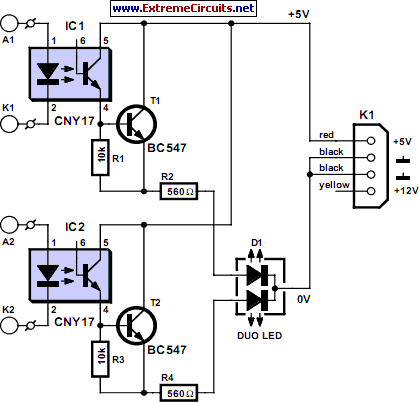
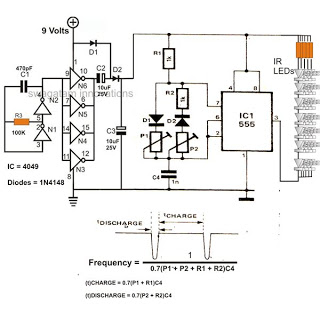
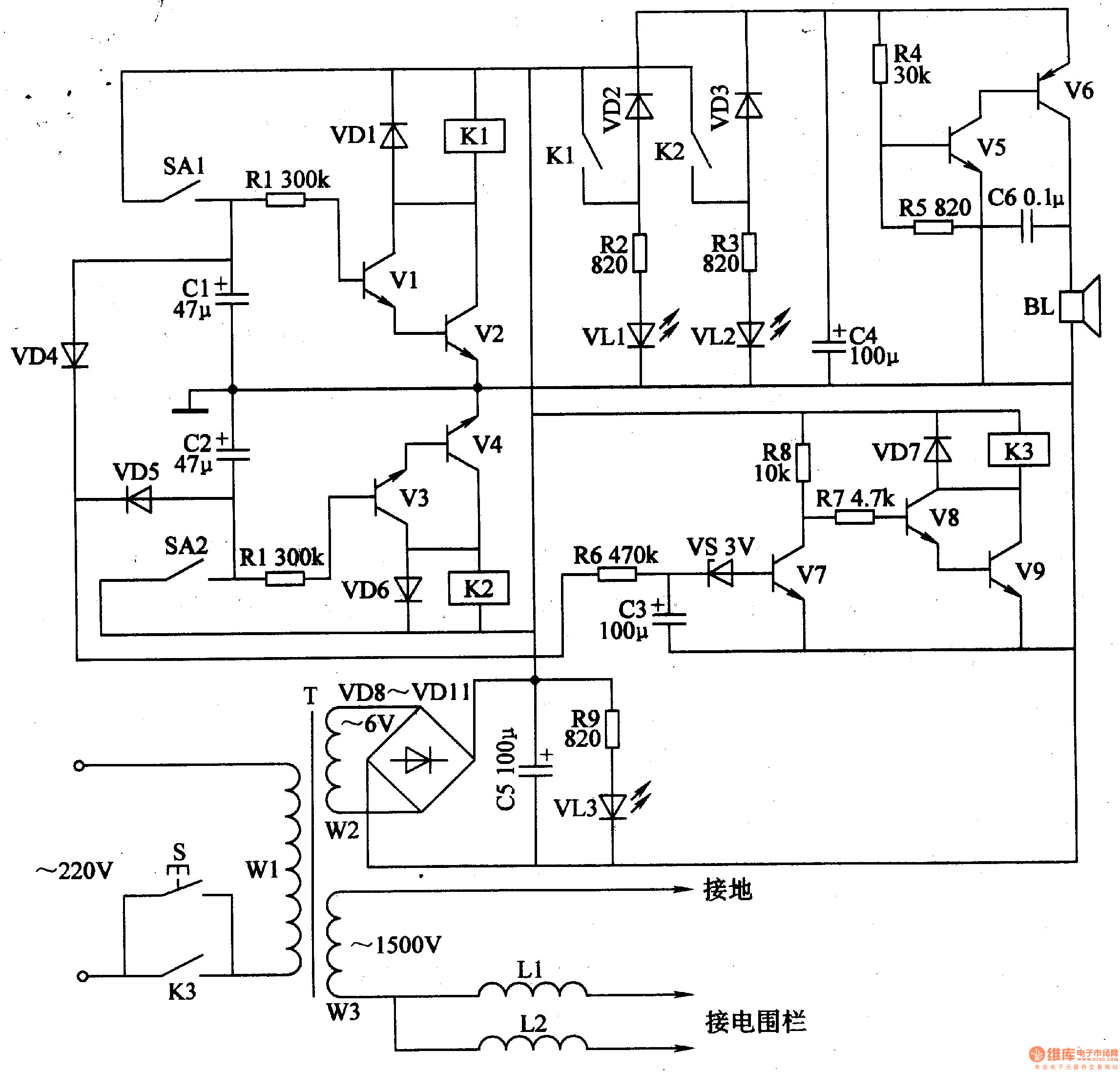
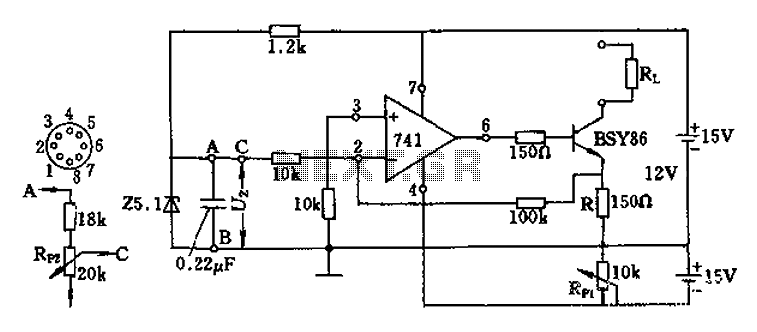
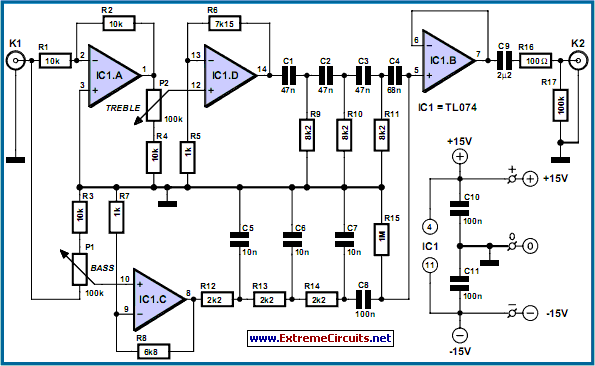
Wireless two-tone electronic doorbell circuit diagram
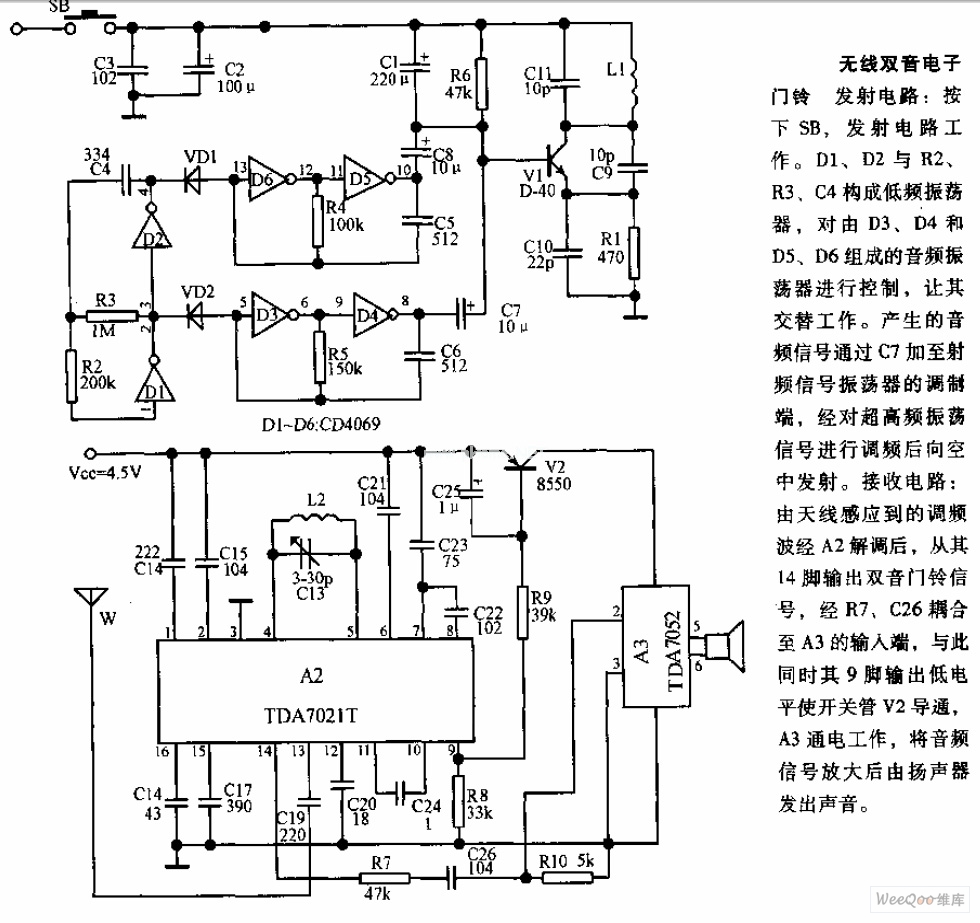
The transmitter circuit is activated by pressing the SB button. Components D1, D2, R2, R3, and C4 form a low-frequency oscillator that controls an audio oscillator made up of D3, D4, D5, and D6, allowing them to operate alternately. The audio signal generated is combined with the modulation side of the RF signal oscillator through capacitor C7. Subsequently, the high-frequency oscillator signal is transmitted.
The transmitter circuit described utilizes a button switch (SB) to initiate operation. Upon activation, the circuit engages a low-frequency oscillator composed of diodes D1 and D2, along with resistors R2 and R3 and capacitor C4. This configuration generates a low-frequency signal that serves as the control mechanism for an audio oscillator, which is comprised of diodes D3, D4, D5, and D6. The alternating operation of these components allows for the modulation of the audio signal.
The audio signal produced by the audio oscillator is then introduced into the modulation side of a radio frequency (RF) signal oscillator. This integration occurs through capacitor C7, which facilitates the coupling of the audio modulation onto the RF carrier wave. The resulting high-frequency oscillator signal is then transmitted, enabling communication or signal transmission over a designated frequency range.
This circuit exemplifies a typical design used in basic transmitter applications, where low-frequency audio signals are modulated onto a higher frequency carrier for effective transmission. The careful selection of components ensures that the circuit operates efficiently, providing reliable performance in various electronic communication scenarios.Transmitter: Pressing the SB will make the transmitter circuit work. D1, D2 and R2, R3, C4 constitute a low-frequency oscillator to control the audio oscillator composed of the D3, D4 and D5, D6, then it works alternately. The generated audio signal is added to modulation side of Rf signal oscillator by C7. Then high-frequency oscillator signal is sent to ai.. 🔗 External reference
The transmitter circuit described utilizes a button switch (SB) to initiate operation. Upon activation, the circuit engages a low-frequency oscillator composed of diodes D1 and D2, along with resistors R2 and R3 and capacitor C4. This configuration generates a low-frequency signal that serves as the control mechanism for an audio oscillator, which is comprised of diodes D3, D4, D5, and D6. The alternating operation of these components allows for the modulation of the audio signal.
The audio signal produced by the audio oscillator is then introduced into the modulation side of a radio frequency (RF) signal oscillator. This integration occurs through capacitor C7, which facilitates the coupling of the audio modulation onto the RF carrier wave. The resulting high-frequency oscillator signal is then transmitted, enabling communication or signal transmission over a designated frequency range.
This circuit exemplifies a typical design used in basic transmitter applications, where low-frequency audio signals are modulated onto a higher frequency carrier for effective transmission. The careful selection of components ensures that the circuit operates efficiently, providing reliable performance in various electronic communication scenarios.Transmitter: Pressing the SB will make the transmitter circuit work. D1, D2 and R2, R3, C4 constitute a low-frequency oscillator to control the audio oscillator composed of the D3, D4 and D5, D6, then it works alternately. The generated audio signal is added to modulation side of Rf signal oscillator by C7. Then high-frequency oscillator signal is sent to ai.. 🔗 External reference