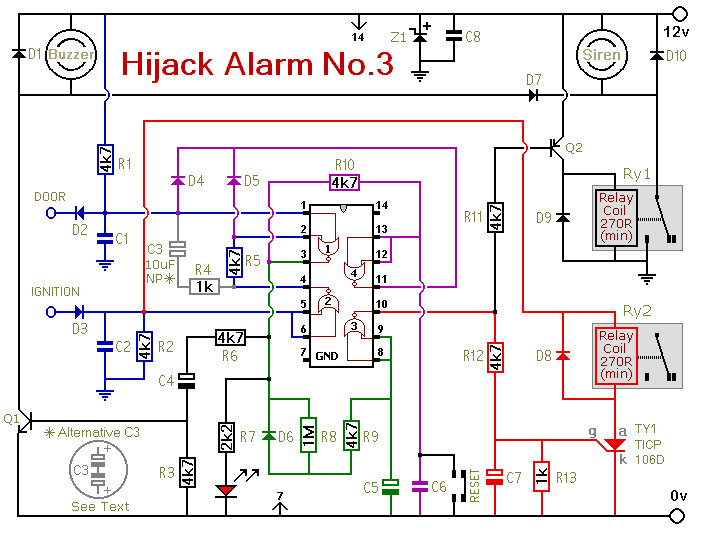
13.8Vdc 2A Regulated Power Supply Circuit
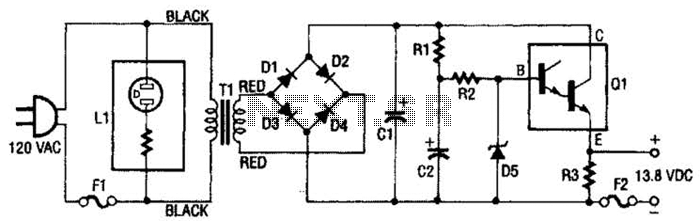
This regulated power supply consists of a step-down transformer T1, a full-wave rectifier bridge (D1 through D4), and a filtering regulator circuit made up of C1, C2, R1, R2, R8, D5, and Q1. When 120 Vac is provided, the neon-lamp assembly L1 lights up, and transformer T1 converts 120 Vac to approximately 28 Vac. The rectifier bridge (D1 through D4) rectifies the AC into pulsating DC, which is then filtered by C1. Capacitor C1 functions as a storage capacitor. The Zener diode D5 maintains a constant voltage across the base of the Darlington regulator Q1, ensuring a steady voltage across resistor R3 and the positive and negative output terminals where the load is connected. Fuse F2 is included to open (blow) if the current through the output terminals exceeds safe levels. Proper precautions should be taken when using projects powered by 120 Vac.
The described regulated power supply is a critical component in various electronic applications, providing a stable voltage output from a high-voltage AC source. The step-down transformer T1 plays a pivotal role in reducing the input voltage from 120 Vac to a safer 28 Vac, suitable for further processing. The full-wave rectifier bridge, composed of diodes D1 through D4, converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into pulsating direct current (DC). This conversion is essential for powering DC devices.
Capacitor C1 functions as a smoothing capacitor, effectively filtering the pulsating DC output to provide a more stable DC voltage. It stores charge and releases it as needed, thereby reducing voltage ripple and ensuring a consistent output voltage. In conjunction with capacitor C2, which may be used for additional filtering or stability, the circuit can handle transient loads more effectively.
The Zener diode D5 is a crucial component in voltage regulation. By maintaining a constant voltage across the base of the Darlington transistor Q1, it ensures that the output voltage remains stable, even with variations in load current. This regulation is vital for sensitive electronic circuits that require a specific voltage for optimal performance. The Darlington pair configuration in Q1 allows for high current gain, making it suitable for driving larger loads while maintaining low output impedance.
Resistor R3, connected to the output, serves to limit the current and protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions. The presence of fuse F2 adds an additional layer of safety by disconnecting the circuit in the event of excessive current flow, thus preventing damage to the components.
Overall, this regulated power supply design is robust and reliable, suitable for various applications where stable DC voltage is required. Proper precautions must be observed when working with 120 Vac sources to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. This regulated power supply consists of step-down transformer Tl, a full-wave rectifier bridge (D1 through D4), and a filtering regulator circuit made up of Cl, C2, Rl, R2, R8, D5, and Ql, When 120 Vac is provided, the neon-lamp assembly LI lights up, and transformer Tl changes 120 Vac to about 28 Vac. The rectifier bridge, )1 through D4, rectifies the ac into pulsating dc, which is then filtered by Cl.
Capacitor Cl acts as a storage capacitor. Zener diode 1)5 keeps the voltage constant across the base of Darlington regulator Ql, causing constant voltage across resistor R3 and the (+) and (-) output terminals, where the load is connected. Fuse F2 is used to open (blow), if the current through the output terminals is too high. Make sure to take proper precautions when using projects powered by 120 Vac. 🔗 External reference
The described regulated power supply is a critical component in various electronic applications, providing a stable voltage output from a high-voltage AC source. The step-down transformer T1 plays a pivotal role in reducing the input voltage from 120 Vac to a safer 28 Vac, suitable for further processing. The full-wave rectifier bridge, composed of diodes D1 through D4, converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into pulsating direct current (DC). This conversion is essential for powering DC devices.
Capacitor C1 functions as a smoothing capacitor, effectively filtering the pulsating DC output to provide a more stable DC voltage. It stores charge and releases it as needed, thereby reducing voltage ripple and ensuring a consistent output voltage. In conjunction with capacitor C2, which may be used for additional filtering or stability, the circuit can handle transient loads more effectively.
The Zener diode D5 is a crucial component in voltage regulation. By maintaining a constant voltage across the base of the Darlington transistor Q1, it ensures that the output voltage remains stable, even with variations in load current. This regulation is vital for sensitive electronic circuits that require a specific voltage for optimal performance. The Darlington pair configuration in Q1 allows for high current gain, making it suitable for driving larger loads while maintaining low output impedance.
Resistor R3, connected to the output, serves to limit the current and protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions. The presence of fuse F2 adds an additional layer of safety by disconnecting the circuit in the event of excessive current flow, thus preventing damage to the components.
Overall, this regulated power supply design is robust and reliable, suitable for various applications where stable DC voltage is required. Proper precautions must be observed when working with 120 Vac sources to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. This regulated power supply consists of step-down transformer Tl, a full-wave rectifier bridge (D1 through D4), and a filtering regulator circuit made up of Cl, C2, Rl, R2, R8, D5, and Ql, When 120 Vac is provided, the neon-lamp assembly LI lights up, and transformer Tl changes 120 Vac to about 28 Vac. The rectifier bridge, )1 through D4, rectifies the ac into pulsating dc, which is then filtered by Cl.
Capacitor Cl acts as a storage capacitor. Zener diode 1)5 keeps the voltage constant across the base of Darlington regulator Ql, causing constant voltage across resistor R3 and the (+) and (-) output terminals, where the load is connected. Fuse F2 is used to open (blow), if the current through the output terminals is too high. Make sure to take proper precautions when using projects powered by 120 Vac. 🔗 External reference