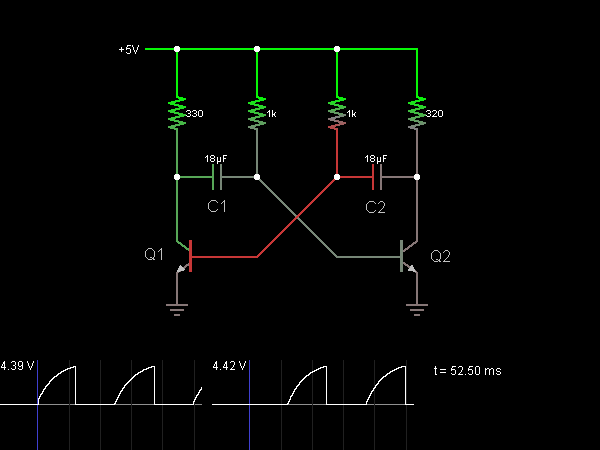
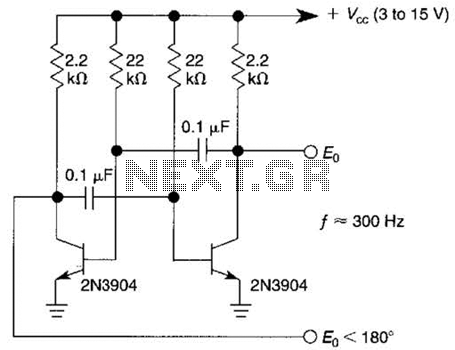
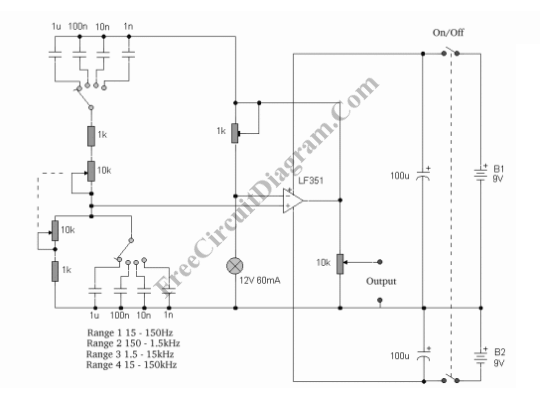
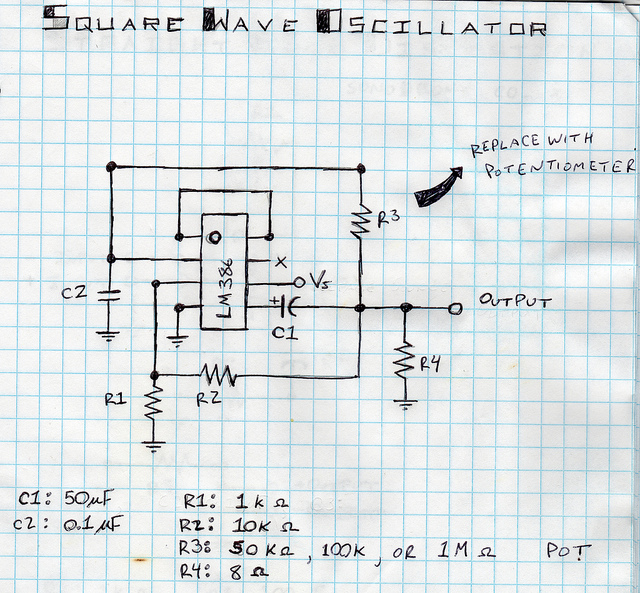
Wien bridge sine wave oscillator
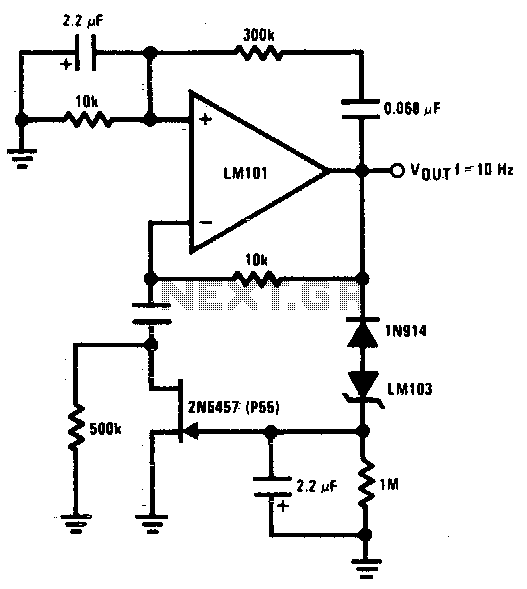
The 2N5457 JFET is utilized as a voltage variable resistor within the amplifier feedback loop, resulting in a low distortion, constant amplitude sine wave and optimizing the amplifier loop gain. The LM103 zener diode serves as the voltage reference for the peak sine wave amplitude.
The circuit employs the 2N5457 JFET, a junction field-effect transistor known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. In this configuration, the JFET is integrated into the feedback loop of an amplifier, where it acts as a variable resistor. By adjusting the gate voltage of the JFET, the resistance can be modulated, allowing for precise control over the feedback level. This modulation is crucial for maintaining a low distortion output while ensuring that the amplitude of the sine wave remains constant, which is essential for high-fidelity applications.
The LM103 zener diode is implemented to provide a stable voltage reference, which is critical for setting the peak amplitude of the sine wave. The LM103 is known for its low temperature coefficient and excellent voltage regulation, making it suitable for applications where precision is paramount. By using the LM103, the circuit can achieve a reliable reference voltage that helps maintain the desired output characteristics of the amplifier, ensuring that the sine wave peaks are consistent and free from fluctuations.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines the properties of the 2N5457 JFET and the LM103 zener diode to create a robust amplifier configuration capable of delivering high-quality sine wave signals with minimal distortion. The feedback loop's design, along with the voltage reference provided by the zener diode, contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the amplifier system.Using the 2N5457 JFET as a voltage variable resistor in the amplifier feedback loop, produces a low distortion, constant amplitude sine wave getting the amplifier loop gain just right The LM103 zener diode provides the voltage reference for the peak sine wave amplitude.
The circuit employs the 2N5457 JFET, a junction field-effect transistor known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. In this configuration, the JFET is integrated into the feedback loop of an amplifier, where it acts as a variable resistor. By adjusting the gate voltage of the JFET, the resistance can be modulated, allowing for precise control over the feedback level. This modulation is crucial for maintaining a low distortion output while ensuring that the amplitude of the sine wave remains constant, which is essential for high-fidelity applications.
The LM103 zener diode is implemented to provide a stable voltage reference, which is critical for setting the peak amplitude of the sine wave. The LM103 is known for its low temperature coefficient and excellent voltage regulation, making it suitable for applications where precision is paramount. By using the LM103, the circuit can achieve a reliable reference voltage that helps maintain the desired output characteristics of the amplifier, ensuring that the sine wave peaks are consistent and free from fluctuations.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines the properties of the 2N5457 JFET and the LM103 zener diode to create a robust amplifier configuration capable of delivering high-quality sine wave signals with minimal distortion. The feedback loop's design, along with the voltage reference provided by the zener diode, contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the amplifier system.Using the 2N5457 JFET as a voltage variable resistor in the amplifier feedback loop, produces a low distortion, constant amplitude sine wave getting the amplifier loop gain just right The LM103 zener diode provides the voltage reference for the peak sine wave amplitude.