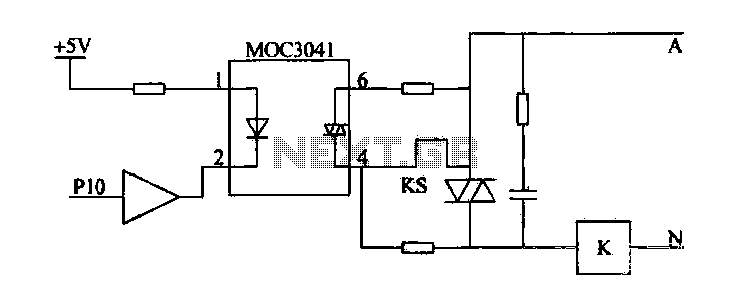
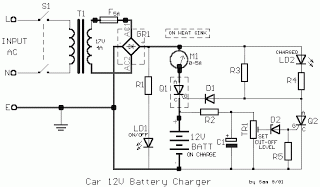
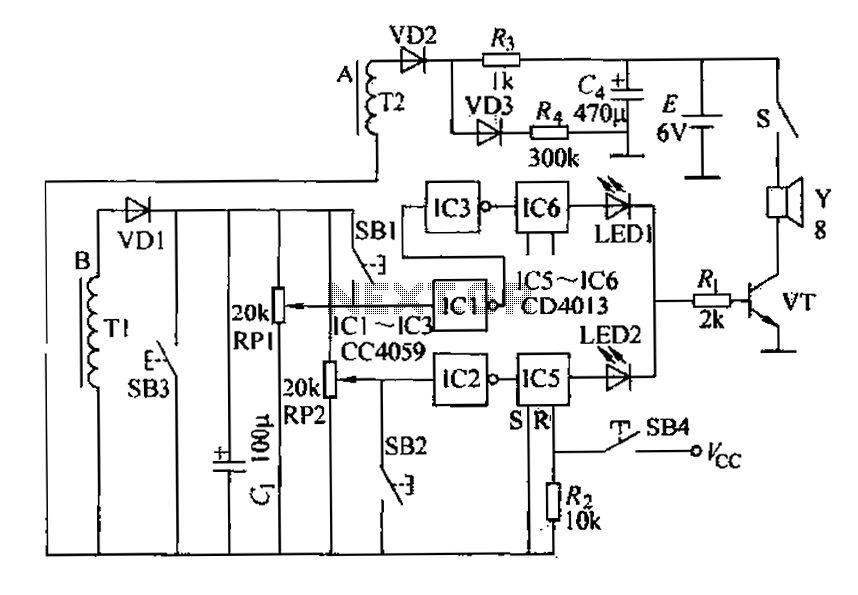
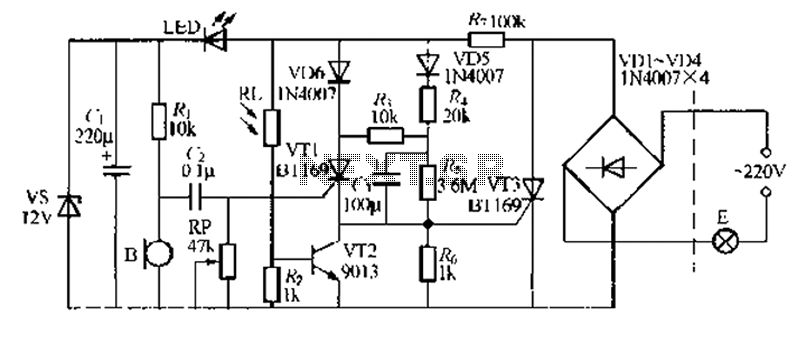
12 Stage Neon Sequencer (NE-2 / NE-51) circuit
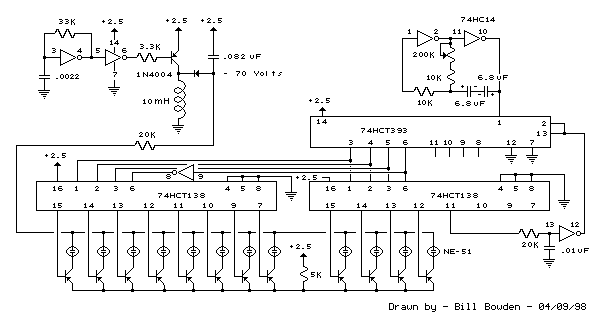
This circuit resembles an LED clock but utilizes 12 neon indicator lamps in place of LEDs. It operates on two high-capacity nickel-cadmium cells (2.5 volts), providing power for several weeks. A small switching power supply generates the high voltage (70 volts) required for the neon lamps, utilizing a 74HC14 Schmitt trigger square wave oscillator, a high-voltage switching transistor, and a high-Q inductor in the millihenry range.
The circuit design consists of several key components that work together to achieve the desired functionality of illuminating the neon lamps in a clock-like manner. The 74HC14 Schmitt trigger serves as the oscillator, creating a square wave signal that drives the switching transistor. This transistor is responsible for controlling the flow of current to the high-Q inductor, which is crucial for stepping up the voltage to the necessary 70 volts for the neon lamps.
The use of two nickel-cadmium cells provides a reliable power source, ensuring that the circuit can function continuously for an extended period. The choice of high-capacity cells allows for a longer operational lifespan, making the circuit suitable for applications where regular battery replacement would be inconvenient.
The high-Q inductor plays a vital role in the voltage amplification process. By storing energy and releasing it at a higher voltage, it enables the neon lamps to operate effectively. The design ensures that the lamps can be lit with a consistent brightness, which is critical for visibility and aesthetic appeal.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a low-voltage power source with a high-voltage generation mechanism to operate neon lamps, demonstrating an innovative approach to clock design using alternative lighting technology.This circuit is similar to the LED clock using 12 neon indicator lamps instead of LEDs. It operates from 2 high capacity ni-cad cells (2.5 volts) which keep it going for a couple weeks. High voltage (70 volts) for the neon lamps is obtained from a small switching power supply using a 74HC14 Schmitt trigger squarewave oscillator, high voltage switching transistor, and mH high Q inductor.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design consists of several key components that work together to achieve the desired functionality of illuminating the neon lamps in a clock-like manner. The 74HC14 Schmitt trigger serves as the oscillator, creating a square wave signal that drives the switching transistor. This transistor is responsible for controlling the flow of current to the high-Q inductor, which is crucial for stepping up the voltage to the necessary 70 volts for the neon lamps.
The use of two nickel-cadmium cells provides a reliable power source, ensuring that the circuit can function continuously for an extended period. The choice of high-capacity cells allows for a longer operational lifespan, making the circuit suitable for applications where regular battery replacement would be inconvenient.
The high-Q inductor plays a vital role in the voltage amplification process. By storing energy and releasing it at a higher voltage, it enables the neon lamps to operate effectively. The design ensures that the lamps can be lit with a consistent brightness, which is critical for visibility and aesthetic appeal.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines a low-voltage power source with a high-voltage generation mechanism to operate neon lamps, demonstrating an innovative approach to clock design using alternative lighting technology.This circuit is similar to the LED clock using 12 neon indicator lamps instead of LEDs. It operates from 2 high capacity ni-cad cells (2.5 volts) which keep it going for a couple weeks. High voltage (70 volts) for the neon lamps is obtained from a small switching power supply using a 74HC14 Schmitt trigger squarewave oscillator, high voltage switching transistor, and mH high Q inductor.. 🔗 External reference