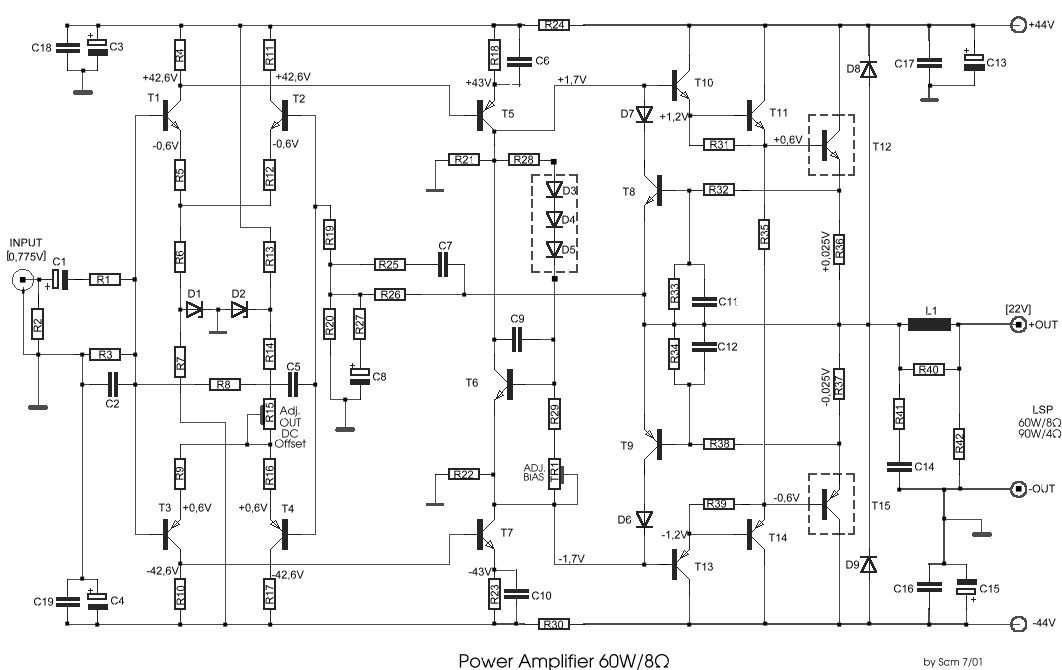
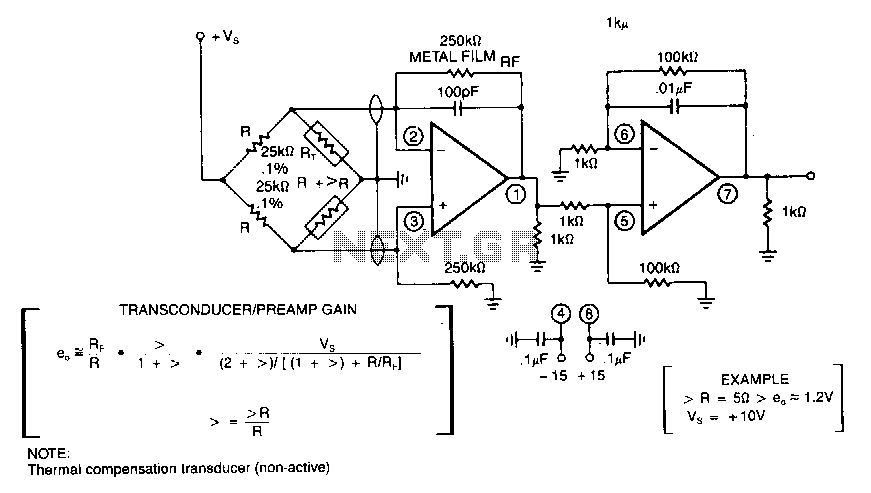
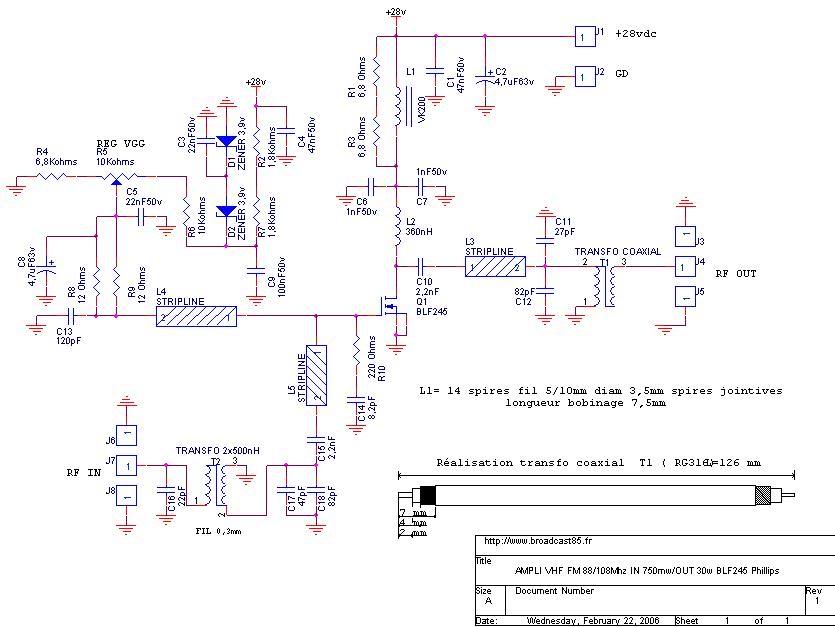
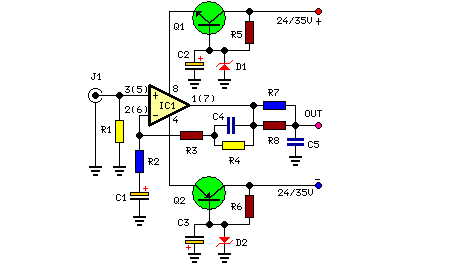
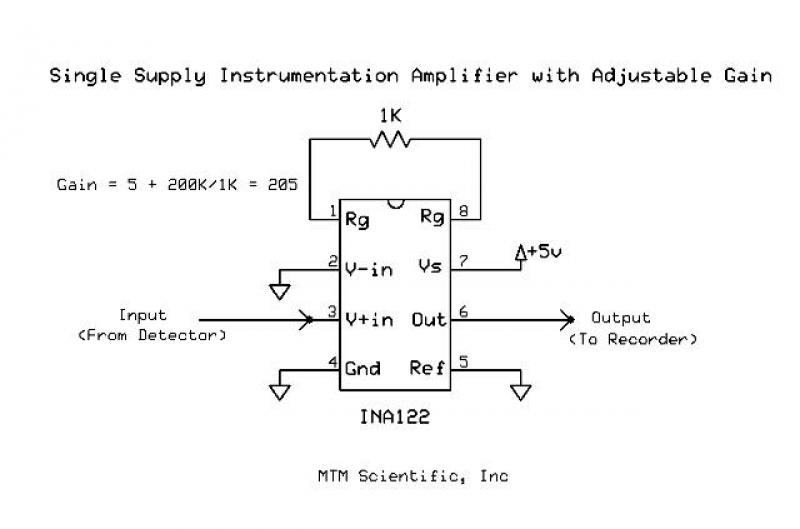
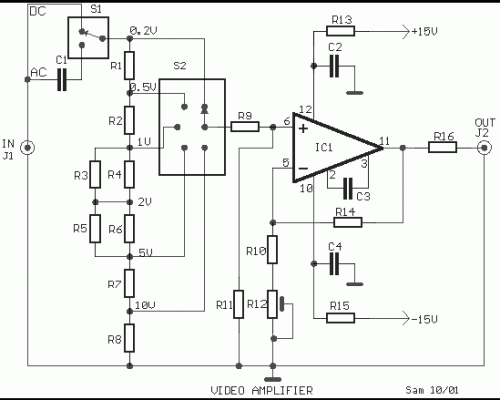
Video amplifier 1
The objective is to enhance information transmission through the distribution of articles. For any issues related to article content, copyright, or other concerns, please reach out via email to [email protected] within 15 days. Prompt action will be taken to address these matters.
In the context of electronic communication systems, the transmission of information can be significantly improved through the integration of various protocols and technologies. The process involves encoding data into a suitable format for transmission, ensuring that the integrity and confidentiality of the information are maintained throughout.
To facilitate this, a well-structured electronic circuit may be employed, which includes components such as microcontrollers, transceivers, and signal processing units. The circuit design would typically feature a microcontroller that manages data processing and controls the transmission of information. This microcontroller can be programmed to handle various communication protocols, such as UART, SPI, or I2C, depending on the application requirements.
Transceivers play a crucial role in this setup, converting digital signals from the microcontroller into analog signals suitable for transmission over various media, such as wired or wireless channels. These components must be carefully selected based on their operating frequency, range, and data rate capabilities to ensure effective communication.
Signal processing units may also be integrated to enhance the quality of the transmitted data, employing techniques such as error correction, modulation, and demodulation. This ensures that any potential issues arising from noise or interference during transmission are mitigated, thus preserving the accuracy and reliability of the information being conveyed.
Overall, a comprehensive approach to circuit design that incorporates these elements will facilitate the effective transmission of information, addressing potential issues related to content and copyright, and ensuring that the communication remains robust and efficient.We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
In the context of electronic communication systems, the transmission of information can be significantly improved through the integration of various protocols and technologies. The process involves encoding data into a suitable format for transmission, ensuring that the integrity and confidentiality of the information are maintained throughout.
To facilitate this, a well-structured electronic circuit may be employed, which includes components such as microcontrollers, transceivers, and signal processing units. The circuit design would typically feature a microcontroller that manages data processing and controls the transmission of information. This microcontroller can be programmed to handle various communication protocols, such as UART, SPI, or I2C, depending on the application requirements.
Transceivers play a crucial role in this setup, converting digital signals from the microcontroller into analog signals suitable for transmission over various media, such as wired or wireless channels. These components must be carefully selected based on their operating frequency, range, and data rate capabilities to ensure effective communication.
Signal processing units may also be integrated to enhance the quality of the transmitted data, employing techniques such as error correction, modulation, and demodulation. This ensures that any potential issues arising from noise or interference during transmission are mitigated, thus preserving the accuracy and reliability of the information being conveyed.
Overall, a comprehensive approach to circuit design that incorporates these elements will facilitate the effective transmission of information, addressing potential issues related to content and copyright, and ensuring that the communication remains robust and efficient.We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference