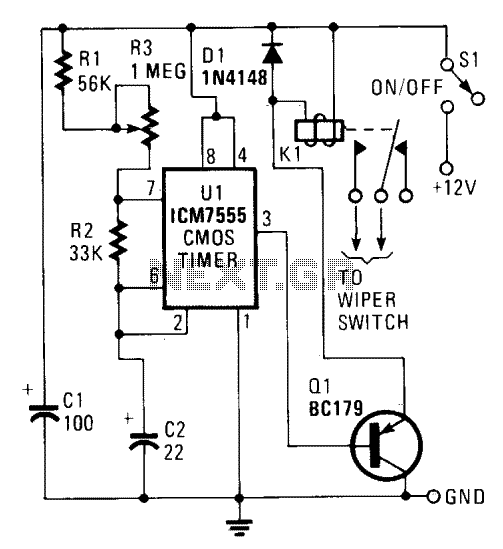
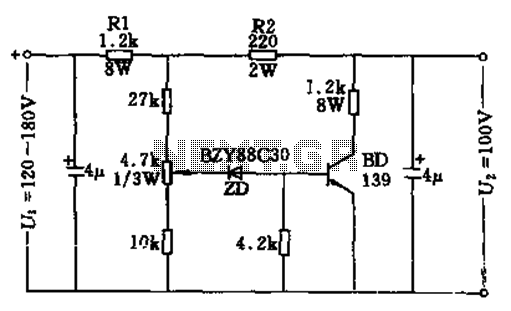
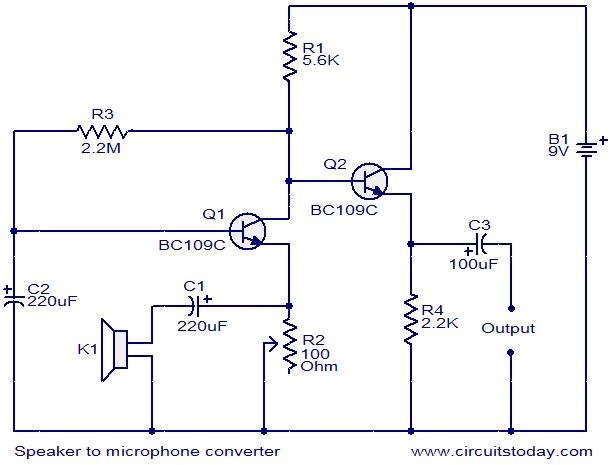
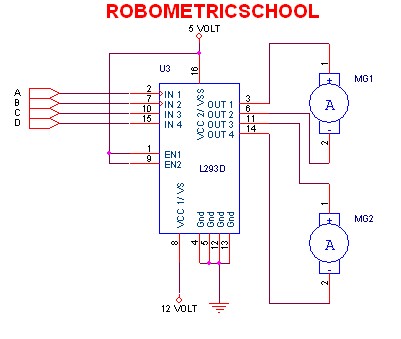
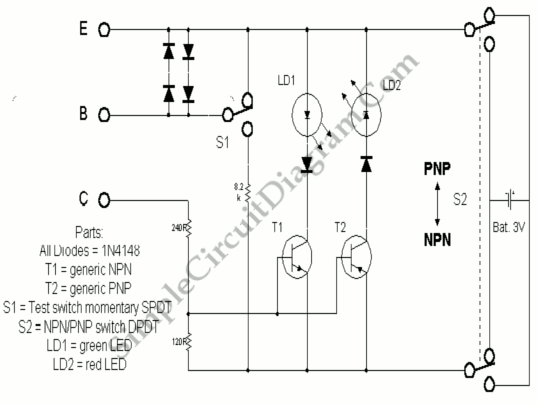
100W full-wave single-junction transistor trigger doer control circuit
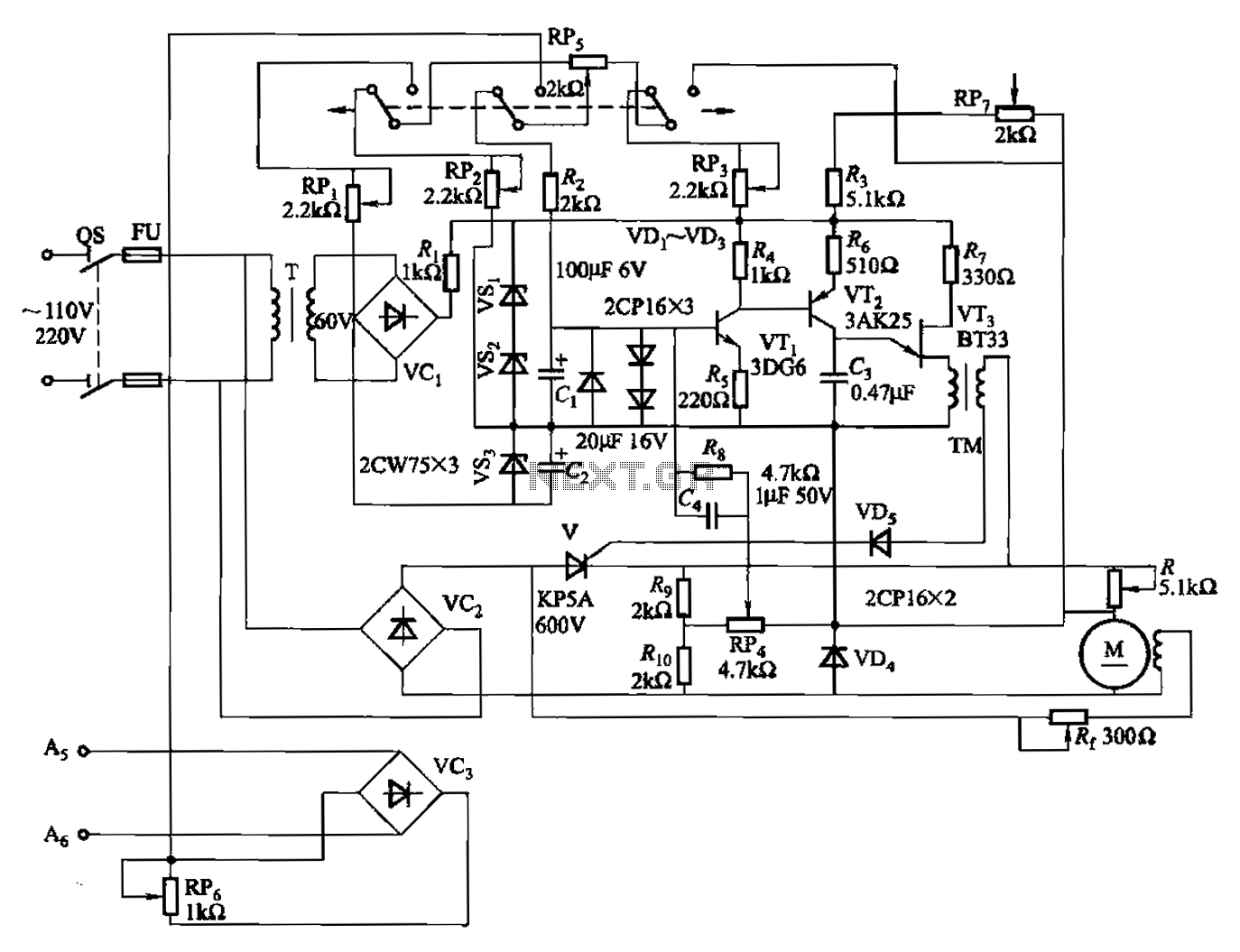
A 100W full-wave single-junction transistor trigger control circuit designed for constant or variable speed control of a wire feed motor. The input control signal consists of a voltage adjusted by the master potentiometer (RPs) and a feedback voltage from potentiometer RP4. When RP4 is at the same position, the motor speed is determined by RPs. In cases where electric arc voltage feedback control is employed, signals A5 and A6 indicate the end of the introduction, with the amount of feedback adjustable via potentiometer RP6. As the arc length increases, the arc pressure rises, leading to an increase in the feedback voltage. This, in turn, enhances the motor's drive, allowing it to maintain the original arc for welding.
The circuit operates by employing a single-junction transistor as the primary control element, enabling the modulation of power to the wire feed motor based on the input control signals. The master potentiometer (RPs) allows for user-defined adjustments to the motor's speed, providing flexibility for various welding applications. The feedback mechanism, facilitated by potentiometer RP4, ensures that the motor responds dynamically to changes in load conditions, maintaining consistent wire feed rates.
Incorporating feedback from the arc voltage is a critical feature of this design. The signals A5 and A6 serve as indicators for the control system, allowing it to determine when to adjust the motor's operation based on the welding conditions. The adjustment of feedback via potentiometer RP6 is essential for tuning the responsiveness of the circuit to variations in arc length, which directly affects welding quality.
As the arc length increases, the circuit compensates by increasing the drive to the motor. This is achieved through a feedback loop that monitors the arc pressure and adjusts the motor's speed accordingly. The design ensures that the welding process remains stable, minimizing the risk of defects caused by inconsistent wire feed rates. Overall, this control circuit exemplifies a robust solution for managing wire feed motors in welding applications, providing both precision and adaptability.100W full-wave single-junction transistor trigger doer control circuit It is suitable for constant or variable speed wire feed control wire feed motor. The input control signal is given voltage (RPs by the Master potentiometer adjustment) and the motor feedback voltage (from potentiometer RP4 taken in) superimposed. When RP4 same position, the motor speed depends on RPs. When using an electric arc voltage feedback control, As, A6 signals the end of the introduction (the amount of feedback is adjusted by potentiometer RP6) quite in RP..
When the arc length increases, the arc pressure is increased when the string l motivation bone incense coupled with feedback voltage increases, I turn to punish Shen j motivation increases, and continue to maintain the original arc welding.
The circuit operates by employing a single-junction transistor as the primary control element, enabling the modulation of power to the wire feed motor based on the input control signals. The master potentiometer (RPs) allows for user-defined adjustments to the motor's speed, providing flexibility for various welding applications. The feedback mechanism, facilitated by potentiometer RP4, ensures that the motor responds dynamically to changes in load conditions, maintaining consistent wire feed rates.
Incorporating feedback from the arc voltage is a critical feature of this design. The signals A5 and A6 serve as indicators for the control system, allowing it to determine when to adjust the motor's operation based on the welding conditions. The adjustment of feedback via potentiometer RP6 is essential for tuning the responsiveness of the circuit to variations in arc length, which directly affects welding quality.
As the arc length increases, the circuit compensates by increasing the drive to the motor. This is achieved through a feedback loop that monitors the arc pressure and adjusts the motor's speed accordingly. The design ensures that the welding process remains stable, minimizing the risk of defects caused by inconsistent wire feed rates. Overall, this control circuit exemplifies a robust solution for managing wire feed motors in welding applications, providing both precision and adaptability.100W full-wave single-junction transistor trigger doer control circuit It is suitable for constant or variable speed wire feed control wire feed motor. The input control signal is given voltage (RPs by the Master potentiometer adjustment) and the motor feedback voltage (from potentiometer RP4 taken in) superimposed. When RP4 same position, the motor speed depends on RPs. When using an electric arc voltage feedback control, As, A6 signals the end of the introduction (the amount of feedback is adjusted by potentiometer RP6) quite in RP..
When the arc length increases, the arc pressure is increased when the string l motivation bone incense coupled with feedback voltage increases, I turn to punish Shen j motivation increases, and continue to maintain the original arc welding.