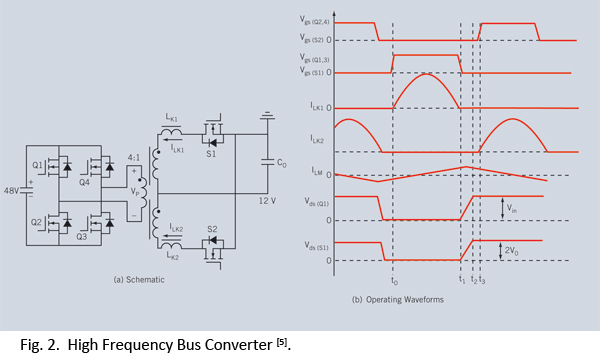
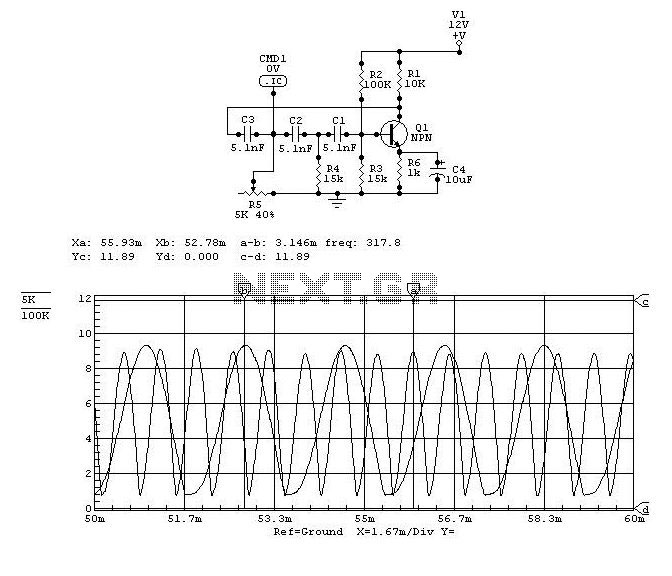
voltage to frequency converter icl8038
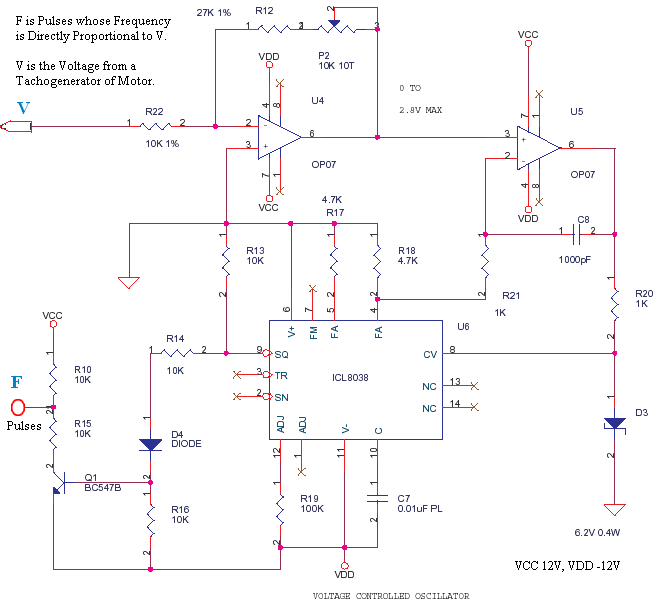
This is a small circuit designed to drive an impact counter, with the central component being the ICL8038. The circuit is intended for use with a motor that drives a conveyor, which includes a feedback mechanism known as a tachogenerator. Only a portion of the circuit is illustrated. The voltage from the tachogenerator is measured using a digital panel meter (DPM) or digital voltmeter (DVM) and is subsequently input into the circuit after being attenuated and filtered. The square wave pulses generated by the ICL8038 are utilized to create a logic pulse train for a CD4040 counter. The CD4040 operates on 0V and 12V, while the circuit itself is powered by +12V and -12V. This configuration necessitates the use of resistors R10-R15 and transistor Q1. The output pulses are 0-12V, with the zero reference being virtual, similar to the virtual ground found in low current power supplies.
The circuit utilizes the ICL8038 waveform generator, known for its precision in generating sine, square, triangular, and pulse waveforms. In this application, it produces square wave pulses that serve as timing signals for the CD4040 binary counter. The CD4040 is a 12-stage binary ripple counter that can count pulses and is capable of operating from a dual power supply, making it suitable for this configuration.
The tachogenerator provides feedback by generating a voltage proportional to the speed of the motor driving the conveyor. This feedback voltage is essential for monitoring the operational speed and ensuring accurate counting of impacts. The voltage is conditioned through attenuation and filtering to prevent noise from affecting the measurement and to ensure compatibility with the input requirements of the ICL8038.
Resistors R10 through R15 are part of a voltage divider network that ensures the correct voltage levels are maintained for the logic circuitry. The inclusion of transistor Q1 serves to buffer the output, allowing the circuit to drive loads effectively while maintaining the integrity of the pulse signals. The virtual ground concept allows the circuit to operate efficiently in a bipolar supply configuration, ensuring that the logic levels are appropriately referenced.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-integrated design that combines waveform generation, feedback control, and counting mechanisms, making it a robust solution for impact counting applications in industrial settings.This was a small circuit made for driving an Impact counter. The heart being ICL8038. It must have been a Motor driving a Conveyor, the motor has a feedback attachment called Tachogenerator. Only part of the circuit is shown here. See the image of product here Tacho Counter. The configuration is derived from the Application Notes of Intersil. T he Voltage from Tachogenerator is Measured on a DPM-DVM and also fed to this circuit after attenuation and filtering. The square pulses of 8038 is used to derive a Logic pulse train for a CD4040. The CD4040 works of 0 and 12V. The above circuit is on +12 and -12. That is the reason R10-R15-Q1 are used. The pulses are 0-12V pulses. The Zero is Virtual like the Virtual Ground in low current power supplies. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the ICL8038 waveform generator, known for its precision in generating sine, square, triangular, and pulse waveforms. In this application, it produces square wave pulses that serve as timing signals for the CD4040 binary counter. The CD4040 is a 12-stage binary ripple counter that can count pulses and is capable of operating from a dual power supply, making it suitable for this configuration.
The tachogenerator provides feedback by generating a voltage proportional to the speed of the motor driving the conveyor. This feedback voltage is essential for monitoring the operational speed and ensuring accurate counting of impacts. The voltage is conditioned through attenuation and filtering to prevent noise from affecting the measurement and to ensure compatibility with the input requirements of the ICL8038.
Resistors R10 through R15 are part of a voltage divider network that ensures the correct voltage levels are maintained for the logic circuitry. The inclusion of transistor Q1 serves to buffer the output, allowing the circuit to drive loads effectively while maintaining the integrity of the pulse signals. The virtual ground concept allows the circuit to operate efficiently in a bipolar supply configuration, ensuring that the logic levels are appropriately referenced.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-integrated design that combines waveform generation, feedback control, and counting mechanisms, making it a robust solution for impact counting applications in industrial settings.This was a small circuit made for driving an Impact counter. The heart being ICL8038. It must have been a Motor driving a Conveyor, the motor has a feedback attachment called Tachogenerator. Only part of the circuit is shown here. See the image of product here Tacho Counter. The configuration is derived from the Application Notes of Intersil. T he Voltage from Tachogenerator is Measured on a DPM-DVM and also fed to this circuit after attenuation and filtering. The square pulses of 8038 is used to derive a Logic pulse train for a CD4040. The CD4040 works of 0 and 12V. The above circuit is on +12 and -12. That is the reason R10-R15-Q1 are used. The pulses are 0-12V pulses. The Zero is Virtual like the Virtual Ground in low current power supplies. 🔗 External reference