136 kHz direct conversion receiver
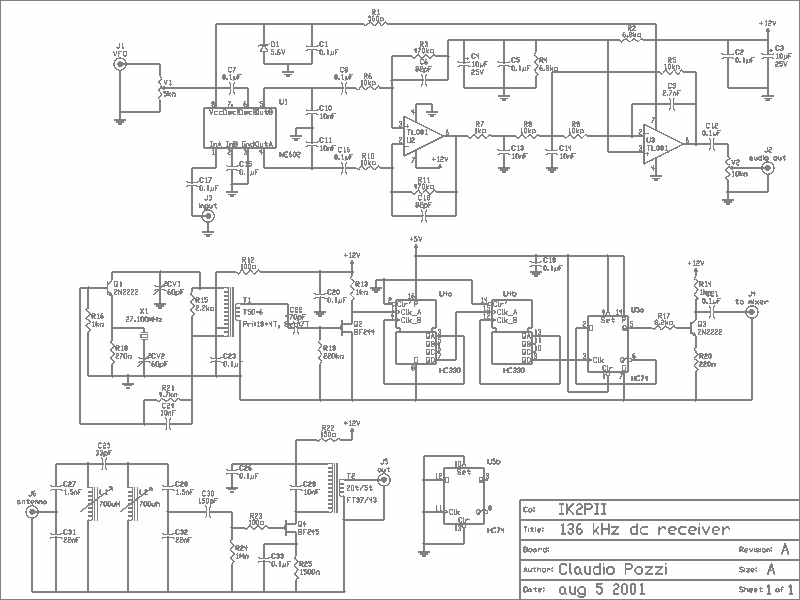
I describe a simple direct conversion receiver, designed for QRSS and DFCW communications, as a companion to ARGO or SPECTRAN programs. The intention is not to surpass the performance of professional or commercial ham radio receivers; rather, the goal is to provide an easy way for beginners to observe signals in this sparsely populated band. The receiver is also useful as a portable device, a fast turn-on receiver for a quick look at the band, or as a very low-cost (and low-performance) spectrum analyzer. This equipment is currently used for testing purposes.
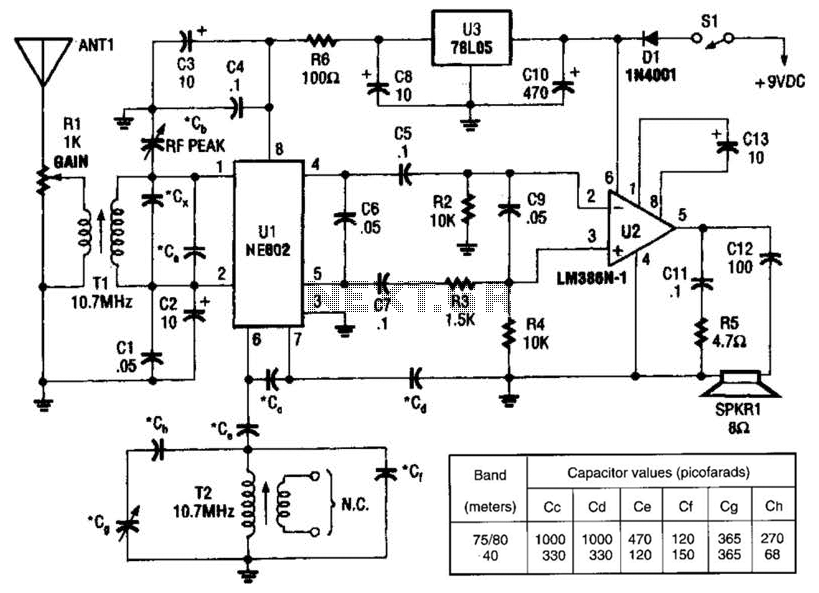
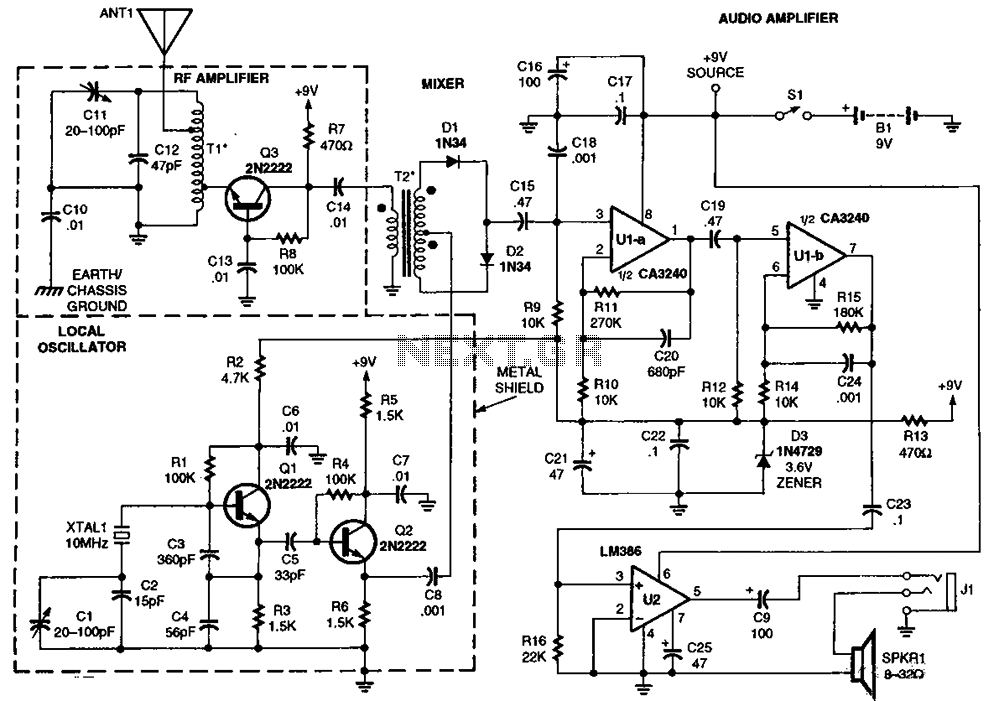
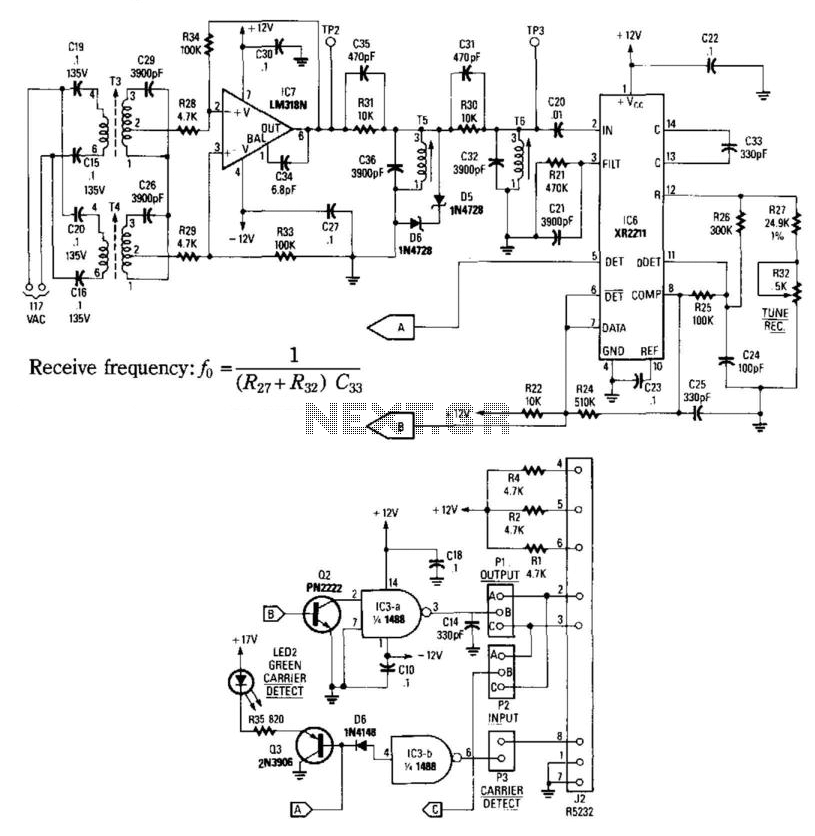
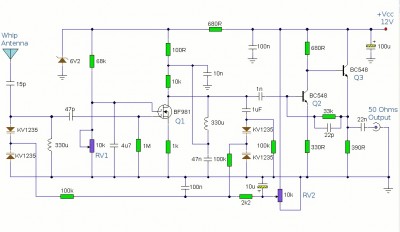
The described direct conversion receiver operates on the principle of mixing the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal with a locally generated oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) of zero Hertz, resulting in baseband audio output. This method simplifies the design and allows for the direct demodulation of amplitude-modulated (AM) and frequency-modulated (FM) signals.
Key components of the circuit typically include a radio frequency amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and an audio amplifier. The RF amplifier boosts the incoming signal to a suitable level before it is mixed. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with the oscillator signal, which is often generated using a simple crystal oscillator or a variable frequency oscillator (VFO) to allow tuning across the desired frequency range.
The output from the mixer is then passed through a low-pass filter to eliminate unwanted high-frequency components, leaving only the audio signal. This audio signal can be further amplified using an audio amplifier stage, which drives a speaker or headphones for audio output.
For portable applications, the design may incorporate battery power options and compact components to facilitate ease of transport. Additionally, a simple tuning mechanism, such as a variable capacitor or a digital tuning circuit, can be integrated to allow users to adjust the frequency of the local oscillator, thereby tuning into different signals within the QRSS and DFCW bands.
Overall, this direct conversion receiver serves as an accessible entry point for beginners interested in exploring the world of low-frequency communications and signal analysis, providing essential functionality without the complexity or cost associated with more advanced radio equipment.I describe a simple direct conversion receiver, thinked for QRSS and DFCW communications, as companion of ARGO or SPECTRAN programs. I don`t pretend to beat the performances of professional or commercial ham radio receiver, the scope is to suggest an easy way for beginner to listen (of course I mean look at) the signals in this poorly populated band.
The receiver is useful also as portable receiver, fast turn-on receiver for a quick look an the band or as very low cost (and performances) spectrum analyzer. I currently use this equipment for tests purposes. 🔗 External reference
The described direct conversion receiver operates on the principle of mixing the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal with a locally generated oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) of zero Hertz, resulting in baseband audio output. This method simplifies the design and allows for the direct demodulation of amplitude-modulated (AM) and frequency-modulated (FM) signals.
Key components of the circuit typically include a radio frequency amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and an audio amplifier. The RF amplifier boosts the incoming signal to a suitable level before it is mixed. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with the oscillator signal, which is often generated using a simple crystal oscillator or a variable frequency oscillator (VFO) to allow tuning across the desired frequency range.
The output from the mixer is then passed through a low-pass filter to eliminate unwanted high-frequency components, leaving only the audio signal. This audio signal can be further amplified using an audio amplifier stage, which drives a speaker or headphones for audio output.
For portable applications, the design may incorporate battery power options and compact components to facilitate ease of transport. Additionally, a simple tuning mechanism, such as a variable capacitor or a digital tuning circuit, can be integrated to allow users to adjust the frequency of the local oscillator, thereby tuning into different signals within the QRSS and DFCW bands.
Overall, this direct conversion receiver serves as an accessible entry point for beginners interested in exploring the world of low-frequency communications and signal analysis, providing essential functionality without the complexity or cost associated with more advanced radio equipment.I describe a simple direct conversion receiver, thinked for QRSS and DFCW communications, as companion of ARGO or SPECTRAN programs. I don`t pretend to beat the performances of professional or commercial ham radio receiver, the scope is to suggest an easy way for beginner to listen (of course I mean look at) the signals in this poorly populated band.
The receiver is useful also as portable receiver, fast turn-on receiver for a quick look an the band or as very low cost (and performances) spectrum analyzer. I currently use this equipment for tests purposes. 🔗 External reference