DC Instrumentation Amplifier Circuit
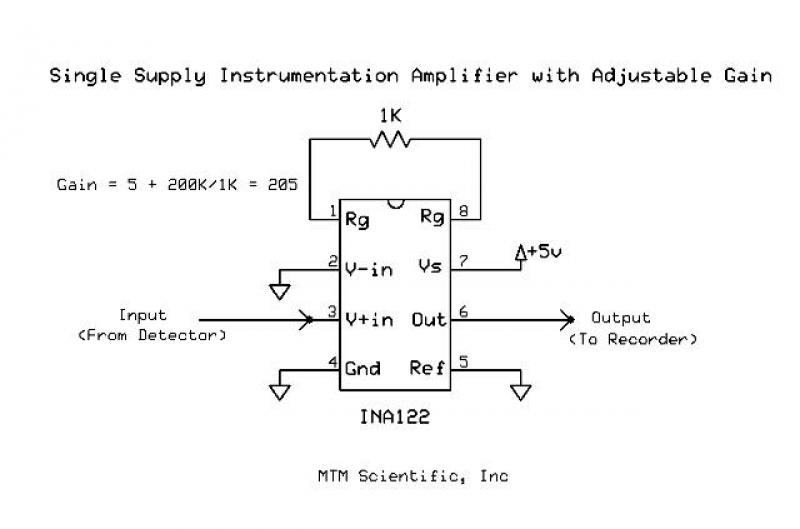
A common challenge for experimenters is increasing the gain of a low-level DC voltage for recording or analysis. Most instrumentation circuits require building a complicated project with dual power supplies and high-accuracy components. A simple solution is to use an Integrated Circuit (IC) specifically designed for this purpose, such as the INA122. This particular instrumentation amplifier IC is very easy to use because it operates from a single supply voltage and only one external resistor is needed to set the DC gain. In this example, the gain is set to 205X. The gain is calculated according to the formula Gain = 5 + (200K / R). The maximum output signal from the amplifier cannot exceed the supply voltage. The meter or device that reads the output from the amplifier should have a high input impedance. This same circuit can be used to amplify a differential voltage by connecting Pin 2 (V- in) to the reference voltage instead of ground. There are many more examples of using this amplifier.
The INA122 is a low-power instrumentation amplifier that is particularly suited for applications requiring high precision and low noise. It is designed to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise, making it ideal for sensor applications. The amplifier operates on a single supply voltage, typically ranging from 2.7V to 36V, which simplifies the power supply requirements when integrating into various systems.
To configure the INA122 for a specific gain, only one resistor is necessary. This resistor, connected between the gain-setting pins, determines the overall gain of the amplifier. For instance, using a 200kΩ resistor will set the gain to 205, as per the formula Gain = 5 + (200K / R). It is crucial to ensure that the resistor is of high quality to maintain the accuracy and stability of the gain.
The output of the INA122 is limited by the supply voltage, meaning that the maximum output signal cannot exceed the voltage provided to the IC. Therefore, careful consideration must be given to the supply voltage to ensure that the output remains within the desired range for the application. Additionally, the load connected to the output of the INA122 should have a high input impedance to avoid loading effects that could degrade the performance of the amplifier.
In applications where differential voltage amplification is required, the INA122 can be configured by connecting Pin 2 (V- in) to a reference voltage instead of ground. This flexibility allows the amplifier to be used in a wide range of measurement scenarios, including sensor signal conditioning and data acquisition systems.
Overall, the INA122 provides a straightforward and effective method for amplifying low-level DC voltages, making it a valuable component in many electronic instrumentation applications. Its ease of use, combined with the ability to achieve high gain with minimal external components, simplifies the design process for engineers and experimenters alike.A common challenge for experimenters is increasing the gain of a low level DC voltage for recording or analysis. Most instrumentation circuits require building a complicated project with dual power supplies and high accuracy components.
A simple solution is to use an Integrated Circuit (IC) specifically designed for the purpose, such as the INA122. This particular instrumentation amplifier IC is very easy to use because it operates from a single supply voltage and only one external resistor is needed to set the DC gain.
Here is the circuit diagram showing how to use the INA122 to make a basic DC amplifier.
The INA122 is a low-power instrumentation amplifier that is particularly suited for applications requiring high precision and low noise. It is designed to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise, making it ideal for sensor applications. The amplifier operates on a single supply voltage, typically ranging from 2.7V to 36V, which simplifies the power supply requirements when integrating into various systems.
To configure the INA122 for a specific gain, only one resistor is necessary. This resistor, connected between the gain-setting pins, determines the overall gain of the amplifier. For instance, using a 200kΩ resistor will set the gain to 205, as per the formula Gain = 5 + (200K / R). It is crucial to ensure that the resistor is of high quality to maintain the accuracy and stability of the gain.
The output of the INA122 is limited by the supply voltage, meaning that the maximum output signal cannot exceed the voltage provided to the IC. Therefore, careful consideration must be given to the supply voltage to ensure that the output remains within the desired range for the application. Additionally, the load connected to the output of the INA122 should have a high input impedance to avoid loading effects that could degrade the performance of the amplifier.
In applications where differential voltage amplification is required, the INA122 can be configured by connecting Pin 2 (V- in) to a reference voltage instead of ground. This flexibility allows the amplifier to be used in a wide range of measurement scenarios, including sensor signal conditioning and data acquisition systems.
Overall, the INA122 provides a straightforward and effective method for amplifying low-level DC voltages, making it a valuable component in many electronic instrumentation applications. Its ease of use, combined with the ability to achieve high gain with minimal external components, simplifies the design process for engineers and experimenters alike.A common challenge for experimenters is increasing the gain of a low level DC voltage for recording or analysis. Most instrumentation circuits require building a complicated project with dual power supplies and high accuracy components.
A simple solution is to use an Integrated Circuit (IC) specifically designed for the purpose, such as the INA122. This particular instrumentation amplifier IC is very easy to use because it operates from a single supply voltage and only one external resistor is needed to set the DC gain.
Here is the circuit diagram showing how to use the INA122 to make a basic DC amplifier.
In this particular example the gain is set to 205X. The gain is calculated according to the formula Gain = 5 + (200K / R). The maximum output signal from the amplifier cannot exceed the supply voltage. The meter or device which reads the output from the amplifier should have a high input impedance. This same circuit can be used to amplify a differential voltage by connecting Pin 2 (V- in) to the reference voltage instead of ground. There are many more examples for using this amplifier.
🔗 External reference