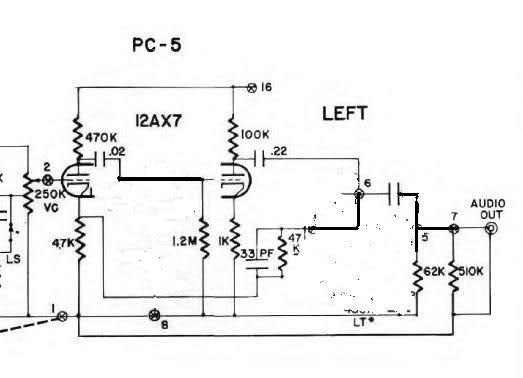
As control the discharge tube type delay circuit
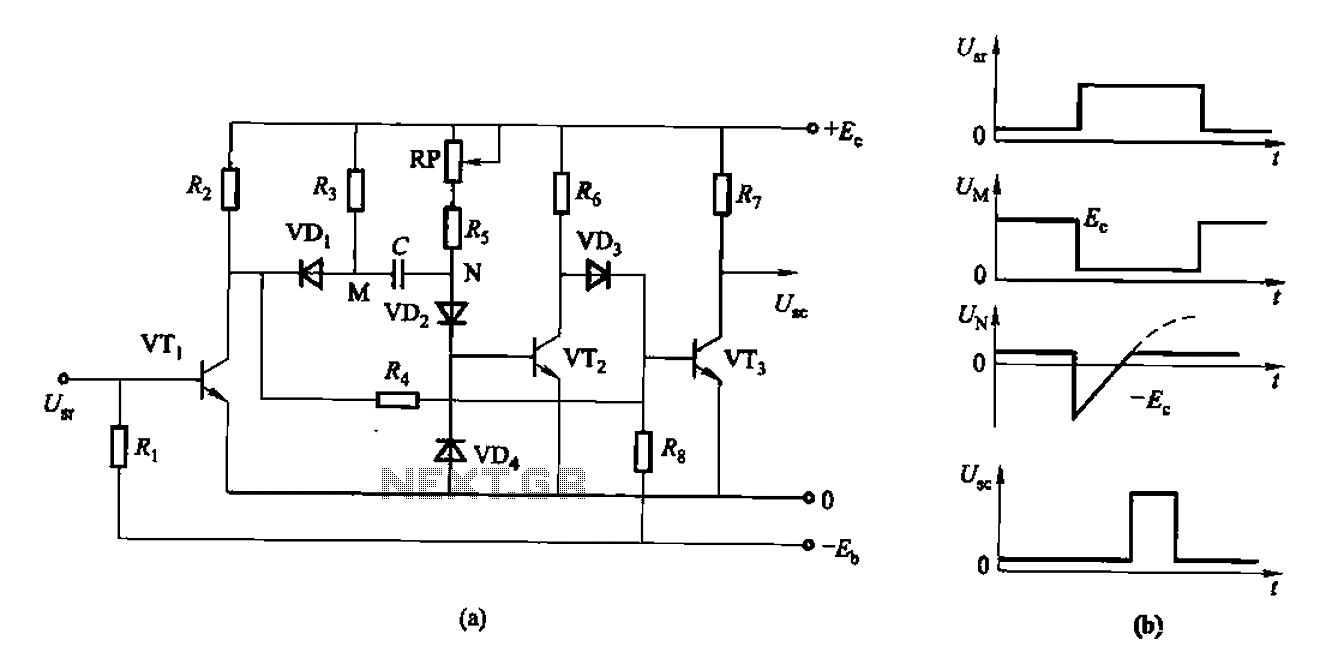
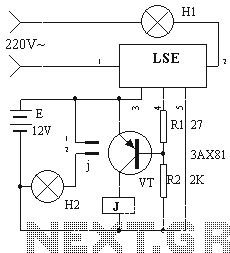
The circuit described is a discharge delay circuit that offers a longer delay compared to a standard rechargeable delay circuit, while also maintaining relatively high accuracy. The schematic diagram illustrates the input and output waveforms. Typically, when there is no input signal, transistor VTi is off, causing VT2 and VTa to conduct, resulting in an output voltage of zero. When a signal voltage is applied to U9r, VTi conducts, VT2 turns off, and VT3 remains on, keeping the output voltage at zero. After a predetermined delay, VT2 conducts, VT3 turns off, and the output voltage becomes high. When the input signal is removed, VTi returns to its off state, and VT2 and VT3 conduct again. The time interval for the signal to appear at the output, U, can be calculated using the formula: t = 0.7 (RP + Rs) C, where R5 and RP are in ohms and C is in farads.
The discharge delay circuit operates by utilizing a combination of transistors to control the timing of the output signal based on the input conditions. The transistors are configured in such a way that they switch states in response to the presence or absence of an input signal. The circuit begins in a quiescent state with no input signal, where VTi is off, and VT2 and VTa are conducting. This configuration results in the output voltage being at ground potential (zero volts).
Upon receiving an input signal, VTi turns on, which disables VT2, while VT3 remains on. The output voltage continues to stay at zero during this initial phase. The delay mechanism is introduced through the charging and discharging of a capacitor, which is connected to the circuit. After a specified delay period dictated by the RC time constant, VT2 turns on, while VT3 turns off, leading to a high output voltage state.
When the input signal is removed, VTi turns off, which allows both VT2 and VT3 to conduct, thus re-establishing the zero potential output. The timing characteristics of the circuit are determined by the resistor values (RP and Rs) and the capacitance (C) in the circuit. The formula provided indicates that the delay time (t) is proportional to the sum of the resistances multiplied by the capacitance, scaled by a factor of 0.7. This relationship allows for precise control over the delay time, making the circuit suitable for applications requiring a reliable and adjustable time delay.As of control type delay circuit discharge Discharge delay circuit and a delay circuit rechargeable compared Discharge delay circuit can obtain a longer delay, and the delay is relatively high accuracy. Wherein the circuit is shown as a schematic diagram for the input and output waveforms. Under normal circumstances, when there is no input signal, the transistor VTi off, VT2, VTa conduction, the output U.. Zero potential. When the signal voltage to U9r VTi conduction, VT2 off, VT3 still turned on, U.. Zero potential. After some delay, VT2 conduction, VT3 off, the output U.. High potential. When the input signal disappears, VTi reply deadline, VT2, VT3 conduction. Usr signal to appear by the U.. Goes high and the delay time interval, t can be calculated as: t O 7 (RP + Rs) C (s). Wherein, R5, RP unit is 0, C is the unit F .
The discharge delay circuit operates by utilizing a combination of transistors to control the timing of the output signal based on the input conditions. The transistors are configured in such a way that they switch states in response to the presence or absence of an input signal. The circuit begins in a quiescent state with no input signal, where VTi is off, and VT2 and VTa are conducting. This configuration results in the output voltage being at ground potential (zero volts).
Upon receiving an input signal, VTi turns on, which disables VT2, while VT3 remains on. The output voltage continues to stay at zero during this initial phase. The delay mechanism is introduced through the charging and discharging of a capacitor, which is connected to the circuit. After a specified delay period dictated by the RC time constant, VT2 turns on, while VT3 turns off, leading to a high output voltage state.
When the input signal is removed, VTi turns off, which allows both VT2 and VT3 to conduct, thus re-establishing the zero potential output. The timing characteristics of the circuit are determined by the resistor values (RP and Rs) and the capacitance (C) in the circuit. The formula provided indicates that the delay time (t) is proportional to the sum of the resistances multiplied by the capacitance, scaled by a factor of 0.7. This relationship allows for precise control over the delay time, making the circuit suitable for applications requiring a reliable and adjustable time delay.As of control type delay circuit discharge Discharge delay circuit and a delay circuit rechargeable compared Discharge delay circuit can obtain a longer delay, and the delay is relatively high accuracy. Wherein the circuit is shown as a schematic diagram for the input and output waveforms. Under normal circumstances, when there is no input signal, the transistor VTi off, VT2, VTa conduction, the output U.. Zero potential. When the signal voltage to U9r VTi conduction, VT2 off, VT3 still turned on, U.. Zero potential. After some delay, VT2 conduction, VT3 off, the output U.. High potential. When the input signal disappears, VTi reply deadline, VT2, VT3 conduction. Usr signal to appear by the U.. Goes high and the delay time interval, t can be calculated as: t O 7 (RP + Rs) C (s). Wherein, R5, RP unit is 0, C is the unit F .
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713