555 Low Voltage Operation
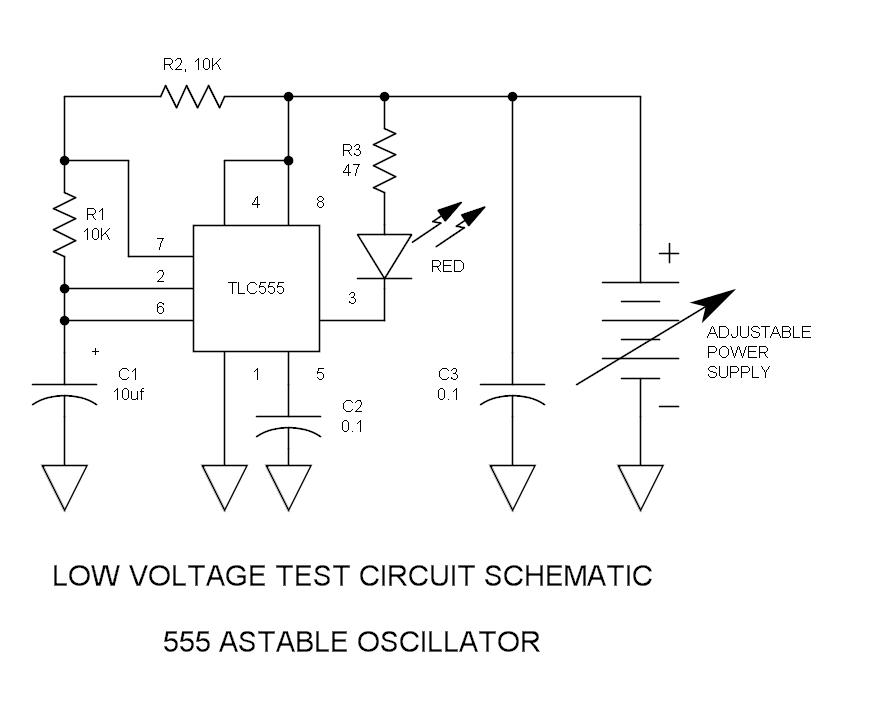
There have been stories regarding the suboptimal performance of the 555 timer IC when operated below a supply voltage (Vcc) of 5V, prompting an investigation into potential improvements for its operation.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile device commonly used in various timing, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Its performance can indeed be affected by the supply voltage, particularly when operating below the nominal 5V. At lower voltages, the internal thresholds for triggering and resetting may not function optimally, leading to unreliable operation.
To enhance the performance of the 555 timer at lower voltages, several strategies can be employed. One approach is to utilize a low-voltage variant of the 555 timer, such as the LMC555 or TLC555, which are specifically designed to operate efficiently at supply voltages down to 2V. These alternatives provide improved performance characteristics and maintain stable operation across a wider voltage range.
Another method involves careful selection of external components, such as resistors and capacitors, to optimize the timing intervals and ensure the circuit functions correctly even at lower voltages. For instance, using precision resistors can help maintain consistent charge and discharge times for the timing capacitor, which is crucial for achieving accurate timing intervals.
Additionally, implementing a voltage regulator or a boost converter can help maintain a stable supply voltage above the critical threshold, ensuring that the 555 timer operates within its optimal range. This can be particularly useful in battery-powered applications where the supply voltage may drop as the battery discharges.
Overall, understanding the limitations of the 555 timer at lower Vcc levels and applying these strategies can lead to improved reliability and functionality in various electronic applications.I had heard some stories in the past concerning how poorly the 555 ran below Vcc = 5V, so I embarked on an endeavor to see if I could improve operation. Th.. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer IC is a versatile device commonly used in various timing, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Its performance can indeed be affected by the supply voltage, particularly when operating below the nominal 5V. At lower voltages, the internal thresholds for triggering and resetting may not function optimally, leading to unreliable operation.
To enhance the performance of the 555 timer at lower voltages, several strategies can be employed. One approach is to utilize a low-voltage variant of the 555 timer, such as the LMC555 or TLC555, which are specifically designed to operate efficiently at supply voltages down to 2V. These alternatives provide improved performance characteristics and maintain stable operation across a wider voltage range.
Another method involves careful selection of external components, such as resistors and capacitors, to optimize the timing intervals and ensure the circuit functions correctly even at lower voltages. For instance, using precision resistors can help maintain consistent charge and discharge times for the timing capacitor, which is crucial for achieving accurate timing intervals.
Additionally, implementing a voltage regulator or a boost converter can help maintain a stable supply voltage above the critical threshold, ensuring that the 555 timer operates within its optimal range. This can be particularly useful in battery-powered applications where the supply voltage may drop as the battery discharges.
Overall, understanding the limitations of the 555 timer at lower Vcc levels and applying these strategies can lead to improved reliability and functionality in various electronic applications.I had heard some stories in the past concerning how poorly the 555 ran below Vcc = 5V, so I embarked on an endeavor to see if I could improve operation. Th.. 🔗 External reference