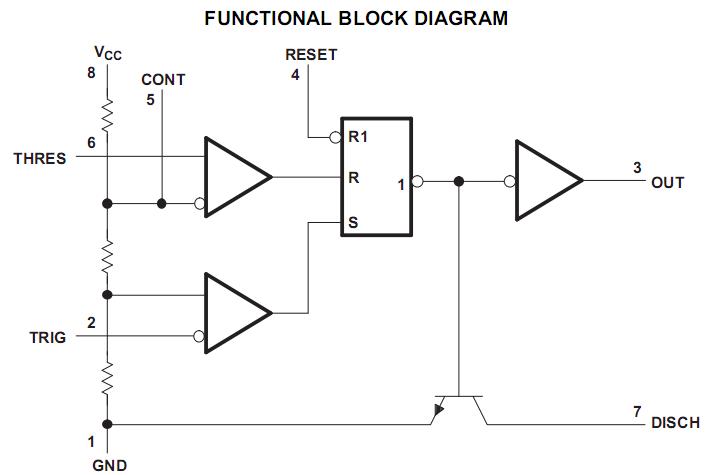
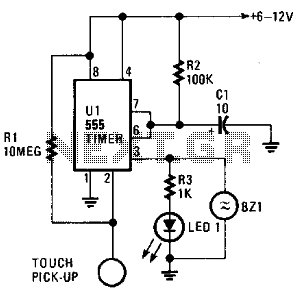
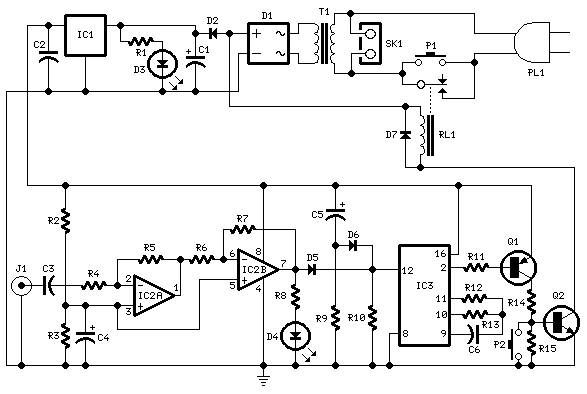
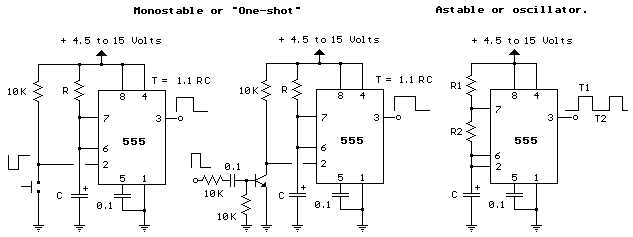
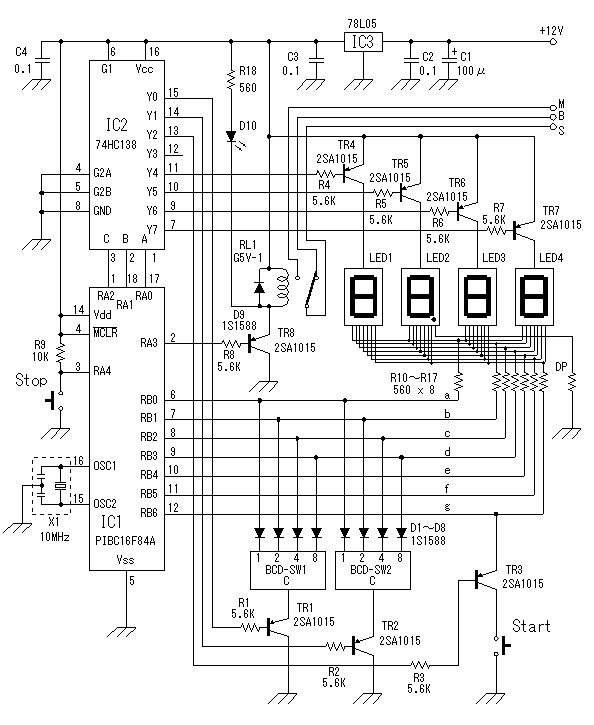
Time Controlled Power-Save Mode
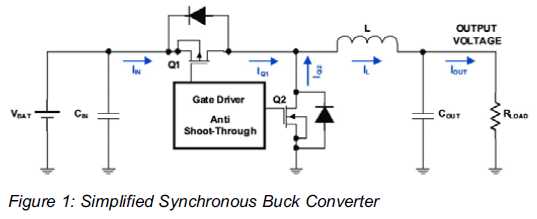
Increased Flexibility for Low-Power Synchronous Buck Converters. Contemporary synchronous buck converters designed for portable applications offer a power-save mode operation to sustain high efficiency throughout the entire range of operation.
Modern low-power synchronous buck converters are essential components in portable electronic devices, where efficiency and battery life are critical. These converters are designed to step down voltage while maintaining high efficiency, which is particularly important in battery-operated applications. The implementation of a power-save mode enhances their operational flexibility, allowing the converters to adjust their performance based on the load conditions.
In power-save mode, the synchronous buck converter reduces its switching frequency and adjusts the on-time and off-time of the switching elements to minimize power loss. This mode is particularly beneficial during periods of low load, as it helps to maintain efficiency by decreasing the quiescent current and reducing switching losses. The converter can seamlessly transition between normal operation and power-save mode, ensuring that it meets the demands of varying load conditions without compromising performance.
Additionally, the design of these converters often includes features such as adaptive voltage positioning, which helps to optimize output voltage regulation under different load scenarios. This further enhances the efficiency and performance of the buck converter across a range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial devices.
The integration of control algorithms within the converter's circuitry allows for real-time adjustments to the switching strategy, further improving efficiency. The ability to maintain high efficiency over the entire load range is critical for extending battery life in portable applications, making modern synchronous buck converters a vital component in the design of energy-efficient electronic systems.More Flexibility For Low-Power Synchronous Buck Converters Modern synchronous buck converters for portable applications provide so called power-save mode operation to maintain high efficiency over the entire.. 🔗 External reference
Modern low-power synchronous buck converters are essential components in portable electronic devices, where efficiency and battery life are critical. These converters are designed to step down voltage while maintaining high efficiency, which is particularly important in battery-operated applications. The implementation of a power-save mode enhances their operational flexibility, allowing the converters to adjust their performance based on the load conditions.
In power-save mode, the synchronous buck converter reduces its switching frequency and adjusts the on-time and off-time of the switching elements to minimize power loss. This mode is particularly beneficial during periods of low load, as it helps to maintain efficiency by decreasing the quiescent current and reducing switching losses. The converter can seamlessly transition between normal operation and power-save mode, ensuring that it meets the demands of varying load conditions without compromising performance.
Additionally, the design of these converters often includes features such as adaptive voltage positioning, which helps to optimize output voltage regulation under different load scenarios. This further enhances the efficiency and performance of the buck converter across a range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial devices.
The integration of control algorithms within the converter's circuitry allows for real-time adjustments to the switching strategy, further improving efficiency. The ability to maintain high efficiency over the entire load range is critical for extending battery life in portable applications, making modern synchronous buck converters a vital component in the design of energy-efficient electronic systems.More Flexibility For Low-Power Synchronous Buck Converters Modern synchronous buck converters for portable applications provide so called power-save mode operation to maintain high efficiency over the entire.. 🔗 External reference