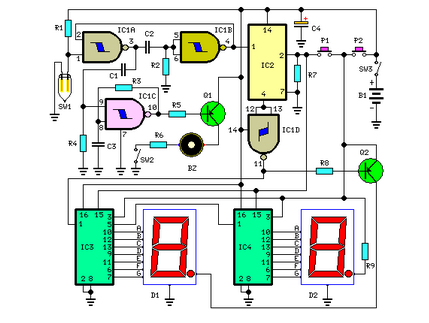
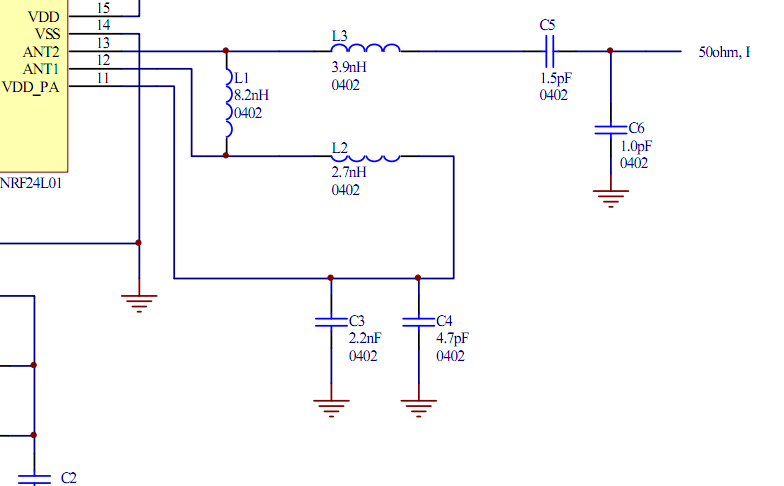
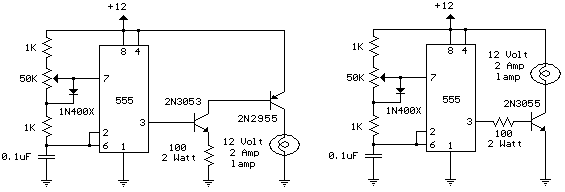
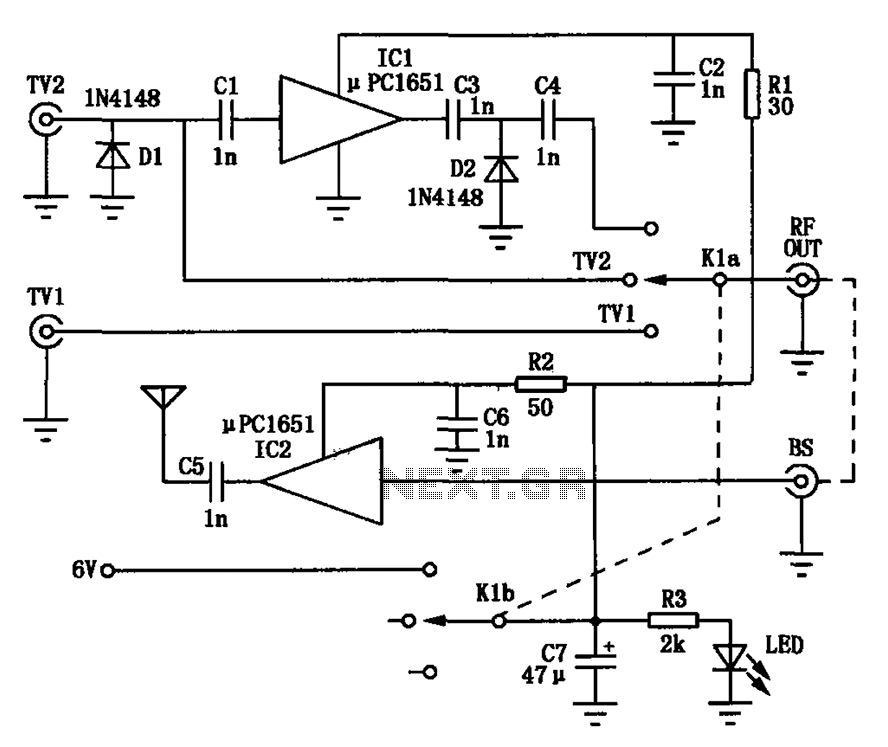
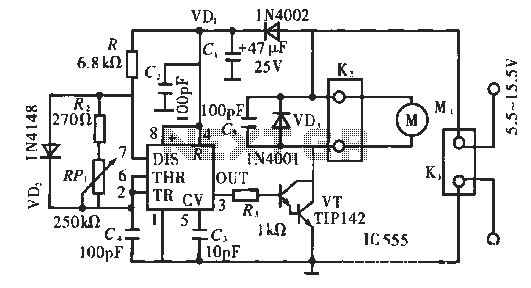
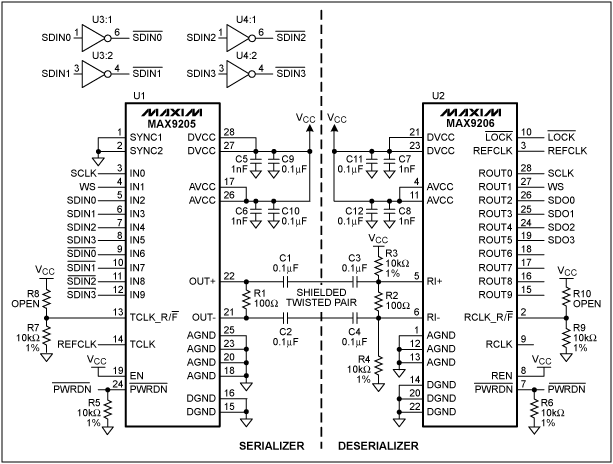
Using current quick break and overcurrent protection circuit overcurrent relay a sensor
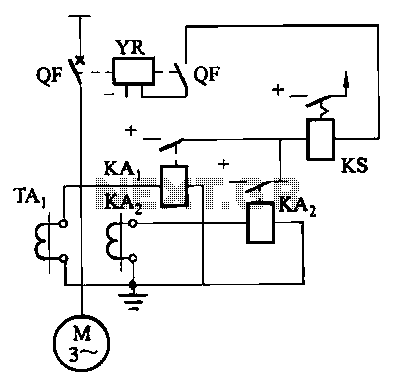
Figure 4-52 (a) illustrates the two-phase wiring for direct current (DC) operation, while Figure 4-52 (b) depicts the two-phase current differential wiring for alternating current (AC) operation.
The schematic in Figure 4-52 (a) represents a two-phase wiring configuration suitable for DC applications. This setup typically involves two distinct phases, each supplying power to a load. The two-phase system allows for a more efficient use of conductors, reducing the amount of copper required compared to single-phase systems. In DC operation, the current flows in one direction, and the circuit components must be rated to handle the continuous voltage and current without overheating or failing.
In contrast, Figure 4-52 (b) showcases a two-phase current differential wiring configuration intended for AC applications. This design is particularly advantageous for systems that require differential current sensing, such as in protective relays or current transformers. In AC operation, the current alternates direction, necessitating components that can handle alternating voltages and currents effectively. The differential wiring arrangement helps to isolate faults and enhances the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Both configurations emphasize the importance of proper component selection, including switches, connectors, and protective devices, to ensure optimal performance and safety in their respective applications. The choice between DC and AC wiring will largely depend on the specific requirements of the application, including load characteristics and the intended use of the electrical system.Figure 4-52 (a) for the two-phase wiring, DC operation; Figure 4r52 (b) for the two-phase current differential wiring, AC operation.
The schematic in Figure 4-52 (a) represents a two-phase wiring configuration suitable for DC applications. This setup typically involves two distinct phases, each supplying power to a load. The two-phase system allows for a more efficient use of conductors, reducing the amount of copper required compared to single-phase systems. In DC operation, the current flows in one direction, and the circuit components must be rated to handle the continuous voltage and current without overheating or failing.
In contrast, Figure 4-52 (b) showcases a two-phase current differential wiring configuration intended for AC applications. This design is particularly advantageous for systems that require differential current sensing, such as in protective relays or current transformers. In AC operation, the current alternates direction, necessitating components that can handle alternating voltages and currents effectively. The differential wiring arrangement helps to isolate faults and enhances the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Both configurations emphasize the importance of proper component selection, including switches, connectors, and protective devices, to ensure optimal performance and safety in their respective applications. The choice between DC and AC wiring will largely depend on the specific requirements of the application, including load characteristics and the intended use of the electrical system.Figure 4-52 (a) for the two-phase wiring, DC operation; Figure 4r52 (b) for the two-phase current differential wiring, AC operation.