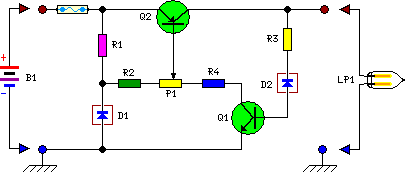
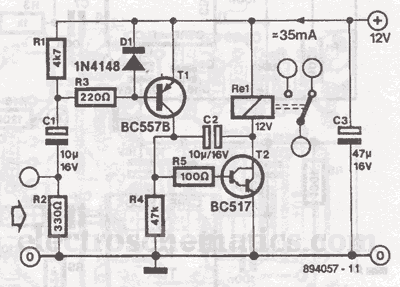
Volume control circuit
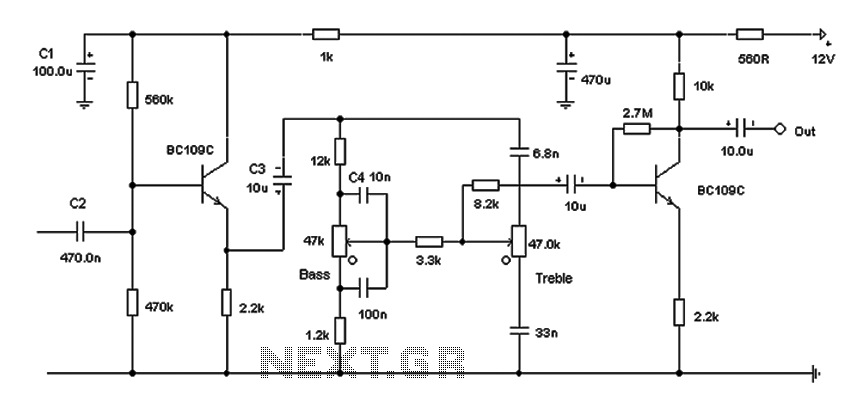
Based on the classic Baxendall tone control circuit, this design offers a maximum cut and boost of approximately 10 dB at 10 kHz and 50 Hz. Since the controls are passive, the final transistor provides a slight boost. The output is intended to connect to an amplifier with an input impedance ranging from 10 kΩ to 250 kΩ.
The Baxendall tone control circuit is a widely recognized design utilized for adjusting the tonal quality of audio signals. The circuit typically consists of two primary controls: one for bass frequencies and another for treble frequencies. In this specific implementation, the circuit achieves a maximum cut and boost of around 10 dB, which is effective at both 10 kHz and 50 Hz, allowing for significant tonal adjustments without introducing excessive distortion.
The passive nature of the tone control means that the adjustments made by the user will not amplify the signal on their own; however, the inclusion of a final transistor stage compensates for this by providing a slight gain. This transistor serves to buffer the output, ensuring that the signal remains strong enough to drive subsequent audio processing equipment, such as amplifiers.
The output stage is designed with compatibility in mind, targeting amplifiers with input impedances between 10 kΩ and 250 kΩ. This range is crucial, as it ensures that the tone control circuit can interface effectively with a variety of audio amplifiers without compromising sound quality or signal integrity. Proper impedance matching is essential for minimizing signal loss and maintaining the desired audio characteristics.
In summary, this Baxendall tone control circuit is an effective solution for audio applications requiring flexible tonal adjustments while preserving signal strength and clarity. Its design allows it to be easily integrated into a range of audio systems, enhancing the overall listening experience. Based on the classic Baxendall tone control circuit, this provides a maximum cut and boost of around 10dB at 10K and 50Hz. As the controls are passive, the last transistor prov ides a slight boost. The output is designed to feed an amplifier with input impedance of 10k to 250k.
The Baxendall tone control circuit is a widely recognized design utilized for adjusting the tonal quality of audio signals. The circuit typically consists of two primary controls: one for bass frequencies and another for treble frequencies. In this specific implementation, the circuit achieves a maximum cut and boost of around 10 dB, which is effective at both 10 kHz and 50 Hz, allowing for significant tonal adjustments without introducing excessive distortion.
The passive nature of the tone control means that the adjustments made by the user will not amplify the signal on their own; however, the inclusion of a final transistor stage compensates for this by providing a slight gain. This transistor serves to buffer the output, ensuring that the signal remains strong enough to drive subsequent audio processing equipment, such as amplifiers.
The output stage is designed with compatibility in mind, targeting amplifiers with input impedances between 10 kΩ and 250 kΩ. This range is crucial, as it ensures that the tone control circuit can interface effectively with a variety of audio amplifiers without compromising sound quality or signal integrity. Proper impedance matching is essential for minimizing signal loss and maintaining the desired audio characteristics.
In summary, this Baxendall tone control circuit is an effective solution for audio applications requiring flexible tonal adjustments while preserving signal strength and clarity. Its design allows it to be easily integrated into a range of audio systems, enhancing the overall listening experience. Based on the classic Baxendall tone control circuit, this provides a maximum cut and boost of around 10dB at 10K and 50Hz. As the controls are passive, the last transistor prov ides a slight boost. The output is designed to feed an amplifier with input impedance of 10k to 250k.