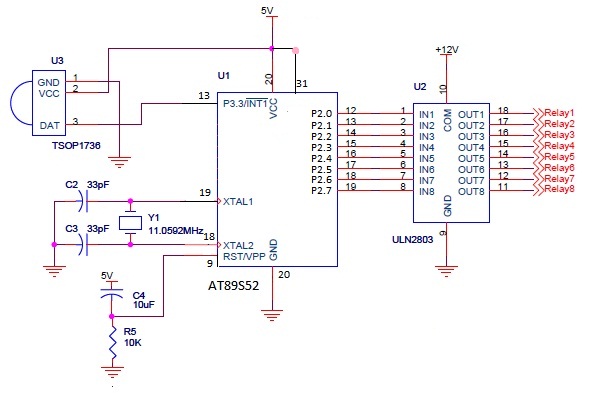
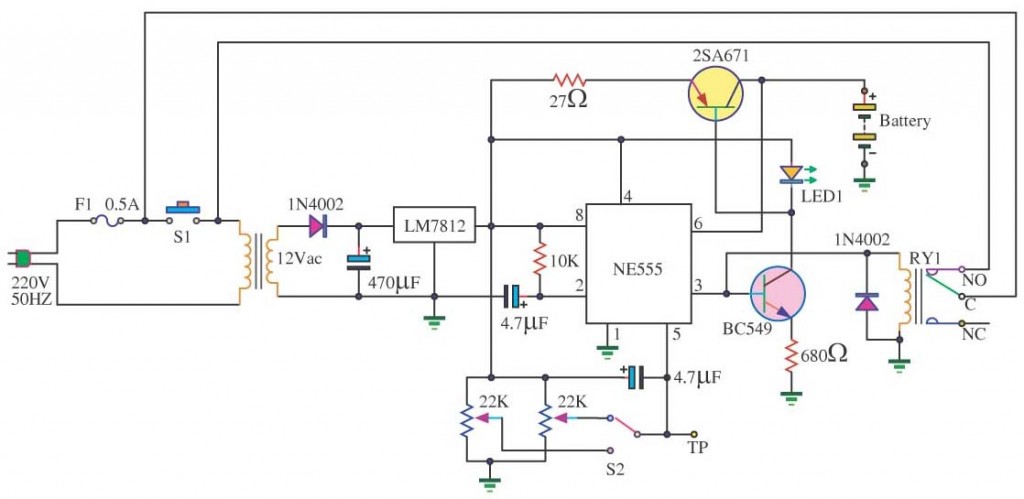
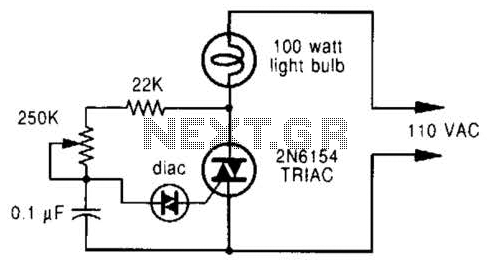
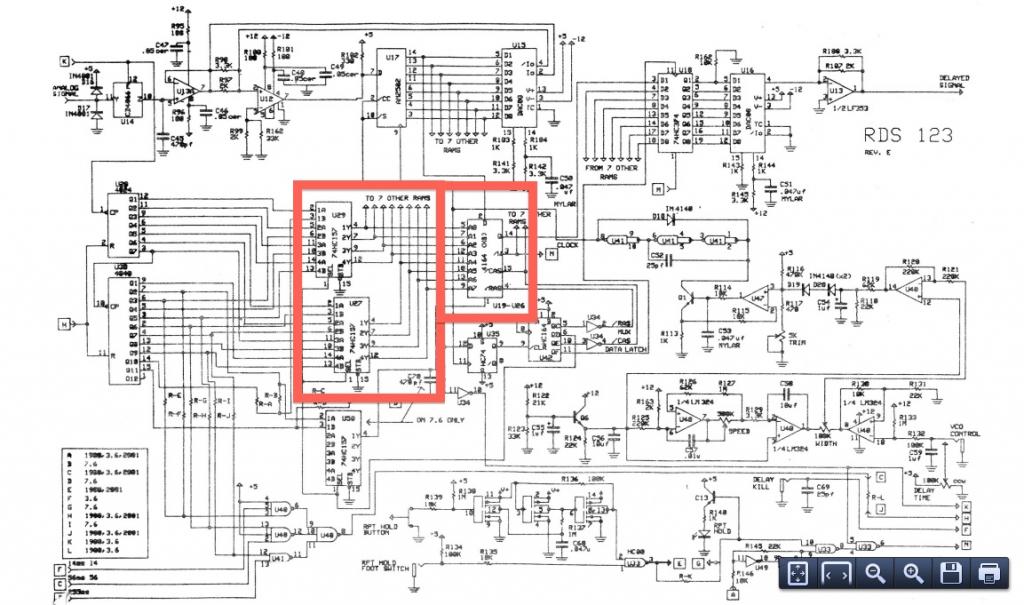
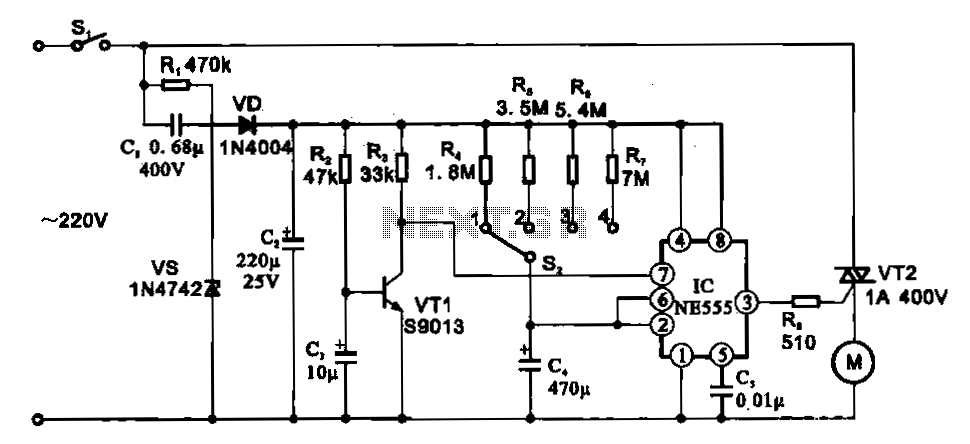
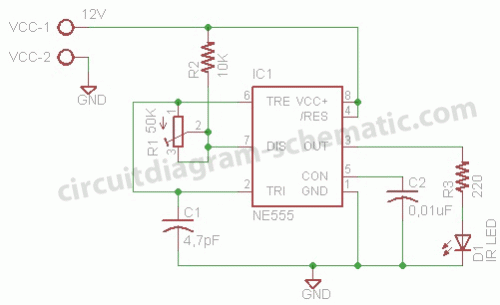
Basic circuit diagram connection ISO122 124 power supply and signal
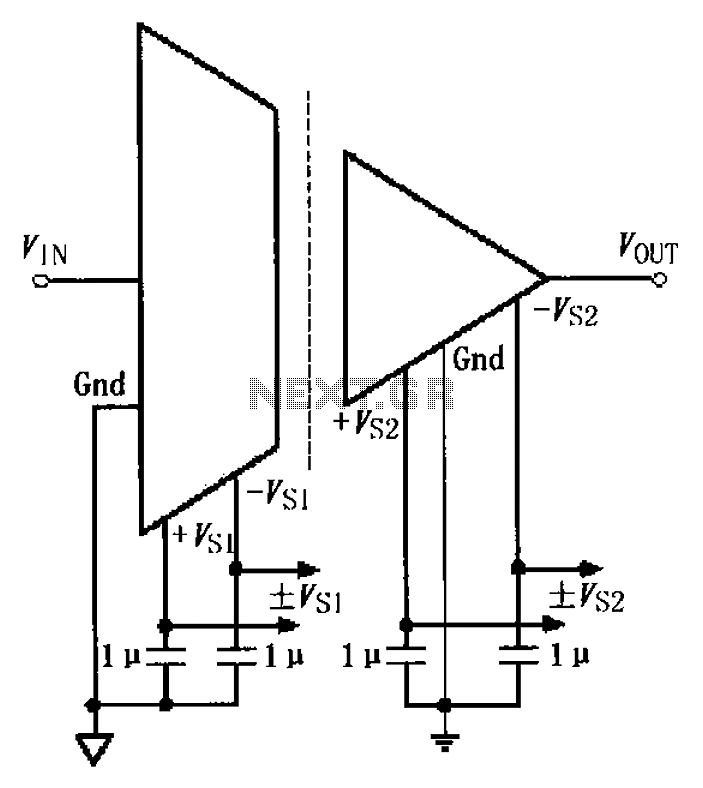
The basic connection circuit for the ISO122/124 includes power and signal connections. Each supply terminal of the ISO122/124 must be equipped with a 1 µF tantalum capacitor serving as a bypass filter. It is important to position the printed circuit board layout and bypass capacitors as close to the chip placement as possible.
The ISO122/124 is a precision isolation amplifier commonly used in applications requiring signal isolation. The circuit design emphasizes the importance of bypass capacitors, which are critical for maintaining stable operation by filtering out high-frequency noise from the power supply. The use of a 1 µF tantalum capacitor is recommended due to its low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and high frequency performance, which ensures effective filtering.
In the schematic, the ISO122/124 should be connected with its power supply terminals receiving the bypass capacitors directly adjacent to the pins. This minimizes the loop area and inductance, which can introduce noise into the system. The placement of the capacitors should be such that the leads are as short as possible, further enhancing the bypassing effect.
Furthermore, the layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) should consider the placement of the ISO122/124 chip and its associated components. Ground planes should be utilized to provide a low-impedance return path, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity. Careful routing of signal traces is also necessary to avoid crosstalk and interference, especially in high-speed applications.
In summary, the proper implementation of the ISO122/124 circuit involves strategic placement of bypass capacitors, careful PCB layout design, and attention to grounding and signal routing. This approach ensures optimal performance of the isolation amplifier in a variety of electronic applications. As shown for the basic connection circuit ISO122/124 power and signals. ISO122/124 each supply terminal must have a 1 F tantalum capacitor as a bypass filter, printed circuit b oard layout and bypass capacitors as close to the chip placement.
The ISO122/124 is a precision isolation amplifier commonly used in applications requiring signal isolation. The circuit design emphasizes the importance of bypass capacitors, which are critical for maintaining stable operation by filtering out high-frequency noise from the power supply. The use of a 1 µF tantalum capacitor is recommended due to its low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and high frequency performance, which ensures effective filtering.
In the schematic, the ISO122/124 should be connected with its power supply terminals receiving the bypass capacitors directly adjacent to the pins. This minimizes the loop area and inductance, which can introduce noise into the system. The placement of the capacitors should be such that the leads are as short as possible, further enhancing the bypassing effect.
Furthermore, the layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) should consider the placement of the ISO122/124 chip and its associated components. Ground planes should be utilized to provide a low-impedance return path, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity. Careful routing of signal traces is also necessary to avoid crosstalk and interference, especially in high-speed applications.
In summary, the proper implementation of the ISO122/124 circuit involves strategic placement of bypass capacitors, careful PCB layout design, and attention to grounding and signal routing. This approach ensures optimal performance of the isolation amplifier in a variety of electronic applications. As shown for the basic connection circuit ISO122/124 power and signals. ISO122/124 each supply terminal must have a 1 F tantalum capacitor as a bypass filter, printed circuit b oard layout and bypass capacitors as close to the chip placement.