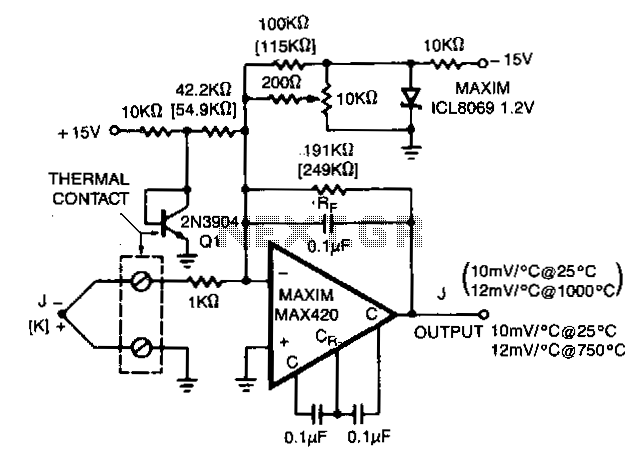
22W Stereo Amplifier Using TDA1554
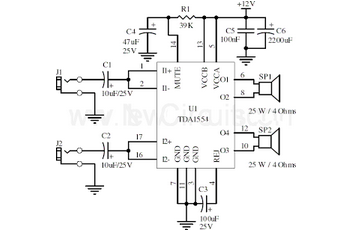
This document presents a 22-watt stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram based on the TDA1554 integrated circuit from NXP Semiconductors (formerly Philips Semiconductors).
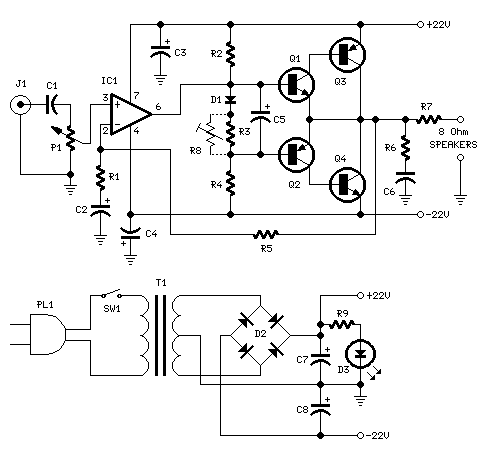
The 22-watt stereo audio power amplifier circuit utilizing the TDA1554 IC is designed to deliver high-quality audio amplification for various applications, such as home audio systems, car audio systems, and portable speakers. The TDA1554 is a dual-channel power amplifier that can provide up to 22 watts of output power per channel, making it suitable for driving speakers with moderate power requirements.
The circuit typically consists of the TDA1554 IC, which incorporates several key features, including thermal protection, short-circuit protection, and a built-in mute function. The amplifier operates in class AB mode, which ensures low distortion and high efficiency, contributing to superior sound quality.
In the schematic, the power supply section is crucial for the amplifier's performance. The TDA1554 operates with a supply voltage range of 12V to 28V, allowing flexibility in power supply design. Proper decoupling capacitors are essential to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply, ensuring reliable operation.
Input signals are usually fed into the amplifier through a coupling capacitor, which blocks any DC component, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by configuring external resistors, enabling customization based on specific application requirements.
Output connections are made to the speakers, with considerations for impedance matching to optimize performance. The circuit may also include additional components such as feedback resistors and capacitors to enhance stability and frequency response.
Overall, this amplifier circuit design provides an effective solution for audio amplification needs, combining efficiency and sound fidelity, making it a popular choice for audio enthusiasts and professionals alike.Here is the 22 watt stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram based on TDA1554 and integrated circuit from NXP semiconductors (formerly PHILIPS semicon.. 🔗 External reference
The 22-watt stereo audio power amplifier circuit utilizing the TDA1554 IC is designed to deliver high-quality audio amplification for various applications, such as home audio systems, car audio systems, and portable speakers. The TDA1554 is a dual-channel power amplifier that can provide up to 22 watts of output power per channel, making it suitable for driving speakers with moderate power requirements.
The circuit typically consists of the TDA1554 IC, which incorporates several key features, including thermal protection, short-circuit protection, and a built-in mute function. The amplifier operates in class AB mode, which ensures low distortion and high efficiency, contributing to superior sound quality.
In the schematic, the power supply section is crucial for the amplifier's performance. The TDA1554 operates with a supply voltage range of 12V to 28V, allowing flexibility in power supply design. Proper decoupling capacitors are essential to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply, ensuring reliable operation.
Input signals are usually fed into the amplifier through a coupling capacitor, which blocks any DC component, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by configuring external resistors, enabling customization based on specific application requirements.
Output connections are made to the speakers, with considerations for impedance matching to optimize performance. The circuit may also include additional components such as feedback resistors and capacitors to enhance stability and frequency response.
Overall, this amplifier circuit design provides an effective solution for audio amplification needs, combining efficiency and sound fidelity, making it a popular choice for audio enthusiasts and professionals alike.Here is the 22 watt stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram based on TDA1554 and integrated circuit from NXP semiconductors (formerly PHILIPS semicon.. 🔗 External reference