The use of low frequency oscillation base 555 circuit made flashing light circuit Circuit II
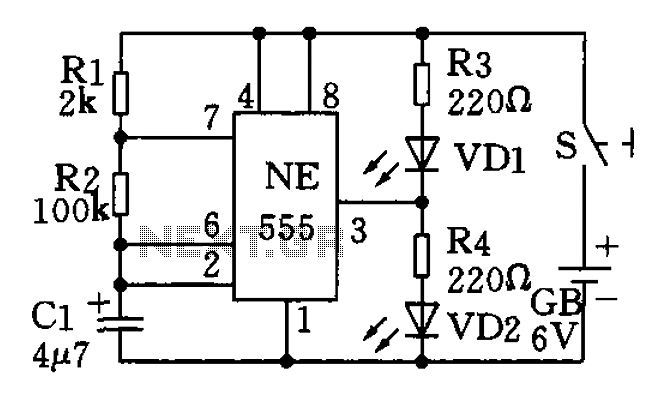
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer as the central component of a flashing light circuit. In normal operation, the light-emitting diodes (LEDs) VD1 and VD2 alternate flashing. The circuit comprises the NE555 timer, resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C1, forming a low-frequency oscillator. Upon circuit activation, the timer generates a signal that alternates between high and low states. When the output at pin 3 is high, VD1 is turned off and does not emit light, while VD2 is powered and emits light. Conversely, when pin 3 is low, VD1 is powered and emits light, while VD2 is turned off. This results in the two LEDs flashing alternately. For visual distinction, red, green, or yellow LEDs can be used.
The described circuit employs the NE555 timer in astable mode, which is essential for generating a continuous square wave output. The resistors R1 and R2 set the charge and discharge times of the capacitor C1, thereby determining the frequency of the output signal. The formula for the frequency (f) of the oscillator can be expressed as:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C1)
This equation highlights the relationship between the values of R1, R2, and C1 in controlling the timing characteristics of the circuit. The duty cycle, which indicates the proportion of time the output is high versus low, can also be adjusted by varying the resistor values.
The output from pin 3 of the NE555 timer is connected to the anodes of the LEDs VD1 and VD2 through appropriate current-limiting resistors to prevent excessive current that could damage the LEDs. The cathodes of the LEDs are connected to ground. When the output is high, current flows through VD2, illuminating it while VD1 remains off. When the output is low, the situation reverses, allowing VD1 to light up while VD2 turns off.
To enhance visibility, especially in outdoor or bright environments, different colored LEDs such as red, green, or yellow can be utilized. This not only aids in distinguishing between the two LEDs but also adds aesthetic value to the circuit. The overall design is simple yet effective for applications requiring visual signaling or decorative lighting, making it suitable for various electronic projects. As shown circuit 555 is at the core of the flash circuit, when their normal work, the light emitting diode and VD2 will VDl alternating flashing circuit principle summarized as follows: The base circuit NE555 and Rl, R2, Cl composed of low-frequency oscillator. After the start-up circuit, time base circuit 555 is 3 feet high and low potential of changing, when 3 feet high when, VDl loss of power does not emit light, VD2 powered light; when 3 feet is low, VDl powered luminous, VD2 loss of power It does not emit light. Therefore, the two light-emitting diodes will flash alternately light. When specific production, the two light-emitting diodes use red, green or yellow, some of the difference may be more visible.
The described circuit employs the NE555 timer in astable mode, which is essential for generating a continuous square wave output. The resistors R1 and R2 set the charge and discharge times of the capacitor C1, thereby determining the frequency of the output signal. The formula for the frequency (f) of the oscillator can be expressed as:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C1)
This equation highlights the relationship between the values of R1, R2, and C1 in controlling the timing characteristics of the circuit. The duty cycle, which indicates the proportion of time the output is high versus low, can also be adjusted by varying the resistor values.
The output from pin 3 of the NE555 timer is connected to the anodes of the LEDs VD1 and VD2 through appropriate current-limiting resistors to prevent excessive current that could damage the LEDs. The cathodes of the LEDs are connected to ground. When the output is high, current flows through VD2, illuminating it while VD1 remains off. When the output is low, the situation reverses, allowing VD1 to light up while VD2 turns off.
To enhance visibility, especially in outdoor or bright environments, different colored LEDs such as red, green, or yellow can be utilized. This not only aids in distinguishing between the two LEDs but also adds aesthetic value to the circuit. The overall design is simple yet effective for applications requiring visual signaling or decorative lighting, making it suitable for various electronic projects. As shown circuit 555 is at the core of the flash circuit, when their normal work, the light emitting diode and VD2 will VDl alternating flashing circuit principle summarized as follows: The base circuit NE555 and Rl, R2, Cl composed of low-frequency oscillator. After the start-up circuit, time base circuit 555 is 3 feet high and low potential of changing, when 3 feet high when, VDl loss of power does not emit light, VD2 powered light; when 3 feet is low, VDl powered luminous, VD2 loss of power It does not emit light. Therefore, the two light-emitting diodes will flash alternately light. When specific production, the two light-emitting diodes use red, green or yellow, some of the difference may be more visible.