Water Activated Relay

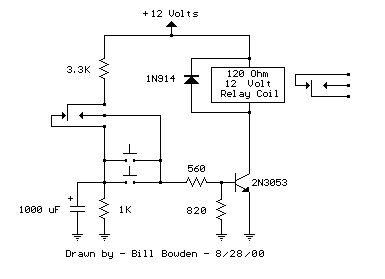
In this circuit, two transistors are configured as a high-gain compound pair. Transistor T1 is likely a 2N2222A, while T2 is identified as a BC108. The current gain is calculated as the product of the beta values of each transistor, which has a minimum of 140 for T1 and 110 for T2, resulting in a current gain of 15,400. The power supply can range from 4.5 to 15 volts. A typical 5-volt relay may require 60 mA to operate, meaning that any fluid conducting a minimum current of 4 µA will activate the relay. This level of current can be easily achieved with tap or rainwater.
The described circuit utilizes two transistors, T1 (2N2222A) and T2 (BC108), arranged in a compound configuration to enhance the overall current gain significantly. The 2N2222A is a popular NPN transistor known for its versatility and robustness, while the BC108 is a general-purpose NPN transistor that complements the 2N2222A in this application. The high gain of 15,400 indicates that even a small input current can be amplified to a much larger output current, making the circuit highly sensitive to small variations in input.
The design allows for a power supply voltage ranging from 4.5 to 15 volts, providing flexibility for various applications. The choice of a 5-volt relay, which typically requires 60 mA to activate, indicates that the circuit can be effectively used in low-power applications where the relay serves as a switch for controlling larger loads. The ability to activate the relay with a minimum input current of 4 µA signifies that the circuit is suitable for use with conductive fluids, such as tap or rainwater, which can easily provide the necessary current.
This circuit can be employed in applications such as liquid level sensing or fluid detection systems, where the presence of a conductive liquid can trigger a relay to control pumps, alarms, or other devices. The high sensitivity and low activation current make it ideal for monitoring systems that require minimal power consumption and reliable operation. Proper biasing and stabilization of the transistors are essential to ensure consistent performance, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the schematic to enhance stability and response time.In his circuit Marin has used two transistors wired as a high gain compound pair. Transistor T1 may be a 2N2222A and T2 a BC108. The current gain will be the product of each transistors beta, which will be a minimum of 140 x 110 or 15400. The power supply used can be any voltage from 4. 5 to 15 volts, a typical 5 volt relay may require 60 mA to operate, in which case any fluid which passes a minimum current of 4 uA will activate the relay. This is easily achieved with tap or rain water. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes two transistors, T1 (2N2222A) and T2 (BC108), arranged in a compound configuration to enhance the overall current gain significantly. The 2N2222A is a popular NPN transistor known for its versatility and robustness, while the BC108 is a general-purpose NPN transistor that complements the 2N2222A in this application. The high gain of 15,400 indicates that even a small input current can be amplified to a much larger output current, making the circuit highly sensitive to small variations in input.
The design allows for a power supply voltage ranging from 4.5 to 15 volts, providing flexibility for various applications. The choice of a 5-volt relay, which typically requires 60 mA to activate, indicates that the circuit can be effectively used in low-power applications where the relay serves as a switch for controlling larger loads. The ability to activate the relay with a minimum input current of 4 µA signifies that the circuit is suitable for use with conductive fluids, such as tap or rainwater, which can easily provide the necessary current.
This circuit can be employed in applications such as liquid level sensing or fluid detection systems, where the presence of a conductive liquid can trigger a relay to control pumps, alarms, or other devices. The high sensitivity and low activation current make it ideal for monitoring systems that require minimal power consumption and reliable operation. Proper biasing and stabilization of the transistors are essential to ensure consistent performance, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the schematic to enhance stability and response time.In his circuit Marin has used two transistors wired as a high gain compound pair. Transistor T1 may be a 2N2222A and T2 a BC108. The current gain will be the product of each transistors beta, which will be a minimum of 140 x 110 or 15400. The power supply used can be any voltage from 4. 5 to 15 volts, a typical 5 volt relay may require 60 mA to operate, in which case any fluid which passes a minimum current of 4 uA will activate the relay. This is easily achieved with tap or rain water. 🔗 External reference