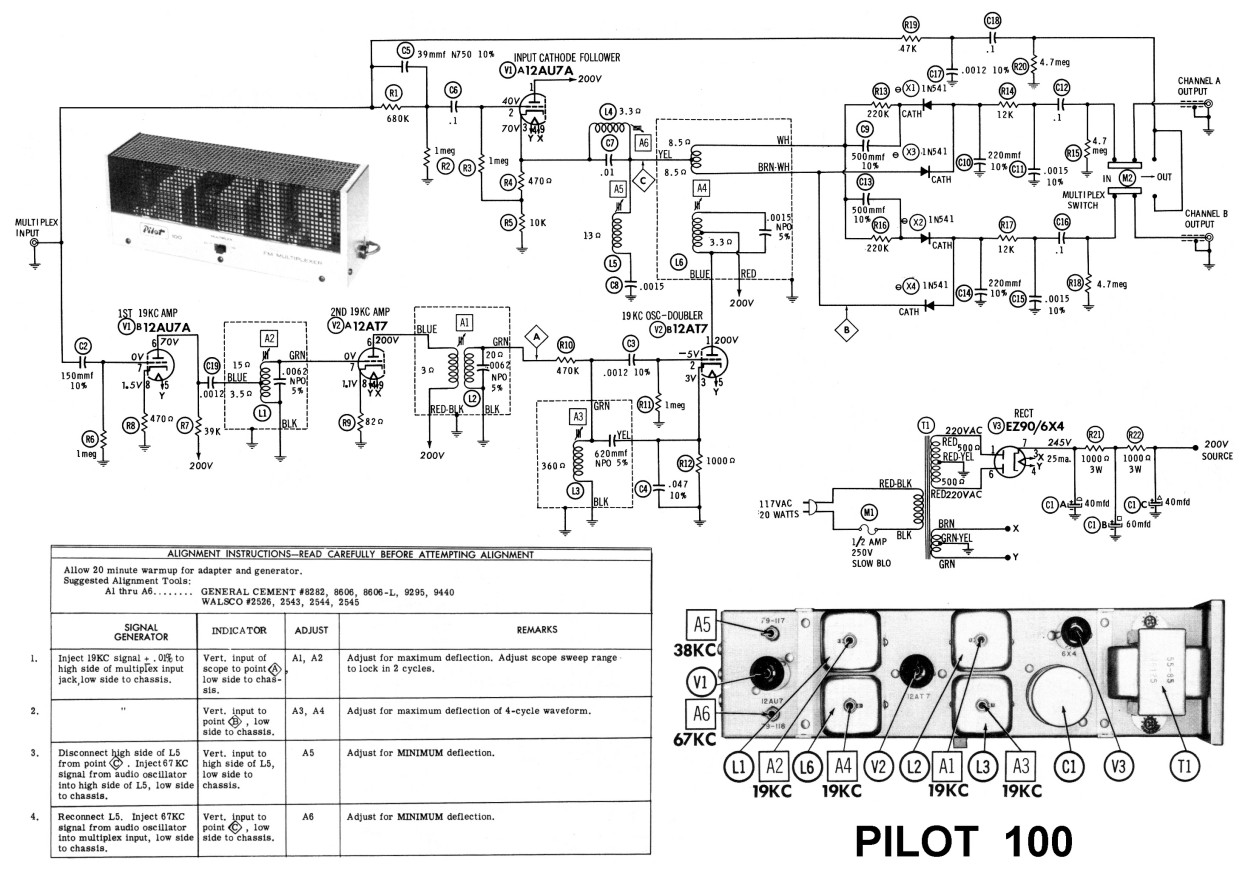
300 KW MAGNETRON MODULATOR
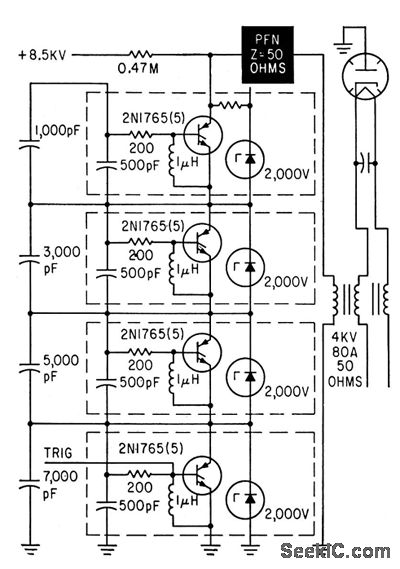
A trigger is applied to the first of four 2-kV switch modules arranged in series, enabling simultaneous triggering of the other modules to deliver a 16-kV, 20-amp pulse to a type 7208 Ku-band coaxial magnetron through a standard 50-ohm pulse-forming network (PFN).
The described circuit utilizes a series configuration of four high-voltage switch modules, each rated at 2 kV. This arrangement is critical for achieving the required output voltage of 16 kV, which is necessary for the operation of the Ku-band magnetron. The switches are designed to be triggered in unison, ensuring that the pulse delivered to the magnetron is both high in voltage and capable of supplying a substantial current of 20 amps.
The pulse-forming network (PFN) plays a vital role in shaping the output pulse characteristics. A standard 50-ohm PFN is employed to match the impedance of the magnetron, minimizing reflections and ensuring efficient energy transfer. The PFN is designed to create a well-defined pulse shape, which is essential for the optimal performance of the magnetron, as it influences the efficiency and stability of the microwave output.
In practical terms, the triggering mechanism must be carefully designed to ensure that all four switch modules activate simultaneously. This can be achieved using a common trigger signal that is distributed to each switch, often implemented using a fast pulse generator. The design must also consider the timing and synchronization of the trigger signal to prevent any delay that could lead to uneven triggering, which could damage the components or lead to suboptimal performance.
The overall system must be housed in a robust enclosure to protect against high-voltage arcing and electromagnetic interference, which are typical concerns in high-power microwave applications. Proper thermal management and safety measures must also be in place to handle the significant power levels involved.
In summary, the circuit described is a sophisticated arrangement designed to generate high-voltage pulses for a Ku-band magnetron, utilizing a series of switch modules and a pulse-forming network, with careful attention to triggering and system integrity to ensure reliable operation.Trigger is applied to first of four 2-kv switch modules arranged in series, for simultaneous triggering of other modules to furnish 16-kv 20-amp pulse to type 7208 Ku-band coaxial magnetron through standard 50-ohm pulseforming network PFN. -F. A. Gateka and M. L. Embree, Semiconductor Modulators for Modern Magnetrons, Electronics, 35:37, p 42-45. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a series configuration of four high-voltage switch modules, each rated at 2 kV. This arrangement is critical for achieving the required output voltage of 16 kV, which is necessary for the operation of the Ku-band magnetron. The switches are designed to be triggered in unison, ensuring that the pulse delivered to the magnetron is both high in voltage and capable of supplying a substantial current of 20 amps.
The pulse-forming network (PFN) plays a vital role in shaping the output pulse characteristics. A standard 50-ohm PFN is employed to match the impedance of the magnetron, minimizing reflections and ensuring efficient energy transfer. The PFN is designed to create a well-defined pulse shape, which is essential for the optimal performance of the magnetron, as it influences the efficiency and stability of the microwave output.
In practical terms, the triggering mechanism must be carefully designed to ensure that all four switch modules activate simultaneously. This can be achieved using a common trigger signal that is distributed to each switch, often implemented using a fast pulse generator. The design must also consider the timing and synchronization of the trigger signal to prevent any delay that could lead to uneven triggering, which could damage the components or lead to suboptimal performance.
The overall system must be housed in a robust enclosure to protect against high-voltage arcing and electromagnetic interference, which are typical concerns in high-power microwave applications. Proper thermal management and safety measures must also be in place to handle the significant power levels involved.
In summary, the circuit described is a sophisticated arrangement designed to generate high-voltage pulses for a Ku-band magnetron, utilizing a series of switch modules and a pulse-forming network, with careful attention to triggering and system integrity to ensure reliable operation.Trigger is applied to first of four 2-kv switch modules arranged in series, for simultaneous triggering of other modules to furnish 16-kv 20-amp pulse to type 7208 Ku-band coaxial magnetron through standard 50-ohm pulseforming network PFN. -F. A. Gateka and M. L. Embree, Semiconductor Modulators for Modern Magnetrons, Electronics, 35:37, p 42-45. 🔗 External reference