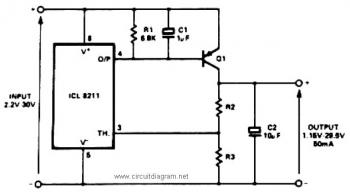
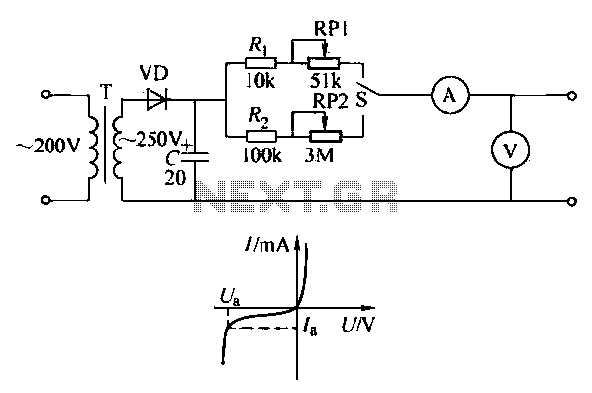
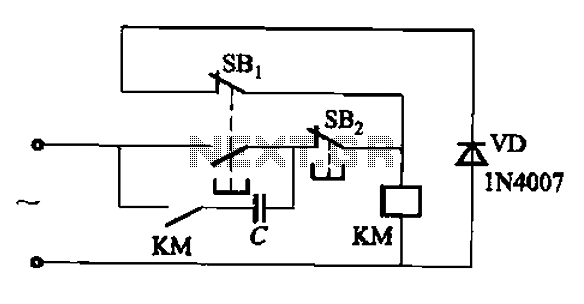
Wireless Ir Headphone Receiver Circuit
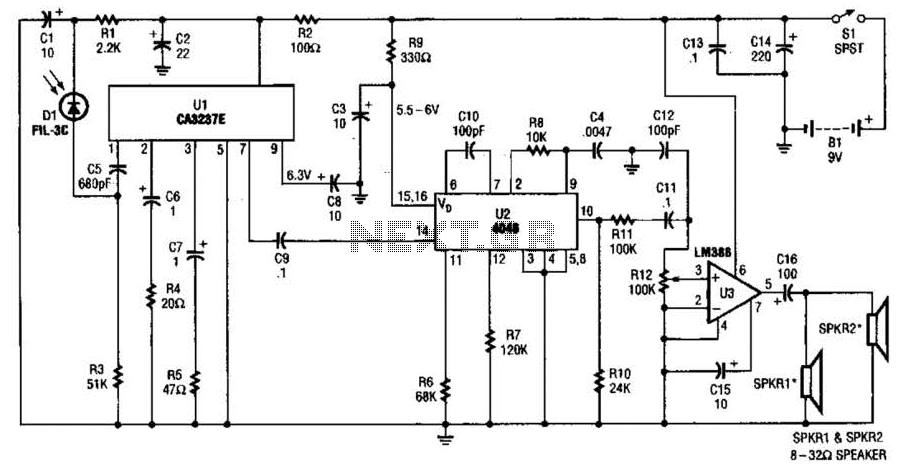
The infrared (IR) detector diode D1 captures the IR signal at approximately 40 kHz and transmits it to U1, a high-gain preamplifier, which then sends the signal to U2, a 4046 phase-locked loop (PLL) configured as a frequency modulation (FM) detector. U3 functions as an audio amplifier, driving either a pair of headphones or a speaker.
The circuit operates by employing an IR detector diode, which is sensitive to the specified frequency of 40 kHz. This diode serves as the initial point of signal reception, converting the incoming IR light pulses into an electrical signal. The high-gain preamplifier (U1) amplifies this weak signal to a level suitable for further processing.
The amplified signal is then routed to the 4046 PLL (U2), which is configured to act as an FM detector. The PLL is adept at locking onto the frequency of the incoming signal, allowing for the extraction of the modulating audio signal. This configuration is beneficial in applications requiring the demodulation of frequency-modulated signals, such as wireless audio transmission.
Following demodulation, the audio signal is forwarded to U3, an audio amplifier. This component is responsible for boosting the audio signal to a level that can effectively drive headphones or a speaker. The choice of output device—either headphones or a speaker—depends on the application requirements, with the amplifier designed to provide sufficient power and fidelity to suit both options.
Overall, this circuit represents a compact and efficient design for receiving and processing IR signals, suitable for various audio applications, including remote control systems and wireless audio transmission systems. The integration of the IR detector, preamplifier, PLL, and audio amplifier showcases a streamlined approach to handling frequency-modulated signals. IR detector diode D1 intercepts the IR signal at around 40 kHz and feeds it from Ul, a high-gain preamp, to PLL, U2, a 4046 configured to serve as an FM detector. U3 is an audio amplifier that feeds a pair of headphones or a speaker.
The circuit operates by employing an IR detector diode, which is sensitive to the specified frequency of 40 kHz. This diode serves as the initial point of signal reception, converting the incoming IR light pulses into an electrical signal. The high-gain preamplifier (U1) amplifies this weak signal to a level suitable for further processing.
The amplified signal is then routed to the 4046 PLL (U2), which is configured to act as an FM detector. The PLL is adept at locking onto the frequency of the incoming signal, allowing for the extraction of the modulating audio signal. This configuration is beneficial in applications requiring the demodulation of frequency-modulated signals, such as wireless audio transmission.
Following demodulation, the audio signal is forwarded to U3, an audio amplifier. This component is responsible for boosting the audio signal to a level that can effectively drive headphones or a speaker. The choice of output device—either headphones or a speaker—depends on the application requirements, with the amplifier designed to provide sufficient power and fidelity to suit both options.
Overall, this circuit represents a compact and efficient design for receiving and processing IR signals, suitable for various audio applications, including remote control systems and wireless audio transmission systems. The integration of the IR detector, preamplifier, PLL, and audio amplifier showcases a streamlined approach to handling frequency-modulated signals. IR detector diode D1 intercepts the IR signal at around 40 kHz and feeds it from Ul, a high-gain preamp, to PLL, U2, a 4046 configured to serve as an FM detector. U3 is an audio amplifier that feeds a pair of headphones or a speaker.