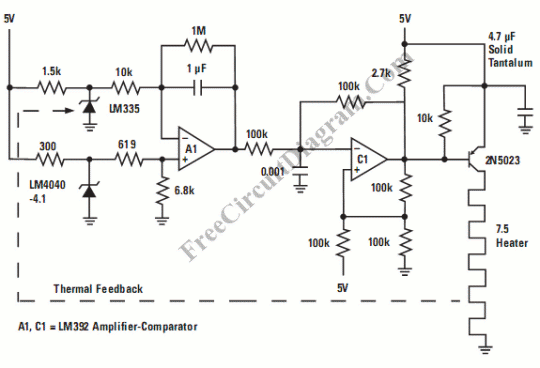
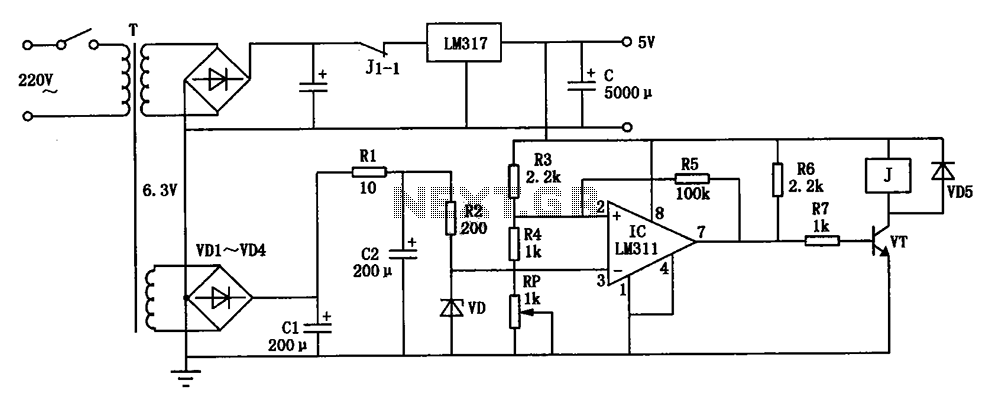
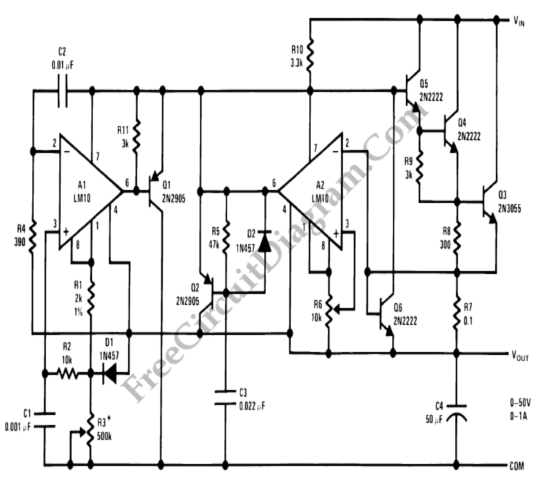
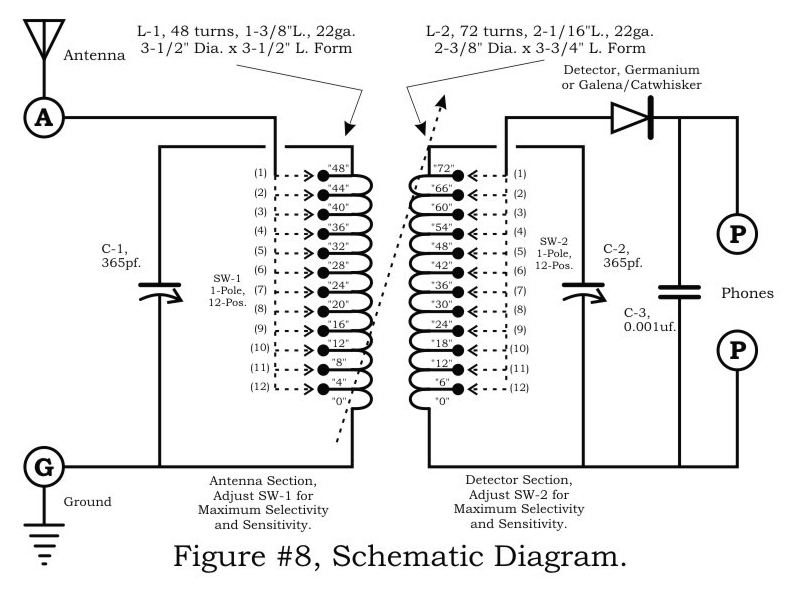
VERY LOW POWER GATED CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
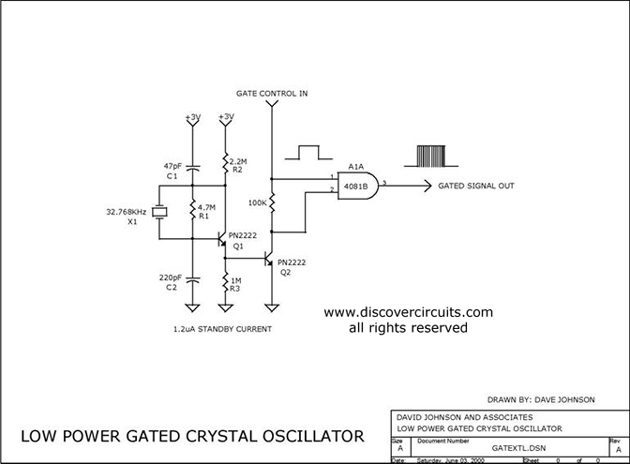
The circuit controls the output of a continuously operating 32KHz crystal oscillator, directing it to the input of a C-MOS buffer when clock pulses are required. This technique addresses the issue of a slow-starting crystal oscillator by maintaining the oscillator's operation and activating a transistor power stage only when necessary. This approach minimizes standby power consumption.
The circuit is designed to efficiently manage the output from a 32KHz crystal oscillator, which serves as a stable timing reference. The oscillator operates continuously, ensuring that clock pulses are readily available without the delays typically associated with starting up a crystal oscillator. By utilizing a C-MOS buffer, the circuit can effectively drive subsequent digital logic circuits while maintaining low power consumption.
The integration of a transistor power stage allows for selective activation of the oscillator's output. This means that the oscillator can remain in a low-power standby mode until clock pulses are required for operation. When the clock signal is needed, the transistor is turned on, allowing the buffered signal to drive the load. This design not only improves response times but also significantly reduces energy usage during periods of inactivity.
In summary, the circuit combines the reliability of a crystal oscillator with the efficiency of C-MOS technology and transistor switching, making it suitable for applications where low power consumption and quick response times are critical. The careful management of power states ensures that the overall system remains efficient while providing the necessary timing signals on demand.The circuit gates the output of a continuously operating 32KHz crystal oscillator to the input of a C-MOS buffer when clock pulses are needed. The technique gets around the problem of a slow starting crystal oscillator by keeping the oscillator going and switching on a transistor power stage only as needed.
The method keeps the standby power consumption to a.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to efficiently manage the output from a 32KHz crystal oscillator, which serves as a stable timing reference. The oscillator operates continuously, ensuring that clock pulses are readily available without the delays typically associated with starting up a crystal oscillator. By utilizing a C-MOS buffer, the circuit can effectively drive subsequent digital logic circuits while maintaining low power consumption.
The integration of a transistor power stage allows for selective activation of the oscillator's output. This means that the oscillator can remain in a low-power standby mode until clock pulses are required for operation. When the clock signal is needed, the transistor is turned on, allowing the buffered signal to drive the load. This design not only improves response times but also significantly reduces energy usage during periods of inactivity.
In summary, the circuit combines the reliability of a crystal oscillator with the efficiency of C-MOS technology and transistor switching, making it suitable for applications where low power consumption and quick response times are critical. The careful management of power states ensures that the overall system remains efficient while providing the necessary timing signals on demand.The circuit gates the output of a continuously operating 32KHz crystal oscillator to the input of a C-MOS buffer when clock pulses are needed. The technique gets around the problem of a slow starting crystal oscillator by keeping the oscillator going and switching on a transistor power stage only as needed.
The method keeps the standby power consumption to a.. 🔗 External reference