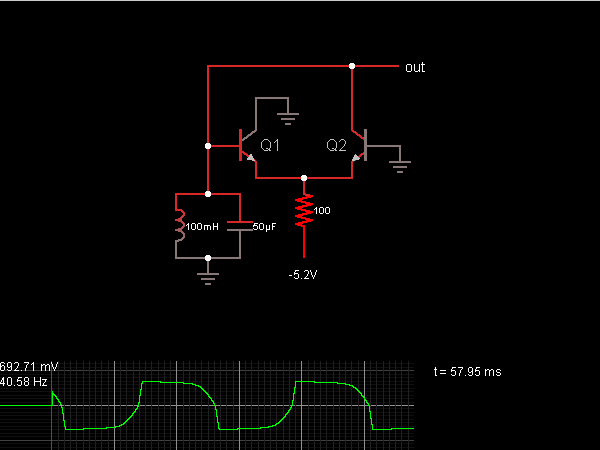
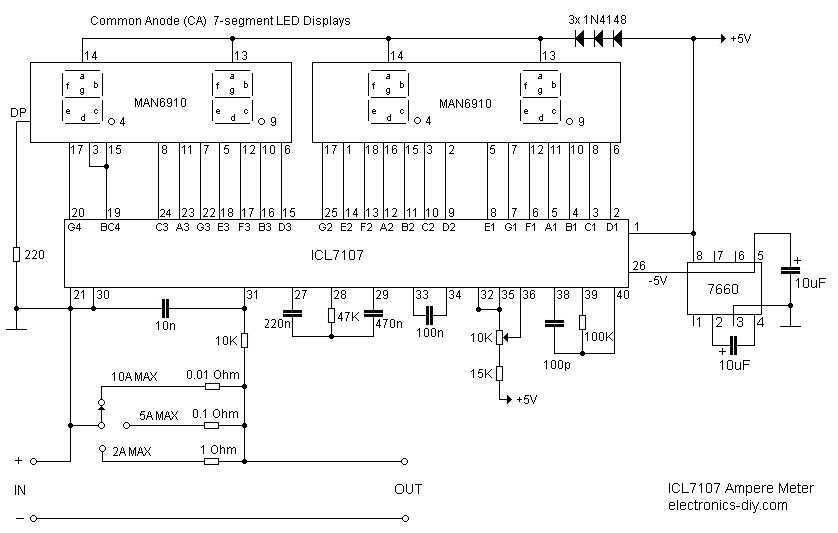
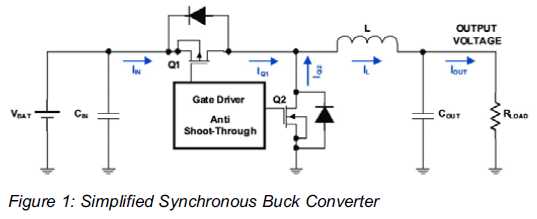
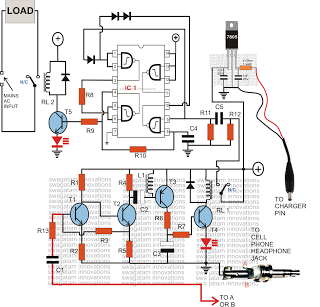
24 LED SpotlightCircuit
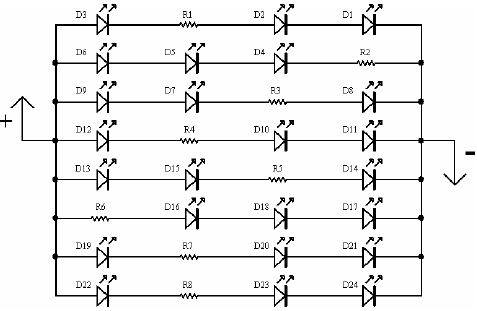
A light-emitting diode (LED) lamp is a solid-state lighting device that utilizes light-emitting diodes as its light source. LEDs are a cost-effective and convenient choice for various lighting applications. They are available in an extensive range of colors, styles, sizes, and intensities, providing economical, highly efficient, low-voltage, and reliable lighting solutions. The advantages of LED spotlights include reduced heat generation, enhanced energy efficacy, absence of UV radiation, extended lifespan, and the absence of non-passive failures. The schematic illustrates a 24 LED spotlight circuit diagram and design, featuring 24 LEDs arranged in a circular configuration on a compact board measuring 2 3/8 inches (60mm) in diameter. The circuit design shows the LEDs connected in groups of three, with each group equipped with its own current-limiting resistor. The complete circuit, with all 24 LEDs operational, draws approximately 160mA.
The LED spotlight circuit is designed to maximize efficiency while ensuring optimal performance. The arrangement of the LEDs in a circular pattern not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also promotes uniform light distribution. Each set of three LEDs is connected in series, allowing for effective voltage division across the group, which is crucial for maintaining consistent brightness levels. The inclusion of current-limiting resistors for each trio of LEDs is essential to prevent excess current from flowing through the diodes, which could lead to premature failure or reduced lifespan.
In terms of power supply, the circuit operates at a low voltage, making it suitable for battery-powered applications as well as mains-powered systems with appropriate voltage regulation. The total current draw of approximately 160mA suggests that the design is energy-efficient, aligning with the advantages of LED technology. This low power consumption is particularly beneficial in applications where energy savings are paramount, such as in residential lighting or portable devices.
The schematic diagram should also include annotations for each component, indicating the values of the resistors used and the specifications of the LEDs, such as their forward voltage and current ratings. Additionally, it may be beneficial to provide a brief explanation of the circuit operation, highlighting the role of each component and how they contribute to the overall functionality of the spotlight. This comprehensive approach ensures that users can easily understand the circuit design and its application in real-world scenarios.A light-emitting-diode lamp is a solid-state lamp that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the source of light. The Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are an attractive, economical and convenient option for lighting applications.
Available in a wide variety of colors, styles, sizes and intensities, LEDs provide for inexpensive, highly-efficient, low-vo ltage, reliable lighting solutions. Some advantages of the LED Spotlight are: Lower Heat; Higher Energy Efficacy; No UV Radiation; Longer Life Expectancy; and No Non-Passive Failures. The following schematic shows the 24 LED Spotlight Circuit Diagram and Design. It holds 24 LEDs in a circular pattern on a compact 2 3/8 (60mm) diameter board. The schematic shows the LEDs wired in sets of three with each set having its own current limiting resistor.
A full 24 LEDs running on the board will draw a total of approximately 160mA. For more information on 24 LED Spotlight Circuit Diagram Design, download the following PDF file. 🔗 External reference
The LED spotlight circuit is designed to maximize efficiency while ensuring optimal performance. The arrangement of the LEDs in a circular pattern not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also promotes uniform light distribution. Each set of three LEDs is connected in series, allowing for effective voltage division across the group, which is crucial for maintaining consistent brightness levels. The inclusion of current-limiting resistors for each trio of LEDs is essential to prevent excess current from flowing through the diodes, which could lead to premature failure or reduced lifespan.
In terms of power supply, the circuit operates at a low voltage, making it suitable for battery-powered applications as well as mains-powered systems with appropriate voltage regulation. The total current draw of approximately 160mA suggests that the design is energy-efficient, aligning with the advantages of LED technology. This low power consumption is particularly beneficial in applications where energy savings are paramount, such as in residential lighting or portable devices.
The schematic diagram should also include annotations for each component, indicating the values of the resistors used and the specifications of the LEDs, such as their forward voltage and current ratings. Additionally, it may be beneficial to provide a brief explanation of the circuit operation, highlighting the role of each component and how they contribute to the overall functionality of the spotlight. This comprehensive approach ensures that users can easily understand the circuit design and its application in real-world scenarios.A light-emitting-diode lamp is a solid-state lamp that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the source of light. The Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are an attractive, economical and convenient option for lighting applications.
Available in a wide variety of colors, styles, sizes and intensities, LEDs provide for inexpensive, highly-efficient, low-vo ltage, reliable lighting solutions. Some advantages of the LED Spotlight are: Lower Heat; Higher Energy Efficacy; No UV Radiation; Longer Life Expectancy; and No Non-Passive Failures. The following schematic shows the 24 LED Spotlight Circuit Diagram and Design. It holds 24 LEDs in a circular pattern on a compact 2 3/8 (60mm) diameter board. The schematic shows the LEDs wired in sets of three with each set having its own current limiting resistor.
A full 24 LEDs running on the board will draw a total of approximately 160mA. For more information on 24 LED Spotlight Circuit Diagram Design, download the following PDF file. 🔗 External reference