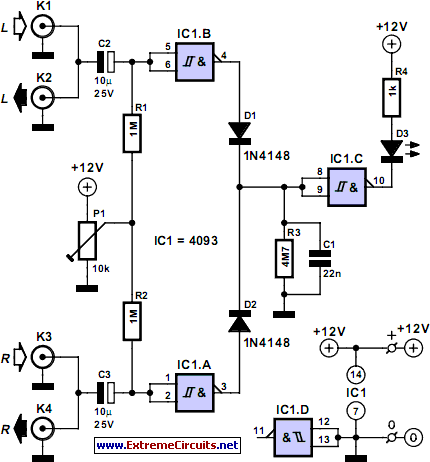
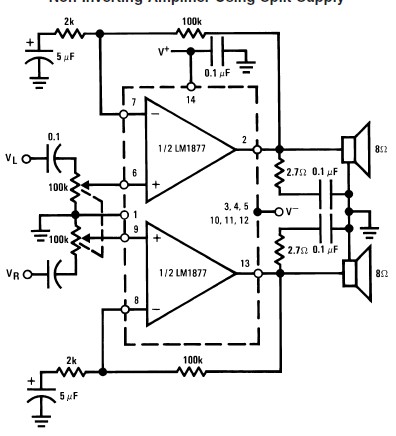
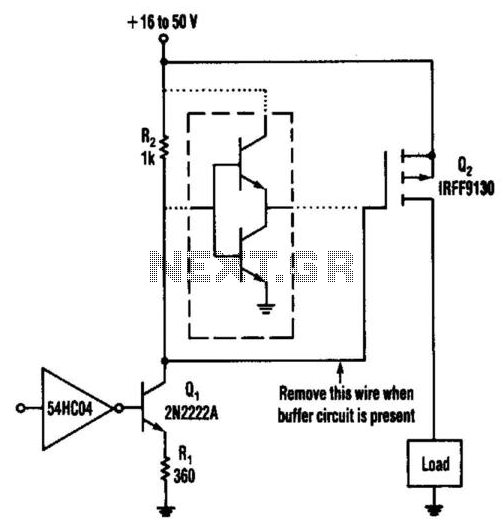
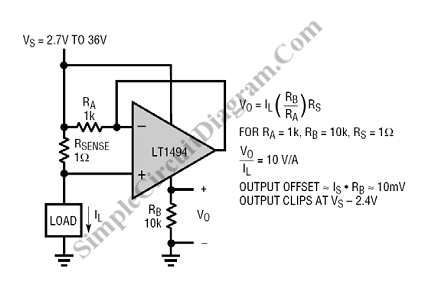
1400w audio power amplifier
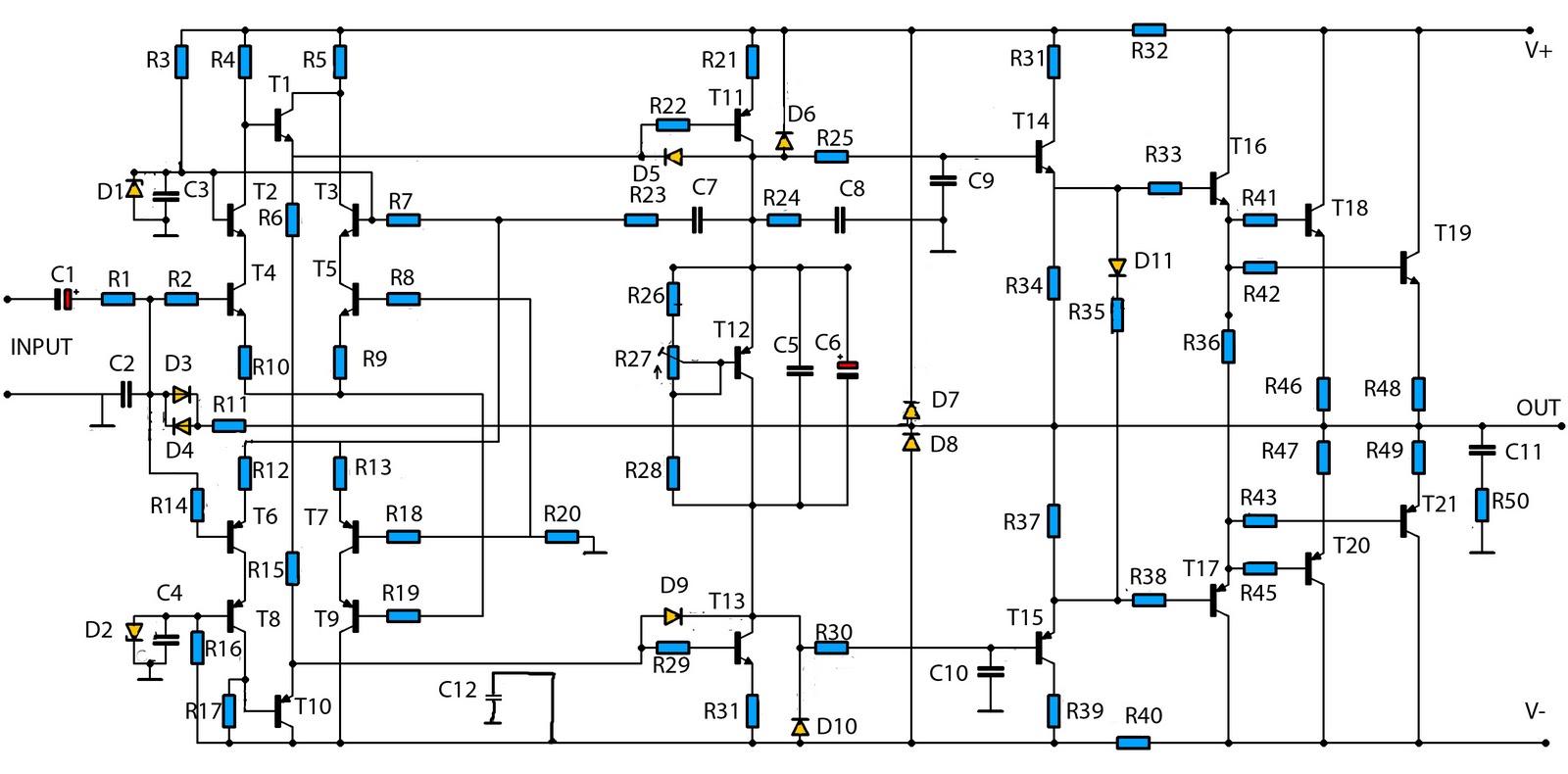
This is a mono amplifier circuit with a high output power of 1400W. It is well-suited for use in large rooms with woofer and full-range speakers, delivering a loud and clear sound with minimal noise. The amplifier utilizes high-quality transistors, and various high-power transistors can be used for the final amplification stage. The minimum required supply voltage is ±25V, while the maximum can reach ±90V. Transistors numbered 11 to 17 require a heatsink due to the heat generated at maximum operating conditions, and it is also essential to provide heatsinks for the final amplifier transistors, specifically transistors 18 to 21.
The amplifier circuit described operates as a high-power audio amplifier designed for mono output, making it ideal for large audio setups where significant sound levels are required. The output stage can deliver up to 1400W, which is suitable for driving large woofer speakers and full-range speakers, ensuring that the audio output is both loud and clear, with a focus on maintaining audio fidelity and minimizing distortion.
The circuit employs high-quality transistors that can handle the substantial output power. The choice of transistors in the final amplification stage is flexible, allowing for the use of various high-power models, which can be selected based on availability and performance characteristics. The power supply requirements are critical, with a minimum voltage of ±25V ensuring adequate headroom for operation, while the maximum voltage of ±90V allows for robust performance under high load conditions.
Thermal management is a significant consideration in the design of this amplifier circuit. Transistors 11 to 17, which are integral to the amplification process, must be mounted with heatsinks to dissipate the heat generated during operation effectively. This is crucial to prevent thermal overload and ensure reliable performance. Additionally, the final amplifier transistors, labeled 18 to 21, also require heatsinking to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent thermal failure.
In summary, this amplifier circuit is engineered for high output power applications, with careful attention to component selection and thermal management, making it suitable for demanding audio environments. Proper implementation of heatsinks and adherence to power supply specifications will ensure that the amplifier operates efficiently and reliably, delivering high-quality audio performance.This is an amplifier circuit that has a high output power is 1400W mono, the audio amplifier circuit is very suitable when used in a large room, using a woofer speaker, and fullrange. To sound out very nice, loud sound and almost no noise. The amplifier using a transistor amplifier-quality, and for the final amplifier transistors can use a variety
of high-power transistors. Minimum required supply voltage + / - 25V and a maximum of up to + /-90V. For transistor 11 to 17 should use a heatsink, because if the maximum working range of the transistor heat and should be to install the heatsink. But do not forget also to the final amplifier transistor circuit should also be given a heatsink such as transistors 18 to 21.
🔗 External reference
The amplifier circuit described operates as a high-power audio amplifier designed for mono output, making it ideal for large audio setups where significant sound levels are required. The output stage can deliver up to 1400W, which is suitable for driving large woofer speakers and full-range speakers, ensuring that the audio output is both loud and clear, with a focus on maintaining audio fidelity and minimizing distortion.
The circuit employs high-quality transistors that can handle the substantial output power. The choice of transistors in the final amplification stage is flexible, allowing for the use of various high-power models, which can be selected based on availability and performance characteristics. The power supply requirements are critical, with a minimum voltage of ±25V ensuring adequate headroom for operation, while the maximum voltage of ±90V allows for robust performance under high load conditions.
Thermal management is a significant consideration in the design of this amplifier circuit. Transistors 11 to 17, which are integral to the amplification process, must be mounted with heatsinks to dissipate the heat generated during operation effectively. This is crucial to prevent thermal overload and ensure reliable performance. Additionally, the final amplifier transistors, labeled 18 to 21, also require heatsinking to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent thermal failure.
In summary, this amplifier circuit is engineered for high output power applications, with careful attention to component selection and thermal management, making it suitable for demanding audio environments. Proper implementation of heatsinks and adherence to power supply specifications will ensure that the amplifier operates efficiently and reliably, delivering high-quality audio performance.This is an amplifier circuit that has a high output power is 1400W mono, the audio amplifier circuit is very suitable when used in a large room, using a woofer speaker, and fullrange. To sound out very nice, loud sound and almost no noise. The amplifier using a transistor amplifier-quality, and for the final amplifier transistors can use a variety
of high-power transistors. Minimum required supply voltage + / - 25V and a maximum of up to + /-90V. For transistor 11 to 17 should use a heatsink, because if the maximum working range of the transistor heat and should be to install the heatsink. But do not forget also to the final amplifier transistor circuit should also be given a heatsink such as transistors 18 to 21.
🔗 External reference