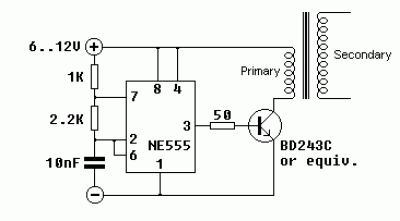
555 circuits 6
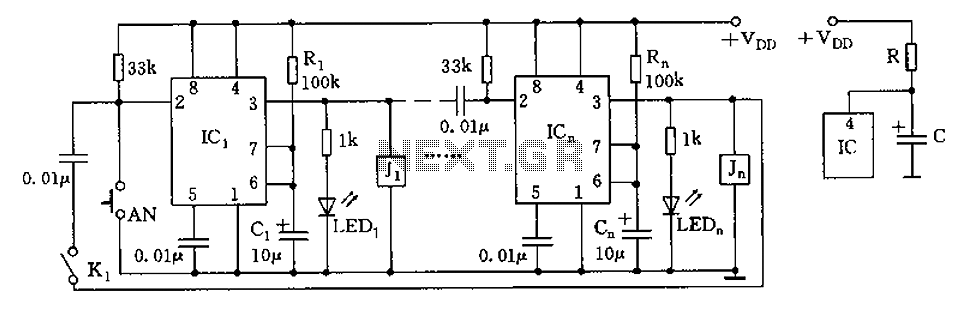
The core component of this circuit is the 555 timer IC. The alert sound does not stop immediately when the switch is activated; instead, it ceases automatically after a predetermined time period, which is set by the resistance of R3. In this case, R3 is configured to provide a time period of 1 minute and 6 seconds. The output of the 555 timer is triggered by a positive voltage on pin 2 when all switches are connected. When a switch disconnects pin 2, it results in a negative voltage, causing the 555 timer to stop. Capacitors C1 and C4 protect against noise signals from the switches that could inadvertently activate the alarm. This circuit can operate with a power supply ranging from 5V to 15V, depending on the relay used. It is designed to allow a user to turn off a lamp using a switch placed far from the bed, providing sufficient time to lie down before the lamp turns off. Users may find various applications for this circuit to meet their needs. Due to its low current consumption, the circuit can be powered directly from a 230VAC mains supply without a transformer. The supply voltage is reduced to 10VDC using C1 for reactance, along with a two-diode rectifier (D1 and D2) and a Zener diode (D3). The circuit employs a CMOS 555 timer (IC1) configured as a monostable multivibrator, which provides a 15-second on-time determined by R3 and C4. When switch SW1 is closed, the output from IC1 (pin 3) remains high, driving a triac (D4) that powers the lamp. When SW1 is opened, the monostable is triggered, and after 15 seconds, pin 3 of IC1 goes low, turning off the lamp. The circuit generates a high frequency using IC1, with the frequency determined by R1, C1, and C2, outputting from pin 3. This frequency is then amplified by IC2 to drive speakers, producing high-frequency sound. When switch S1 is activated, capacitor C1 continues to cycle in parallel with C2, resulting in a lower frequency output from pin 3 of IC1, which drives the speakers via IC2. The audio source generates two frequencies when the power is supplied to IC1, with pin 3 outputting at a frequency of 1 kHz. Transistors Q1 and Q2 operate in a push-pull configuration, alternating their functions. The circuit also features an LED indicator (LED2) that lights up when there is no output from pin 3, allowing current to flow through R2. The light from LED2 is shielded by a light-dependent resistor (LDR) when it is dark, increasing its resistance and generating a sufficient voltage drop across the LDR to activate IC1. The operation of the circuit relies on the interaction between IC1, R1, R2, and C1, forming an astable multivibrator that produces a square wave output at a frequency of 2.3 kHz from pin 3 of IC1. Capacitor C3 and diode D1 work together to clamp the signal, converting positive pulse signals to negative. Diodes D2 and C3 further convert the negative pulse signals to direct current (DC) electrical signals. This circuit diagram illustrates a ding-dong sound generator based on two NE555 timer ICs, designed to alternate between two adjustable frequencies to create the ding-dong sound. The first NE555 (IC1) operates as an astable multivibrator at 1 Hz, while the output from IC1 modulates the frequency of the second NE555 (IC2) by connecting it to the control pin (pin 5) of IC2. The tone of the sound is dependent on the frequency of IC2, while the changeover time is influenced by the frequency settings.
This circuit operates on the principle of using the 555 timer IC in various configurations to create timed events and sound generation. The primary function is to provide a delayed action for lamp control, allowing users to switch off the light without immediate disruption. The use of capacitors for noise filtering ensures stable operation, while the inclusion of transistors for audio output enhances the overall functionality. The design allows for flexibility in power supply options and provides a practical solution for everyday applications, such as lighting control and sound generation, thus enhancing user convenience and efficiency. The circuit can be adapted for various uses, making it a versatile addition to electronic projects.The heart of this circuit is IC No. 555. When the alert sound was working, even though the switch will continue to be the same, the sound still does not stop immediately. But it will stops automatically, when a set time period, Depending on the resistance of R3, the circuit so I set a time period equal to 1M for 1 minute 6 seconds.
The output of IC 555 is triggered by a positive voltage on pin 2, when all switches are connected together. When the something switch is cut off pin 2, it will be negative voltage and the trigger IC 555 will stop. The C1, C4 to protects a noise signal from either switch, which may cause the alarm to be up. This circuit can be used with power supply from 5V to 15V depending on relay sure enough. This circuit is intended to let the user turn off a lamp by means of a switch placed far from bed, allowing him enough time to lie down before the lamp really switches off.
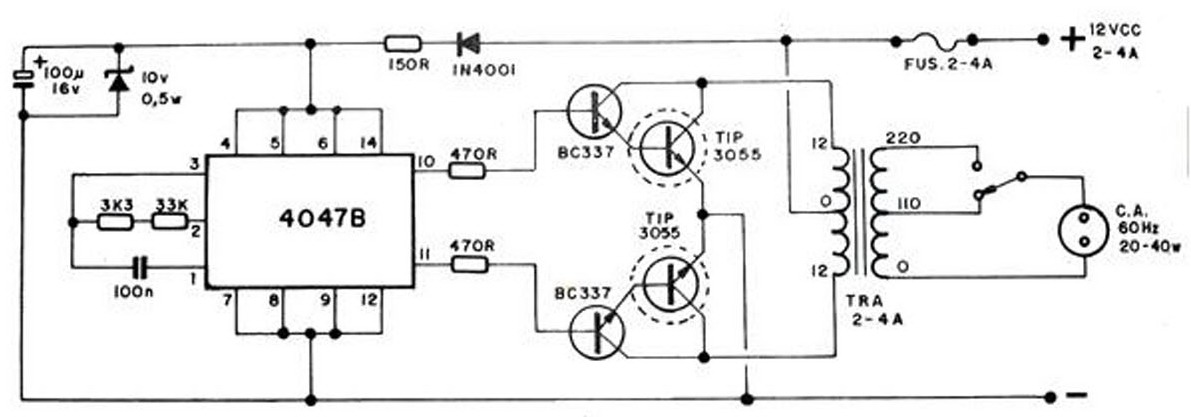
Obviously, users will be able to find different applications for this circuit in order to suit their needs. Due to the low current drawing, the circuit can be supplied from 230Vac mains without a transformer. Supply voltage is reduced to 10Vdc by means of C1 reactance, a two diode rectifier cell D1 & D2 and Zener diode D3.
IC1 is a CMos 555 timer wired as a monostable, providing 15 seconds on-time set by R3 & C4. When SW1 is closed, IC1 output (pin 3) is permanently on, driving Triac D4 which in turn feeds the lamp. Opening SW1 operates the monostable and, after 15 seconds, pin 3 of IC1 goes low switching off the lamp Operation of the circuit is when the power supply to the circuit.
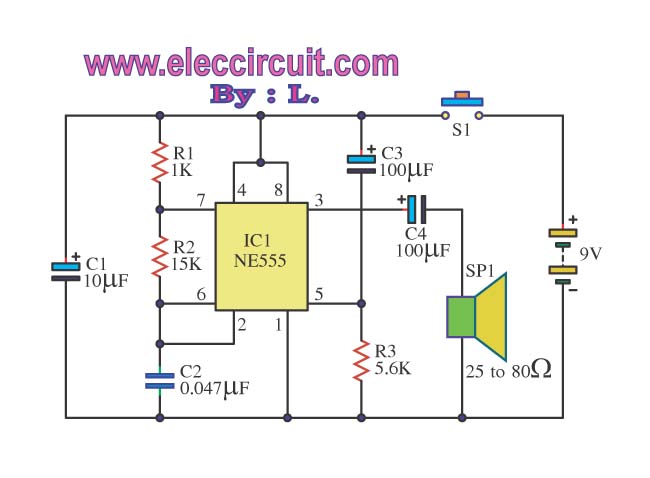
It will give birth to high frequency by using a circuit IC1 to a multi-state Devices Bill Brett Foster. The frequency with which R1, C1 and C2. The frequency will be out in three legs. And will be expanded with the IC2 output pin out of 5 in order to drive the speakers. The high-frequency sound. But when the switch S1, capacitor. C1, which continue to cycle in a manner parallel to the C2 value higher density. IC1 will give birth to low-frequency out of pin 3 to IC2 then drive the speakers. This circuit can cause the audio source has two frequency When the power supply input to IC1 is the output pin 3 at a frequency of 1 kHz.
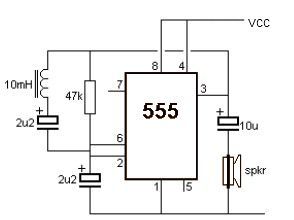
The frequency is Q1 and Q2, which will continue to use push pool work interchangeably. If this is the positive output signal Q1 Q2 will run the delete function this reason, C2 and C3 capacitors are half-wave alternating. Living in the current rush to waste time to even have little value. Electronic circuits, so one is important in everyday life. Which saves time and convenience. There is no output from the 3 pin. It make the current flows through R2, LED2 into three legs of IC1. The light LED2. But when a letter in the mail box to shield the light from the lamp. The LDR is not light. LDR will be much resistance. Voltage drop across the LDR is high enough to make IC1 work. Work of the circuit is IC1, R1, R2 and C1. The range of the A Stable Multi Vibrator, and the output is a square wave. It is a positive signal pulse frequency of 2. 3 kHz output pin 3 of IC1. And C3 and D1 connected to circuit CLAMP. That it serves to signal a positive pulse to pulse signal negative. The D2 and C3 act negative pulse signal is converted direct current (DCV) electrical signals. The negative power. Thus the output voltage to a negative DC electrical This is the circuit diagram of a ding dong sound generator based on two NE555 timer ICs.
The circuit is designed to toggle between two adjustable frequencies to produce the ding dong sound. The first NE555 (IC1) is wires as an astable multivibrator operating at 1Hz. The frequency of the second NE555 (IC2) is modulated by the output from the first IC. This is attained by connecting the output of first IC to the control pin (pin5) of the second IC. The tone of the sound depends on the frequency of the second IC and the changeover time depends on the freq 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates on the principle of using the 555 timer IC in various configurations to create timed events and sound generation. The primary function is to provide a delayed action for lamp control, allowing users to switch off the light without immediate disruption. The use of capacitors for noise filtering ensures stable operation, while the inclusion of transistors for audio output enhances the overall functionality. The design allows for flexibility in power supply options and provides a practical solution for everyday applications, such as lighting control and sound generation, thus enhancing user convenience and efficiency. The circuit can be adapted for various uses, making it a versatile addition to electronic projects.The heart of this circuit is IC No. 555. When the alert sound was working, even though the switch will continue to be the same, the sound still does not stop immediately. But it will stops automatically, when a set time period, Depending on the resistance of R3, the circuit so I set a time period equal to 1M for 1 minute 6 seconds.
The output of IC 555 is triggered by a positive voltage on pin 2, when all switches are connected together. When the something switch is cut off pin 2, it will be negative voltage and the trigger IC 555 will stop. The C1, C4 to protects a noise signal from either switch, which may cause the alarm to be up. This circuit can be used with power supply from 5V to 15V depending on relay sure enough. This circuit is intended to let the user turn off a lamp by means of a switch placed far from bed, allowing him enough time to lie down before the lamp really switches off.
Obviously, users will be able to find different applications for this circuit in order to suit their needs. Due to the low current drawing, the circuit can be supplied from 230Vac mains without a transformer. Supply voltage is reduced to 10Vdc by means of C1 reactance, a two diode rectifier cell D1 & D2 and Zener diode D3.
IC1 is a CMos 555 timer wired as a monostable, providing 15 seconds on-time set by R3 & C4. When SW1 is closed, IC1 output (pin 3) is permanently on, driving Triac D4 which in turn feeds the lamp. Opening SW1 operates the monostable and, after 15 seconds, pin 3 of IC1 goes low switching off the lamp Operation of the circuit is when the power supply to the circuit.
It will give birth to high frequency by using a circuit IC1 to a multi-state Devices Bill Brett Foster. The frequency with which R1, C1 and C2. The frequency will be out in three legs. And will be expanded with the IC2 output pin out of 5 in order to drive the speakers. The high-frequency sound. But when the switch S1, capacitor. C1, which continue to cycle in a manner parallel to the C2 value higher density. IC1 will give birth to low-frequency out of pin 3 to IC2 then drive the speakers. This circuit can cause the audio source has two frequency When the power supply input to IC1 is the output pin 3 at a frequency of 1 kHz.
The frequency is Q1 and Q2, which will continue to use push pool work interchangeably. If this is the positive output signal Q1 Q2 will run the delete function this reason, C2 and C3 capacitors are half-wave alternating. Living in the current rush to waste time to even have little value. Electronic circuits, so one is important in everyday life. Which saves time and convenience. There is no output from the 3 pin. It make the current flows through R2, LED2 into three legs of IC1. The light LED2. But when a letter in the mail box to shield the light from the lamp. The LDR is not light. LDR will be much resistance. Voltage drop across the LDR is high enough to make IC1 work. Work of the circuit is IC1, R1, R2 and C1. The range of the A Stable Multi Vibrator, and the output is a square wave. It is a positive signal pulse frequency of 2. 3 kHz output pin 3 of IC1. And C3 and D1 connected to circuit CLAMP. That it serves to signal a positive pulse to pulse signal negative. The D2 and C3 act negative pulse signal is converted direct current (DCV) electrical signals. The negative power. Thus the output voltage to a negative DC electrical This is the circuit diagram of a ding dong sound generator based on two NE555 timer ICs.
The circuit is designed to toggle between two adjustable frequencies to produce the ding dong sound. The first NE555 (IC1) is wires as an astable multivibrator operating at 1Hz. The frequency of the second NE555 (IC2) is modulated by the output from the first IC. This is attained by connecting the output of first IC to the control pin (pin5) of the second IC. The tone of the sound depends on the frequency of the second IC and the changeover time depends on the freq 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713