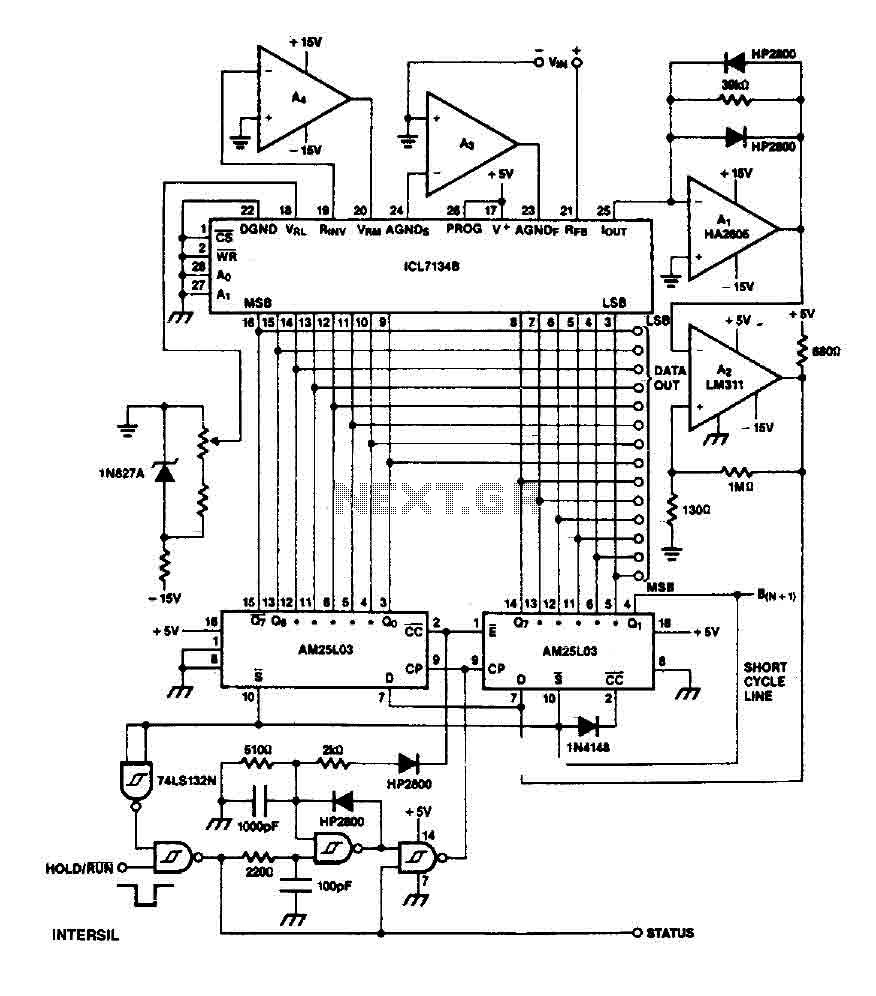
VFC110: Single Chip High-Frequency Voltage-to-Frequency Converter (VFC)
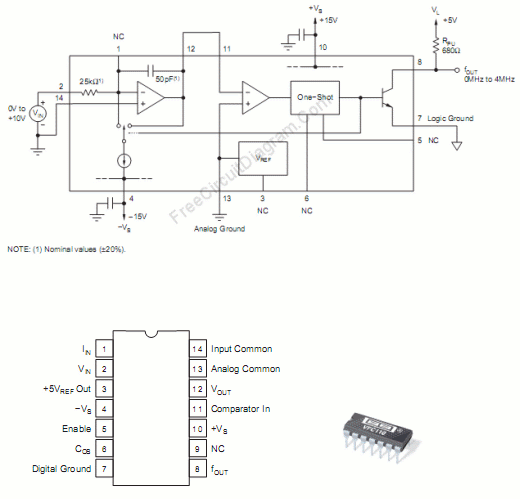
The VFC110 chip can be utilized to construct a high-frequency voltage-to-frequency converter. This chip features high-frequency operation capability, a disable function, and an on-board precision 5V reference. This precision reference can serve to offset the VFC transfer function and provide excitation for transducers or bridges. Additionally, the enable function allows for multiplexing multiple VFC outputs. The output stage is an open collector that is compatible with TTL or CMOS logic levels. The schematic diagram of the circuit indicates that it employs only a pull-up resistor for the output and two bypass capacitors for power supply filtering. A 100nF mylar capacitor is suitable for these bypassing capacitors. With a minimal component count, this circuit delivers a 0-4 MHz output for a 0-10V input voltage.
The VFC110 voltage-to-frequency converter is designed to convert an analog voltage input into a frequency output, making it suitable for various applications requiring frequency modulation of voltage signals. The high-frequency capability of the VFC110 enables it to handle input voltages ranging from 0V to 10V, translating this range into a frequency output from 0 Hz to 4 MHz.
The chip's internal architecture includes a precision 5V reference, which is crucial for maintaining accuracy in the conversion process. This reference voltage can be used to calibrate the output frequency, ensuring that the converter operates within specified tolerances. The disable function allows for power management by turning off the chip when not in use, thus reducing power consumption.
The output stage, designed as an open collector, allows for easy interfacing with other digital circuits. This configuration means that the output can be connected to various logic families, including TTL and CMOS, making the VFC110 versatile for integration into different electronic systems.
For the circuit design, the use of a pull-up resistor is essential for ensuring that the output signal is pulled to a high state when the open collector output is not actively driven low. The inclusion of two bypass capacitors is vital for filtering power supply noise, which can adversely affect the performance of the voltage-to-frequency conversion. The recommended 100nF mylar capacitors are effective in providing stable power supply conditions, enhancing the reliability of the converter's output.
Overall, the VFC110 chip represents an efficient solution for converting voltage levels into corresponding frequency signals, suitable for applications in signal processing, sensor interfacing, and data acquisition systems.Using VFC110 chip, we can build a high frequency voltage-to-frequency converter. The features of this chip include the capability of high frequency operation, disable function, and an on-board precision 5V reference. This precision reference can be used to provide reference for offsetting the VFC transfer function, as well as provide transducer or
bridge excitation. As well as shutting off the single VFC chip, Multiplexing several VFC outputs can be done by the enable function. The output is an open collector stage that is compatible with TTL or CMOS logics. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: You can see that this circuit only use a pull up resistor for the output and two bypass capacitors for power supply filtering.
You can use a 100nF mylar cap for these two bypassing capacitors. Using minimum the component count, this circuit provide 0-4MHz output for 0-10V input voltage. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: Texas Instruments Application Notes] 🔗 External reference
The VFC110 voltage-to-frequency converter is designed to convert an analog voltage input into a frequency output, making it suitable for various applications requiring frequency modulation of voltage signals. The high-frequency capability of the VFC110 enables it to handle input voltages ranging from 0V to 10V, translating this range into a frequency output from 0 Hz to 4 MHz.
The chip's internal architecture includes a precision 5V reference, which is crucial for maintaining accuracy in the conversion process. This reference voltage can be used to calibrate the output frequency, ensuring that the converter operates within specified tolerances. The disable function allows for power management by turning off the chip when not in use, thus reducing power consumption.
The output stage, designed as an open collector, allows for easy interfacing with other digital circuits. This configuration means that the output can be connected to various logic families, including TTL and CMOS, making the VFC110 versatile for integration into different electronic systems.
For the circuit design, the use of a pull-up resistor is essential for ensuring that the output signal is pulled to a high state when the open collector output is not actively driven low. The inclusion of two bypass capacitors is vital for filtering power supply noise, which can adversely affect the performance of the voltage-to-frequency conversion. The recommended 100nF mylar capacitors are effective in providing stable power supply conditions, enhancing the reliability of the converter's output.
Overall, the VFC110 chip represents an efficient solution for converting voltage levels into corresponding frequency signals, suitable for applications in signal processing, sensor interfacing, and data acquisition systems.Using VFC110 chip, we can build a high frequency voltage-to-frequency converter. The features of this chip include the capability of high frequency operation, disable function, and an on-board precision 5V reference. This precision reference can be used to provide reference for offsetting the VFC transfer function, as well as provide transducer or
bridge excitation. As well as shutting off the single VFC chip, Multiplexing several VFC outputs can be done by the enable function. The output is an open collector stage that is compatible with TTL or CMOS logics. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: You can see that this circuit only use a pull up resistor for the output and two bypass capacitors for power supply filtering.
You can use a 100nF mylar cap for these two bypassing capacitors. Using minimum the component count, this circuit provide 0-4MHz output for 0-10V input voltage. [Circuit`s schematic diagram source: Texas Instruments Application Notes] 🔗 External reference