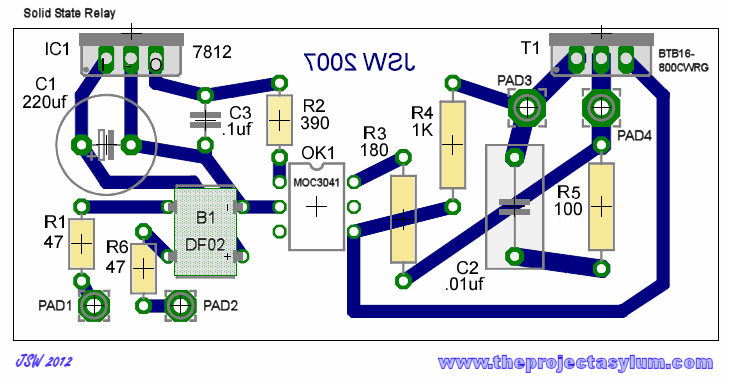
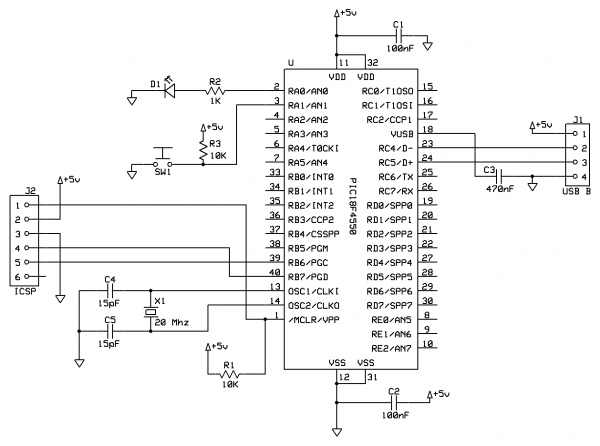
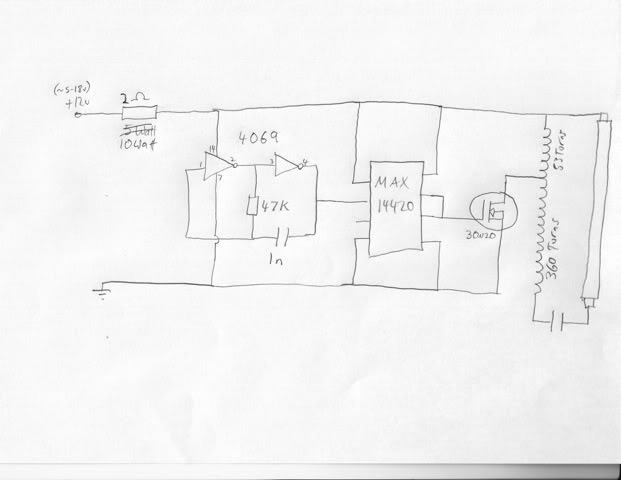
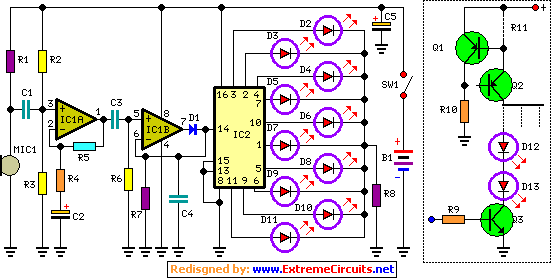
Want To Dim Your LEDs with a TRIAC Dimmer?
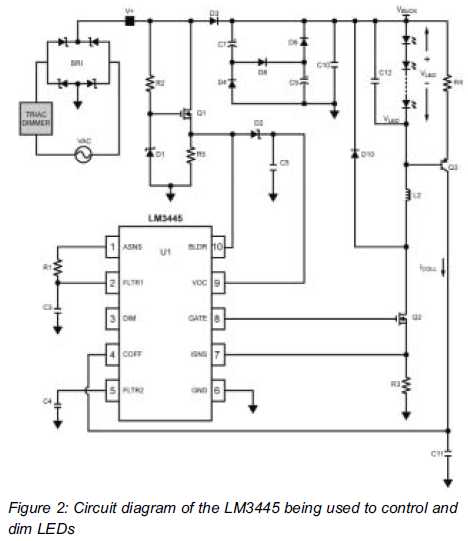
LEDs react much faster than conventional bulbs. Light dimmers for standard bulb-based lighting have been in use for many years. The most common implementation of such dimmers...
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Their rapid response time is a significant advantage over traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, which have slower warm-up times. This characteristic makes LEDs ideal for applications requiring quick on/off cycles, such as in automotive lighting, display backlighting, and decorative lighting.
Light dimmers, which allow users to adjust the brightness of lighting systems, have evolved significantly over the years. The most common implementation of dimmers for incandescent bulbs involves a variable resistor or a triac-based phase control system. These dimmers work by cutting off a portion of the AC waveform, effectively reducing the power delivered to the bulb and allowing for brightness adjustments.
However, the application of dimming technology to LED lighting requires specific considerations due to the different electrical characteristics of LEDs. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which can operate effectively with simple resistive dimmers, LEDs require compatible dimming circuits to ensure proper operation. This often involves the use of pulse-width modulation (PWM) or specialized LED drivers that can handle the unique load characteristics of LEDs.
PWM dimming works by rapidly switching the LED on and off at a frequency that is imperceptible to the human eye. By varying the ratio of on-time to off-time, the perceived brightness of the LED can be adjusted. This method is highly efficient and minimizes energy waste, making it an excellent choice for LED applications.
In summary, the integration of LED technology with light dimmers not only enhances the versatility of lighting systems but also promotes energy efficiency and improved user experience. Careful selection of compatible dimming methods is essential to maintain the performance and longevity of LED lighting solutions.LEDs simply react a lot faster than conventional bulbs Light dimmers for common bulb based lighting have been around for ages. The most common implementation of such.. 🔗 External reference
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Their rapid response time is a significant advantage over traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, which have slower warm-up times. This characteristic makes LEDs ideal for applications requiring quick on/off cycles, such as in automotive lighting, display backlighting, and decorative lighting.
Light dimmers, which allow users to adjust the brightness of lighting systems, have evolved significantly over the years. The most common implementation of dimmers for incandescent bulbs involves a variable resistor or a triac-based phase control system. These dimmers work by cutting off a portion of the AC waveform, effectively reducing the power delivered to the bulb and allowing for brightness adjustments.
However, the application of dimming technology to LED lighting requires specific considerations due to the different electrical characteristics of LEDs. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which can operate effectively with simple resistive dimmers, LEDs require compatible dimming circuits to ensure proper operation. This often involves the use of pulse-width modulation (PWM) or specialized LED drivers that can handle the unique load characteristics of LEDs.
PWM dimming works by rapidly switching the LED on and off at a frequency that is imperceptible to the human eye. By varying the ratio of on-time to off-time, the perceived brightness of the LED can be adjusted. This method is highly efficient and minimizes energy waste, making it an excellent choice for LED applications.
In summary, the integration of LED technology with light dimmers not only enhances the versatility of lighting systems but also promotes energy efficiency and improved user experience. Careful selection of compatible dimming methods is essential to maintain the performance and longevity of LED lighting solutions.LEDs simply react a lot faster than conventional bulbs Light dimmers for common bulb based lighting have been around for ages. The most common implementation of such.. 🔗 External reference