Voltage monitor circuit
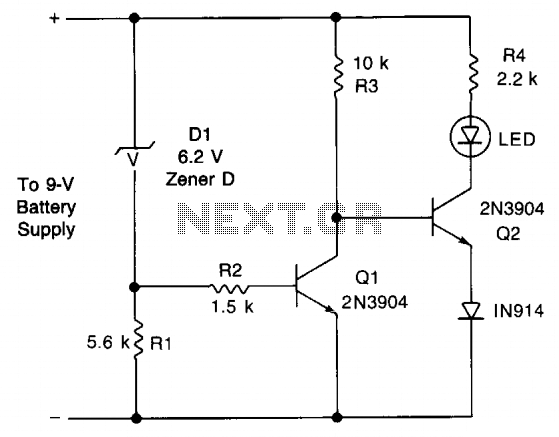
This circuit provides an early warning for battery discharge. A Zener diode (D1) is selected to indicate when the voltage falls below 9 V. If the supply voltage drops below 7 V, D1 will stop conducting, which will cause transistor Q1 to turn off. Consequently, the collector voltage of Q1 will rise, leading to the conduction of transistor Q2 through LED1 and its current-limiting resistor R4.
The described circuit employs a Zener diode (D1) to create a voltage reference point at 9 V. This component is critical in monitoring the voltage level of the battery. When the battery voltage is above 9 V, D1 remains in a conducting state, allowing current to flow through Q1, keeping it in the 'on' state. This action ensures that the output remains stable and does not trigger any warning signals.
As the battery discharges and the voltage drops to 7 V, D1 will no longer conduct. This cessation of current flow causes Q1 to turn off, which results in an increase in the collector voltage of Q1. The increased voltage at the collector will forward-bias Q2, allowing it to conduct. This conduction of Q2 activates LED1, providing a visual indication that the battery voltage has fallen below the critical threshold.
Resistor R4 is incorporated in series with LED1 to limit the current flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from excessive current which could lead to failure. The choice of resistor value is essential to ensure that LED1 operates within its specified current range.
This circuit is particularly useful in battery-operated devices where monitoring battery health is crucial for reliable operation. By providing an early warning signal, it allows users to take action before the battery voltage drops to a level that could lead to device malfunction or damage.This circuit gives an early warning of the discharge of batteries. Zener diode Dl is chosen for the voltage below which an indication is required (9 V). Should the supply drop to below 7 V, Dl will cease conducting causing Ql to shut off. Its collector voltage will now increase causing Q2 to start conducting via LED1 and its limiting resistor R4.
The described circuit employs a Zener diode (D1) to create a voltage reference point at 9 V. This component is critical in monitoring the voltage level of the battery. When the battery voltage is above 9 V, D1 remains in a conducting state, allowing current to flow through Q1, keeping it in the 'on' state. This action ensures that the output remains stable and does not trigger any warning signals.
As the battery discharges and the voltage drops to 7 V, D1 will no longer conduct. This cessation of current flow causes Q1 to turn off, which results in an increase in the collector voltage of Q1. The increased voltage at the collector will forward-bias Q2, allowing it to conduct. This conduction of Q2 activates LED1, providing a visual indication that the battery voltage has fallen below the critical threshold.
Resistor R4 is incorporated in series with LED1 to limit the current flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from excessive current which could lead to failure. The choice of resistor value is essential to ensure that LED1 operates within its specified current range.
This circuit is particularly useful in battery-operated devices where monitoring battery health is crucial for reliable operation. By providing an early warning signal, it allows users to take action before the battery voltage drops to a level that could lead to device malfunction or damage.This circuit gives an early warning of the discharge of batteries. Zener diode Dl is chosen for the voltage below which an indication is required (9 V). Should the supply drop to below 7 V, Dl will cease conducting causing Ql to shut off. Its collector voltage will now increase causing Q2 to start conducting via LED1 and its limiting resistor R4.