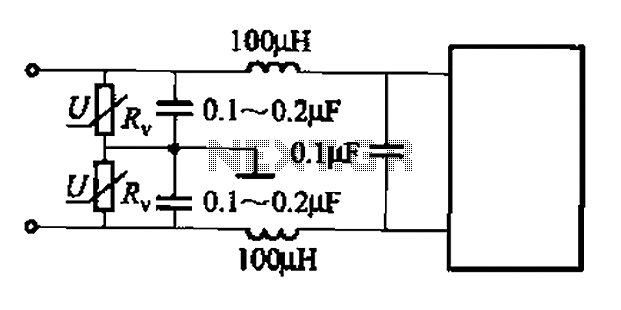
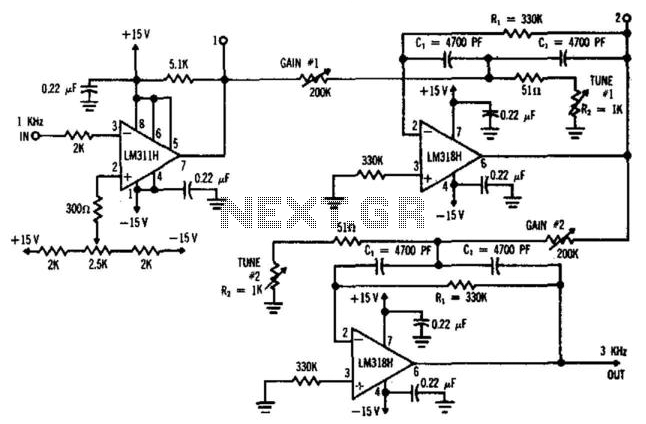
Ultra low noise preamplifier

The SL561 utilized in this circuit functions as a high-gain, low-noise preamplifier intended for audio and video applications at frequencies reaching up to 6 MHz. Figure 2-6B illustrates the gain in relation to frequency for different capacitance values of C1, while Figure 2-6C depicts the gain corresponding to various resistance values of RSET. Additionally, Figure 2-6D presents the electrical characteristics, and Figure 2-6E demonstrates harmonic distortion.
The SL561 preamplifier is engineered to amplify weak audio or video signals with minimal added noise, making it suitable for high-fidelity applications. Its design features a high input impedance, allowing it to interface effectively with various signal sources without loading them down. The preamplifier's gain can be adjusted by varying the capacitance (C1) and resistance (RSET) components in the circuit, which are critical for optimizing performance across the specified frequency range.
In practical applications, the circuit may include additional components such as bypass capacitors to filter out power supply noise, and feedback networks to stabilize gain and improve bandwidth. The output stage of the SL561 typically drives subsequent stages in the signal chain, such as filters or analog-to-digital converters, ensuring that the amplified signal maintains integrity and fidelity.
Figures referenced in the description provide essential visual data for understanding the performance characteristics of the SL561. The gain versus frequency plot (Figure 2-6B) is crucial for determining the operational bandwidth of the preamplifier, while the gain versus RSET (Figure 2-6C) assists in selecting appropriate resistor values for desired gain settings. The electrical characteristics (Figure 2-6D) offer insights into parameters such as supply voltage, input/output impedance, and power consumption, which are vital for system integration. Finally, the harmonic distortion graph (Figure 2-6E) is important for assessing the linearity of the amplifier and its suitability for high-quality audio or video applications.
This circuit exemplifies the essential role of preamplifiers in signal processing, particularly in scenarios where signal integrity and low noise are paramount. Proper selection and configuration of the SL561 and its associated components can significantly enhance system performance, making it a valuable asset in audio/video electronics design.The SL561 used in this circuit is a high-gain low-noise preamplifier designed for audio/video applications at frequencies up to 6 MHz. Figure 2-6B shows gain versus frequency for various values of C1, and Fig. 2-6C shows gain versus various values of RSET. Figure 2-6D shows the electrical characteristics. Figure 2-6E shows harmonic distortion. 🔗 External reference
The SL561 preamplifier is engineered to amplify weak audio or video signals with minimal added noise, making it suitable for high-fidelity applications. Its design features a high input impedance, allowing it to interface effectively with various signal sources without loading them down. The preamplifier's gain can be adjusted by varying the capacitance (C1) and resistance (RSET) components in the circuit, which are critical for optimizing performance across the specified frequency range.
In practical applications, the circuit may include additional components such as bypass capacitors to filter out power supply noise, and feedback networks to stabilize gain and improve bandwidth. The output stage of the SL561 typically drives subsequent stages in the signal chain, such as filters or analog-to-digital converters, ensuring that the amplified signal maintains integrity and fidelity.
Figures referenced in the description provide essential visual data for understanding the performance characteristics of the SL561. The gain versus frequency plot (Figure 2-6B) is crucial for determining the operational bandwidth of the preamplifier, while the gain versus RSET (Figure 2-6C) assists in selecting appropriate resistor values for desired gain settings. The electrical characteristics (Figure 2-6D) offer insights into parameters such as supply voltage, input/output impedance, and power consumption, which are vital for system integration. Finally, the harmonic distortion graph (Figure 2-6E) is important for assessing the linearity of the amplifier and its suitability for high-quality audio or video applications.
This circuit exemplifies the essential role of preamplifiers in signal processing, particularly in scenarios where signal integrity and low noise are paramount. Proper selection and configuration of the SL561 and its associated components can significantly enhance system performance, making it a valuable asset in audio/video electronics design.The SL561 used in this circuit is a high-gain low-noise preamplifier designed for audio/video applications at frequencies up to 6 MHz. Figure 2-6B shows gain versus frequency for various values of C1, and Fig. 2-6C shows gain versus various values of RSET. Figure 2-6D shows the electrical characteristics. Figure 2-6E shows harmonic distortion. 🔗 External reference