1 Transistor Audio Mixer
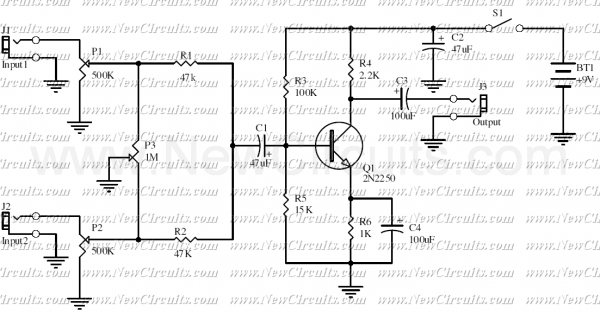
This is a classic signal mixer that is used for audio purpose. VR1 & VR2 are inputs audio volume controllers and VR3 is used to control the balance between Input1 and Input2. Connect a dynamic microphone to Input1 and a music without vocal to Input2, then adjust the VR1, VR2 and VR3 for obtaining a good mixed audio signal from the circuit Output. VR4 is an optional volume control for output audio signal.
The described circuit functions as a basic audio signal mixer, allowing users to blend two distinct audio sources effectively. The primary inputs, designated as Input1 and Input2, serve different purposes: Input1 is intended for a dynamic microphone, which captures vocal audio, while Input2 is designed for instrumental music tracks that do not contain vocal elements.
The variable resistors (VR1 and VR2) act as volume controls for each input, enabling the user to adjust the amplitude of the audio signals independently before mixing. This feature is crucial for achieving a balanced output, as it allows the user to increase or decrease the volume of each source according to preference.
VR3 serves as a balance control, allowing for fine-tuning between the two inputs. By adjusting VR3, the user can emphasize one audio source over the other, facilitating a more tailored sound experience.
The output of the mixer combines the adjusted signals from Input1 and Input2, producing a mixed audio signal that can be sent to a speaker or other audio output device. An additional variable resistor, VR4, is included as an optional feature to control the overall output volume, providing further flexibility in managing the final audio level.
In summary, this classic signal mixer circuit is designed for straightforward audio mixing applications, making it suitable for various scenarios, such as live performances, home studios, or any setting where mixing vocal and instrumental audio is required.This is a classic signal mixer that is used for audio purpose. VR1 & VR2 are inputs audio volume controlers and VR3 is used to control the balance between Input1 and Input2. connect a dynamic microphone to Input1 and a music without vocal to Input2, then adjust the VR1, VR2 and VR3 for obtaining a good mixed audio signal from the circuit Output.
VR4 is an optional volume control for output audio signal. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a basic audio signal mixer, allowing users to blend two distinct audio sources effectively. The primary inputs, designated as Input1 and Input2, serve different purposes: Input1 is intended for a dynamic microphone, which captures vocal audio, while Input2 is designed for instrumental music tracks that do not contain vocal elements.
The variable resistors (VR1 and VR2) act as volume controls for each input, enabling the user to adjust the amplitude of the audio signals independently before mixing. This feature is crucial for achieving a balanced output, as it allows the user to increase or decrease the volume of each source according to preference.
VR3 serves as a balance control, allowing for fine-tuning between the two inputs. By adjusting VR3, the user can emphasize one audio source over the other, facilitating a more tailored sound experience.
The output of the mixer combines the adjusted signals from Input1 and Input2, producing a mixed audio signal that can be sent to a speaker or other audio output device. An additional variable resistor, VR4, is included as an optional feature to control the overall output volume, providing further flexibility in managing the final audio level.
In summary, this classic signal mixer circuit is designed for straightforward audio mixing applications, making it suitable for various scenarios, such as live performances, home studios, or any setting where mixing vocal and instrumental audio is required.This is a classic signal mixer that is used for audio purpose. VR1 & VR2 are inputs audio volume controlers and VR3 is used to control the balance between Input1 and Input2. connect a dynamic microphone to Input1 and a music without vocal to Input2, then adjust the VR1, VR2 and VR3 for obtaining a good mixed audio signal from the circuit Output.
VR4 is an optional volume control for output audio signal. 🔗 External reference