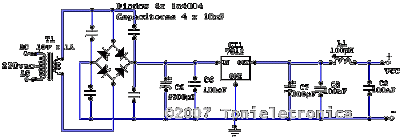
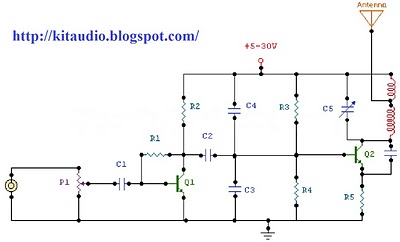
3w fm transmitter
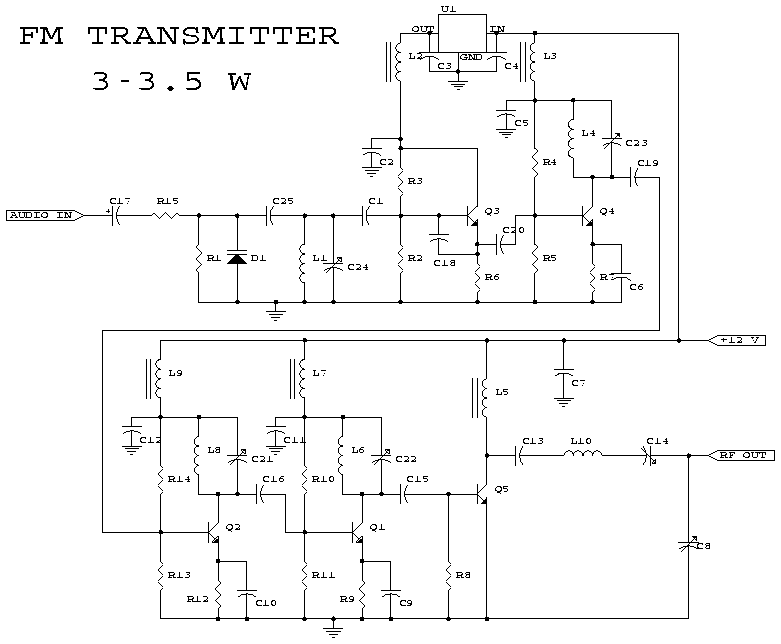
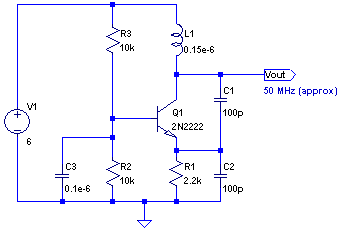
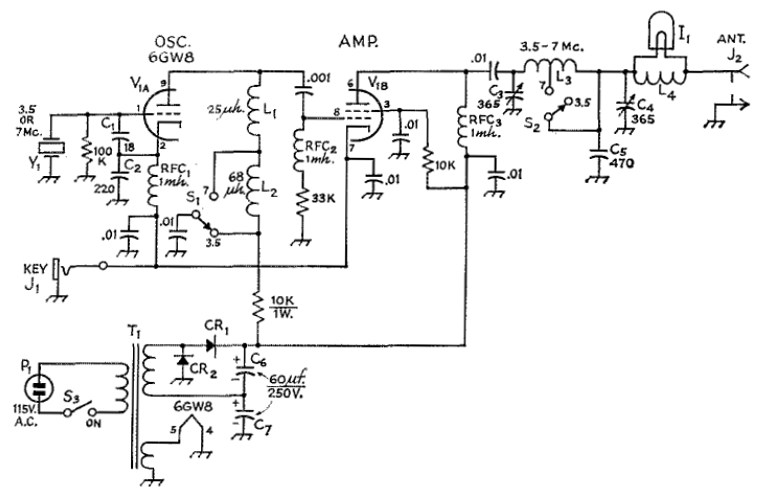
This schematic represents an FM transmitter capable of delivering an output power of 3 to 3.5 W, operating within the frequency range of 90 to 110 MHz. While the stability of the circuit is acceptable, a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can be integrated for enhanced performance. The circuit was previously constructed for a friend, who utilized it in conjunction with the BLY88 amplifier to achieve an output power of 20 W. According to notes made on the original schematic, the transmitter functioned effectively with a Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) of 1:1.05, which is typical for the antenna setup used. The circuit was tested on a standard RF-testing breadboard featuring a copper side, with necessary connections established between both sides. It is recommended to house the transmitter in an RF-proof enclosure, utilize high-quality connectors and cables, implement shielding between different stages, and adhere to established RF construction guidelines.
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to operate efficiently within the specified frequency range, providing a balance between output power and signal integrity. The use of a PLL can significantly improve frequency stability, reducing drift and enhancing overall performance, particularly in varying environmental conditions. The BLY88 amplifier serves as a crucial component, allowing the transmitter to achieve higher output power levels, making it suitable for more extensive coverage.
The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining a low SWR, as indicated by the observed value of 1:1.05, which minimizes signal reflection and potential damage to the transmitter. The RF-testing breadboard configuration allows for preliminary testing and adjustments before final implementation. The construction process should involve careful attention to detail, ensuring that all connections are secure and that the circuit is housed in an appropriate enclosure to prevent interference and signal degradation.
Proper shielding is essential in preventing unwanted emissions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Using quality connectors and cables reduces losses and enhances signal quality, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the transmitter. Following established RF building practices will help mitigate issues related to interference and enhance the reliability of the transmitter in practical applications.This is the schematic for an FM transmitter with 3 to 3. 5 W output power that can be used between 90 and 110 MHz. Although the stability isn`t so bad, a PLL can be used on this circuit. This is a circuit that I`ve build a few years ago for a friend, who used it in combination with the BLY88 amplifier to obtain 20 W output power. From the notes tha t I made at the original schematic, it worked fine with a SWR of 1 : 1. 05 (quite normal at my place with my antenna). The circuit has been tested on a normal RF-testing breadboard (with one side copper). Make some connections between the two sides. Build the transmitter in a RF-proof casing, use good connectors and cable, make a shielding between the different stages, and be aware of all the other RF rules of building. 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to operate efficiently within the specified frequency range, providing a balance between output power and signal integrity. The use of a PLL can significantly improve frequency stability, reducing drift and enhancing overall performance, particularly in varying environmental conditions. The BLY88 amplifier serves as a crucial component, allowing the transmitter to achieve higher output power levels, making it suitable for more extensive coverage.
The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining a low SWR, as indicated by the observed value of 1:1.05, which minimizes signal reflection and potential damage to the transmitter. The RF-testing breadboard configuration allows for preliminary testing and adjustments before final implementation. The construction process should involve careful attention to detail, ensuring that all connections are secure and that the circuit is housed in an appropriate enclosure to prevent interference and signal degradation.
Proper shielding is essential in preventing unwanted emissions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Using quality connectors and cables reduces losses and enhances signal quality, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the transmitter. Following established RF building practices will help mitigate issues related to interference and enhance the reliability of the transmitter in practical applications.This is the schematic for an FM transmitter with 3 to 3. 5 W output power that can be used between 90 and 110 MHz. Although the stability isn`t so bad, a PLL can be used on this circuit. This is a circuit that I`ve build a few years ago for a friend, who used it in combination with the BLY88 amplifier to obtain 20 W output power. From the notes tha t I made at the original schematic, it worked fine with a SWR of 1 : 1. 05 (quite normal at my place with my antenna). The circuit has been tested on a normal RF-testing breadboard (with one side copper). Make some connections between the two sides. Build the transmitter in a RF-proof casing, use good connectors and cable, make a shielding between the different stages, and be aware of all the other RF rules of building. 🔗 External reference