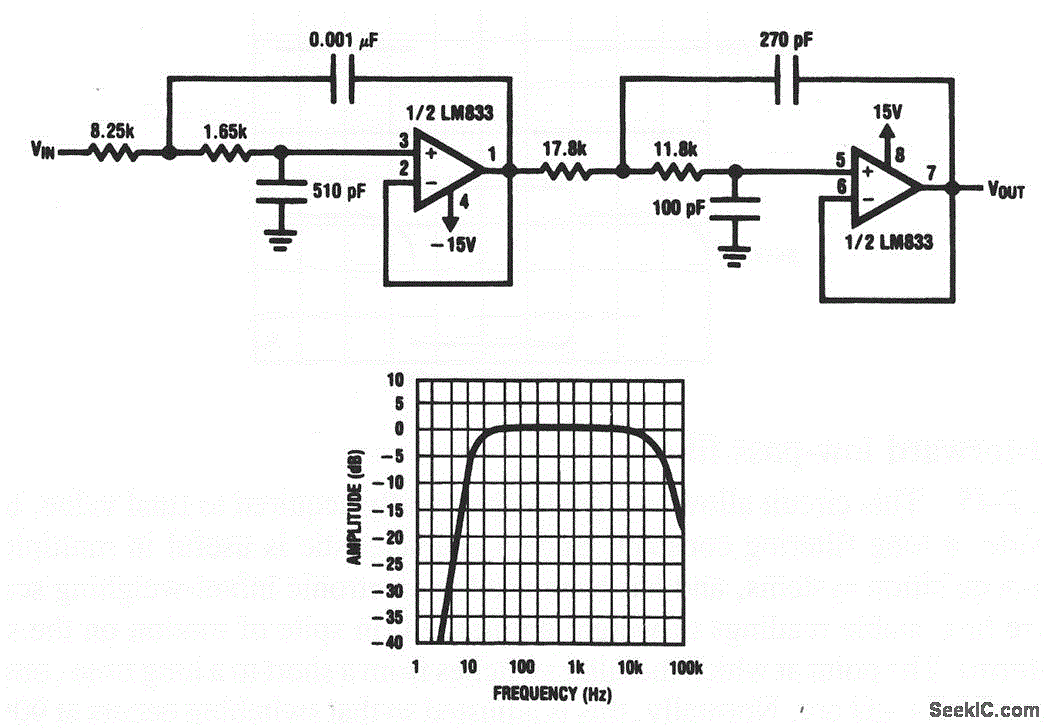
Variable bandwidth bandpass active filter
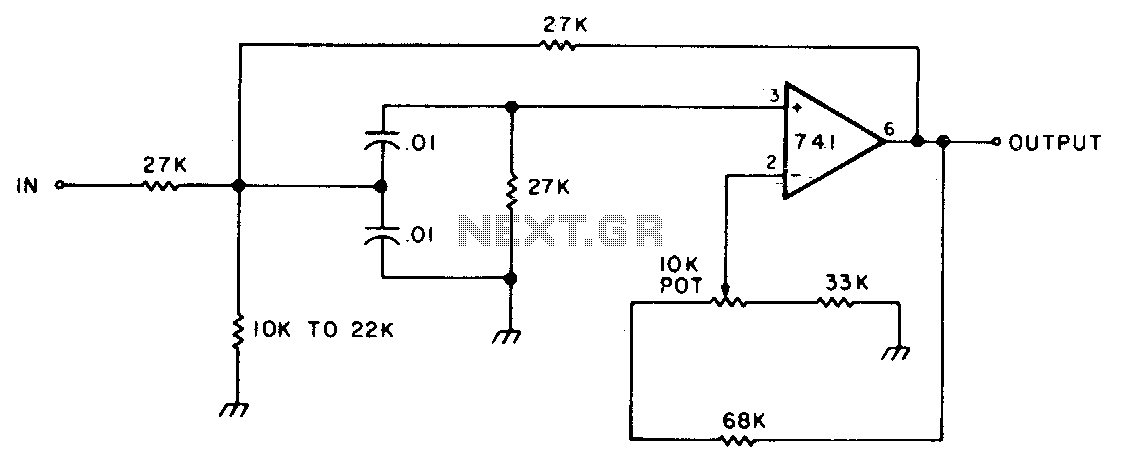
This circuit features adjustable bandwidth with a center frequency of approximately 800 Hz. A 10 kΩ potentiometer is used to adjust the bandwidth, varying from approximately ±350 Hz to ±140 Hz at the 3 dB down points.
The circuit operates around a central frequency of 800 Hz, which is essential for applications requiring precise frequency selection and filtering. The use of a 10 kΩ potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the bandwidth, providing flexibility in signal processing. The bandwidth adjustment range is significant, spanning ±350 Hz to ±140 Hz, which corresponds to the 3 dB down points of the frequency response curve.
In practical terms, this means that the circuit can effectively filter signals within a range of frequencies centered around 800 Hz. When the bandwidth is set to its maximum of ±350 Hz, the circuit can accommodate a broader range of input signals, making it suitable for applications where signal variability is expected. Conversely, narrowing the bandwidth to ±140 Hz allows for more selective filtering, which is advantageous in scenarios where precision is critical, such as in audio processing or communication systems.
The design may incorporate operational amplifiers or active filters to achieve the desired frequency response characteristics. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can modify the gain and phase response of the circuit, thereby tailoring the performance to specific requirements. The circuit's ability to adjust bandwidth dynamically makes it a versatile component in various electronic systems, enhancing its applicability in both consumer and professional audio equipment.This circuit has adjustable bandwidth with values for a center frequency of about 800 Hz The 10-K pot adjusts bandwidth from approximately ±350 Hz to ±140 Hz at 3 dB down points.
The circuit operates around a central frequency of 800 Hz, which is essential for applications requiring precise frequency selection and filtering. The use of a 10 kΩ potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the bandwidth, providing flexibility in signal processing. The bandwidth adjustment range is significant, spanning ±350 Hz to ±140 Hz, which corresponds to the 3 dB down points of the frequency response curve.
In practical terms, this means that the circuit can effectively filter signals within a range of frequencies centered around 800 Hz. When the bandwidth is set to its maximum of ±350 Hz, the circuit can accommodate a broader range of input signals, making it suitable for applications where signal variability is expected. Conversely, narrowing the bandwidth to ±140 Hz allows for more selective filtering, which is advantageous in scenarios where precision is critical, such as in audio processing or communication systems.
The design may incorporate operational amplifiers or active filters to achieve the desired frequency response characteristics. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can modify the gain and phase response of the circuit, thereby tailoring the performance to specific requirements. The circuit's ability to adjust bandwidth dynamically makes it a versatile component in various electronic systems, enhancing its applicability in both consumer and professional audio equipment.This circuit has adjustable bandwidth with values for a center frequency of about 800 Hz The 10-K pot adjusts bandwidth from approximately ±350 Hz to ±140 Hz at 3 dB down points.