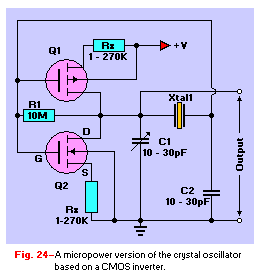
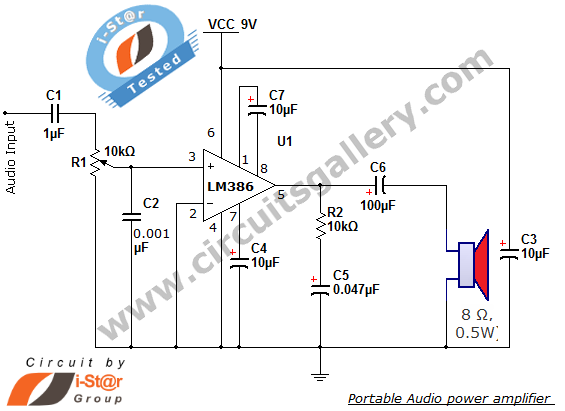
Audio Mixer with one transistor
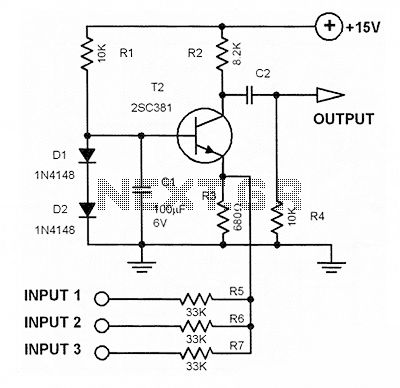
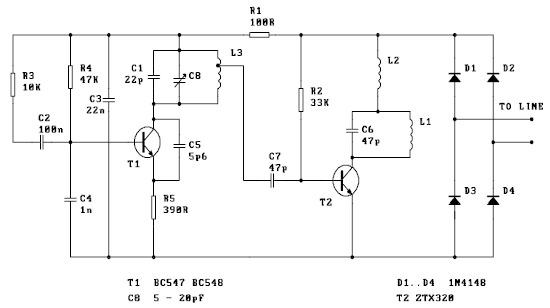
This single transistor audio mixer is utilized in an amplifier circuit design featuring a base-driven transistor, where the emitter is current-controlled. The majority of the driving current flows through the collector.
This audio mixer circuit employs a single transistor to mix multiple audio signals into one output. The configuration typically involves a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET) that serves as the primary amplifying element. In this design, the base of the transistor is driven by the input audio signals, which can be derived from various sources such as microphones or other audio devices.
The emitter of the transistor is configured to be current-controlled, allowing for precise regulation of the output signal. This current control mechanism helps to maintain a stable output level despite variations in input signal amplitudes. The collector is the output terminal where the mixed audio signal is taken. The design ensures that the majority of the driving current is directed through the collector, optimizing the efficiency of the circuit.
To implement this mixer, appropriate resistor values must be selected to set the biasing conditions for the transistor. The resistors connected to the base determine the input impedance and affect the overall gain of the circuit. Capacitors may also be included in the design to filter out unwanted frequencies and to couple audio signals without affecting the DC biasing of the transistor.
The overall performance of the audio mixer can be enhanced by ensuring proper power supply decoupling and grounding techniques to minimize noise and interference. When designing the circuit, considerations such as the required gain, bandwidth, and load impedance should be taken into account to achieve the desired audio quality.This one transistor audio mixer is used in an amplifier circuit design with base driven transistor and with its emitter being current controlled, most of the driving current flows through the collector away. Using the values in the audio mi.. 🔗 External reference
This audio mixer circuit employs a single transistor to mix multiple audio signals into one output. The configuration typically involves a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET) that serves as the primary amplifying element. In this design, the base of the transistor is driven by the input audio signals, which can be derived from various sources such as microphones or other audio devices.
The emitter of the transistor is configured to be current-controlled, allowing for precise regulation of the output signal. This current control mechanism helps to maintain a stable output level despite variations in input signal amplitudes. The collector is the output terminal where the mixed audio signal is taken. The design ensures that the majority of the driving current is directed through the collector, optimizing the efficiency of the circuit.
To implement this mixer, appropriate resistor values must be selected to set the biasing conditions for the transistor. The resistors connected to the base determine the input impedance and affect the overall gain of the circuit. Capacitors may also be included in the design to filter out unwanted frequencies and to couple audio signals without affecting the DC biasing of the transistor.
The overall performance of the audio mixer can be enhanced by ensuring proper power supply decoupling and grounding techniques to minimize noise and interference. When designing the circuit, considerations such as the required gain, bandwidth, and load impedance should be taken into account to achieve the desired audio quality.This one transistor audio mixer is used in an amplifier circuit design with base driven transistor and with its emitter being current controlled, most of the driving current flows through the collector away. Using the values in the audio mi.. 🔗 External reference