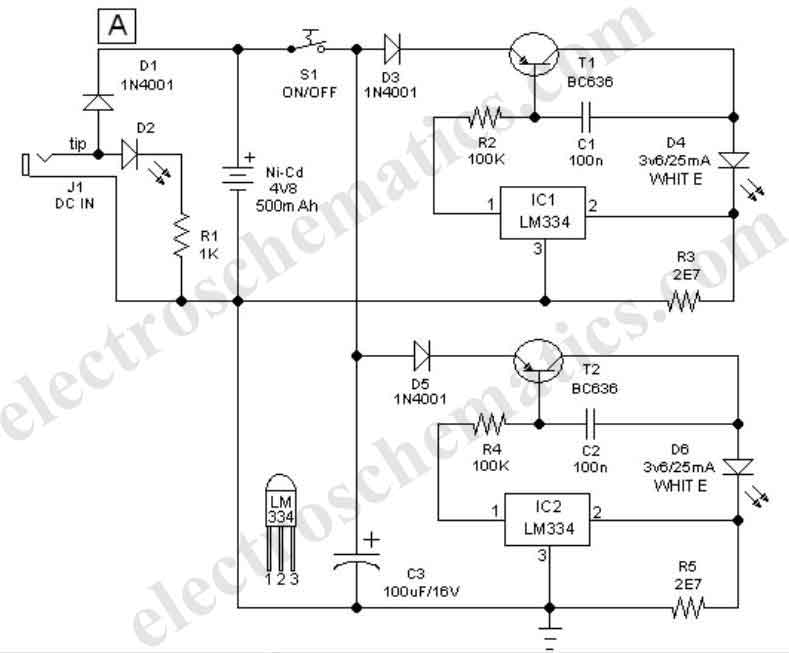
INA321 322 input current protection circuit diagram
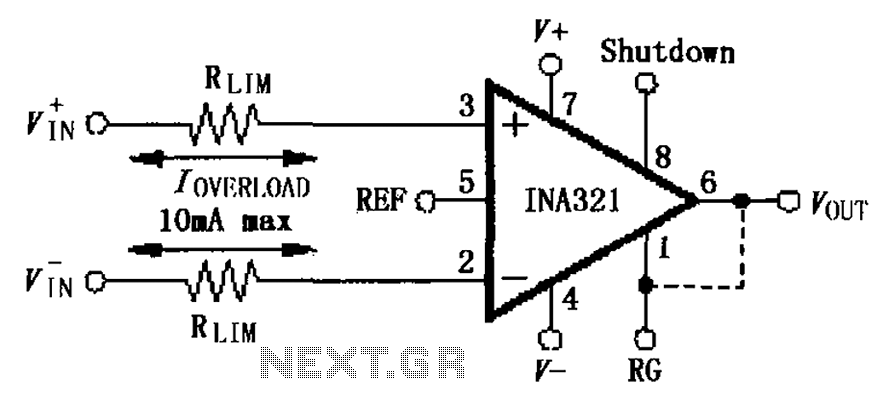
The input current protection circuit for the INA321/322 is illustrated. The INA321/322 features input terminal electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection diodes that become conductive when the input voltage exceeds the supply voltage by 500mV. The protection diodes will conduct, and the resistor RLIM will limit the input current to a maximum of 10mA, thereby serving its purpose in the protection circuit. Several input signals inherently possess limiting functions, and in such cases, the flow resistance RLIM may not be effective.
The INA321/322 integrated circuits are designed for precision applications requiring low offset voltages and low noise. The input current protection circuit is critical for safeguarding the device from overvoltage conditions. The ESD protection diodes are typically connected from the input pins to the power supply rails, allowing them to clamp any excess voltage to a safe level. When the input voltage exceeds the supply voltage by 500mV, these diodes become forward-biased and begin to conduct.
The resistor RLIM serves a dual purpose in this configuration. Firstly, it limits the input current to a maximum of 10mA, which is crucial for preventing damage to both the ESD protection diodes and the internal circuitry of the INA321/322. Secondly, RLIM helps to maintain the integrity of the input signal by preventing excessive current draw that could distort the signal.
In scenarios where the input signal itself has a built-in limiting function, RLIM may not be necessary or effective. This is often the case with signals that are inherently designed to operate within specific voltage ranges. In such instances, the input protection mechanism relies primarily on the characteristics of the signal itself to prevent overcurrent conditions.
Overall, the design of the input current protection circuit for the INA321/322 ensures reliable operation in various applications, providing essential safeguards against voltage spikes and excessive current that could compromise the performance and longevity of the device. As shown by INA321/322 input current protection circuit shown. INA321/322 has the input end of the inner electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection diodes when the input voltage exceeds the supply voltage 500mV, protection diodes will conduct case RLIM will limit the input current (maximum 10mA), play a role in the protection circuit. Many of the input signal itself limiting function, and this time the flow resistance RLIM can not.
The INA321/322 integrated circuits are designed for precision applications requiring low offset voltages and low noise. The input current protection circuit is critical for safeguarding the device from overvoltage conditions. The ESD protection diodes are typically connected from the input pins to the power supply rails, allowing them to clamp any excess voltage to a safe level. When the input voltage exceeds the supply voltage by 500mV, these diodes become forward-biased and begin to conduct.
The resistor RLIM serves a dual purpose in this configuration. Firstly, it limits the input current to a maximum of 10mA, which is crucial for preventing damage to both the ESD protection diodes and the internal circuitry of the INA321/322. Secondly, RLIM helps to maintain the integrity of the input signal by preventing excessive current draw that could distort the signal.
In scenarios where the input signal itself has a built-in limiting function, RLIM may not be necessary or effective. This is often the case with signals that are inherently designed to operate within specific voltage ranges. In such instances, the input protection mechanism relies primarily on the characteristics of the signal itself to prevent overcurrent conditions.
Overall, the design of the input current protection circuit for the INA321/322 ensures reliable operation in various applications, providing essential safeguards against voltage spikes and excessive current that could compromise the performance and longevity of the device. As shown by INA321/322 input current protection circuit shown. INA321/322 has the input end of the inner electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection diodes when the input voltage exceeds the supply voltage 500mV, protection diodes will conduct case RLIM will limit the input current (maximum 10mA), play a role in the protection circuit. Many of the input signal itself limiting function, and this time the flow resistance RLIM can not.