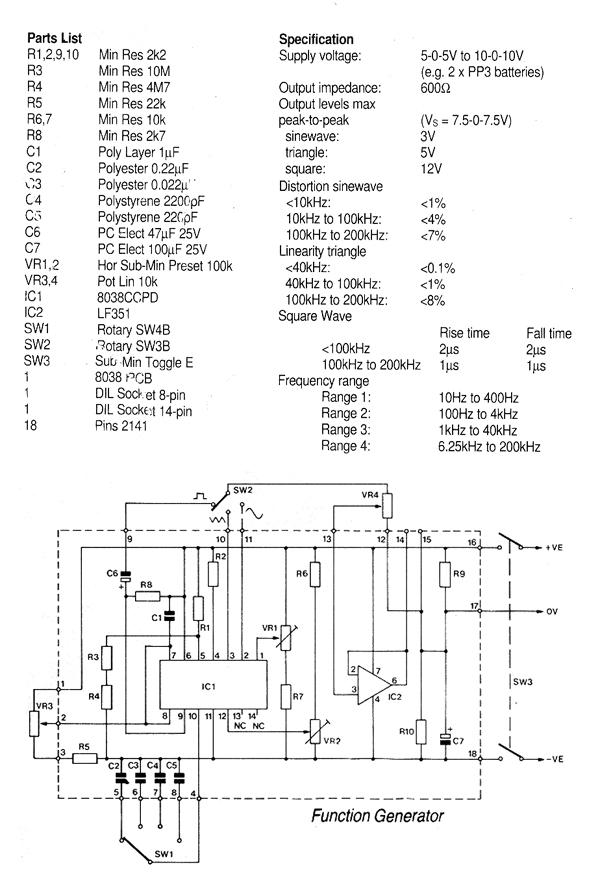
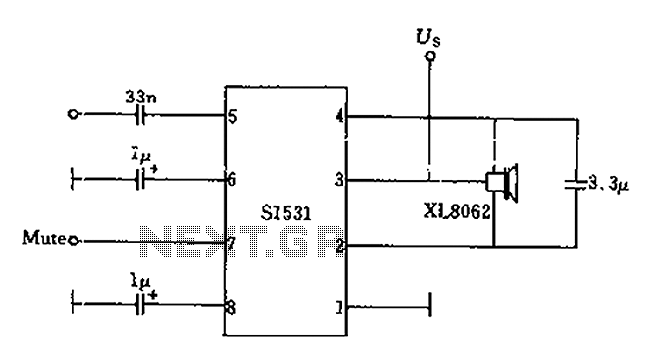
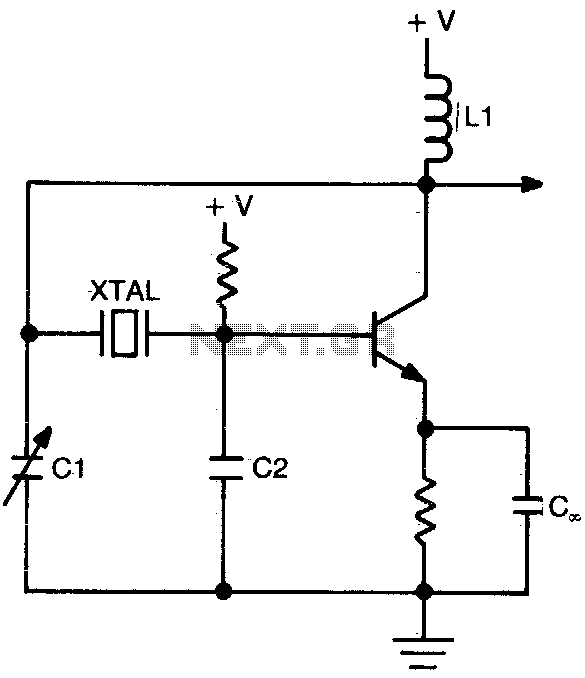
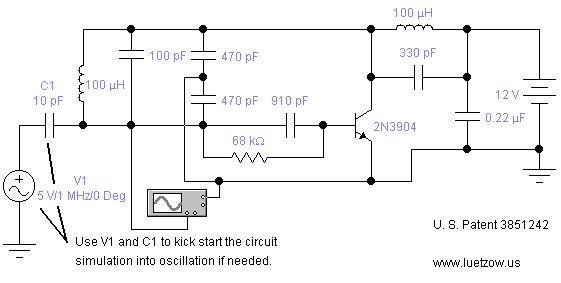
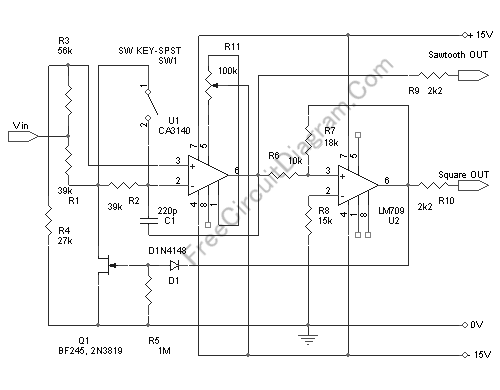
voltage controlled oscillator

A voltage-controlled oscillator is an oscillator whose frequency of oscillation can be varied by changing an applied voltage.
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an essential component in various electronic systems, particularly in communication devices, signal processing, and modulation applications. The fundamental operation of a VCO relies on the relationship between an input voltage and the frequency of the output signal. By adjusting the input voltage, the frequency of the oscillation can be finely tuned, allowing for dynamic frequency modulation.
Typically, a VCO is implemented using various configurations, including LC (inductor-capacitor) circuits, ring oscillators, or relaxation oscillators. In an LC VCO, the oscillation frequency is determined by the resonant frequency of the LC tank circuit, which consists of an inductor and a capacitor. The capacitance in the circuit can be varied using a variable capacitor or a voltage-controlled capacitor, such as a varactor diode, to achieve the desired frequency modulation.
In practical applications, VCOs are often characterized by their tuning range, phase noise, and linearity of frequency response concerning the control voltage. The tuning range defines the span of frequencies over which the oscillator can operate effectively, while phase noise indicates the stability of the frequency output over time. Linearity is crucial for applications where precise frequency control is required, such as in phase-locked loops (PLLs) and frequency synthesizers.
The output of a VCO can be a sine wave, square wave, or triangular wave, depending on the design and application. The choice of output waveform will influence the subsequent stages of the circuit, including filtering, amplification, and modulation.
In summary, a voltage-controlled oscillator is a versatile and critical component in modern electronics, enabling precise control of frequency in various applications, from simple tone generation to complex communication systems.voltage-controlled oscillator. An oscillator whose frequency of oscillation can be varied by changing an applied.. 🔗 External reference
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an essential component in various electronic systems, particularly in communication devices, signal processing, and modulation applications. The fundamental operation of a VCO relies on the relationship between an input voltage and the frequency of the output signal. By adjusting the input voltage, the frequency of the oscillation can be finely tuned, allowing for dynamic frequency modulation.
Typically, a VCO is implemented using various configurations, including LC (inductor-capacitor) circuits, ring oscillators, or relaxation oscillators. In an LC VCO, the oscillation frequency is determined by the resonant frequency of the LC tank circuit, which consists of an inductor and a capacitor. The capacitance in the circuit can be varied using a variable capacitor or a voltage-controlled capacitor, such as a varactor diode, to achieve the desired frequency modulation.
In practical applications, VCOs are often characterized by their tuning range, phase noise, and linearity of frequency response concerning the control voltage. The tuning range defines the span of frequencies over which the oscillator can operate effectively, while phase noise indicates the stability of the frequency output over time. Linearity is crucial for applications where precise frequency control is required, such as in phase-locked loops (PLLs) and frequency synthesizers.
The output of a VCO can be a sine wave, square wave, or triangular wave, depending on the design and application. The choice of output waveform will influence the subsequent stages of the circuit, including filtering, amplification, and modulation.
In summary, a voltage-controlled oscillator is a versatile and critical component in modern electronics, enabling precise control of frequency in various applications, from simple tone generation to complex communication systems.voltage-controlled oscillator. An oscillator whose frequency of oscillation can be varied by changing an applied.. 🔗 External reference