555 timer astable multivibrator
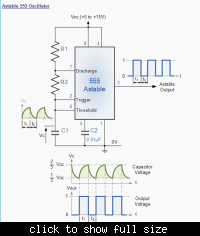
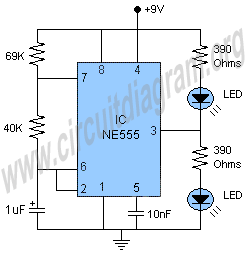
In the following astable multivibrator circuit, some sources state that the duty cycle is represented as d = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 * R2), while other sources provide different information.
The astable multivibrator circuit is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. This circuit typically consists of two resistors (R1 and R2), a capacitor (C), and a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to operate in a feedback loop.
The duty cycle, defined as the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active, is crucial for determining the output waveform characteristics. In this context, the formula d = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 * R2) calculates the duty cycle based on the resistors' values. The components' values influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform, which can be adjusted by changing R1, R2, or C.
In a typical astable multivibrator setup, the output frequency (f) can be derived from the formula f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C). This relationship indicates that both the resistor and capacitor values directly affect the frequency of oscillation. The output waveform will alternate between high and low states, with the duration of each state determined by the duty cycle.
The astable multivibrator can be implemented using various configurations, such as using a 555 timer IC or discrete components. The choice of components and their values will dictate the performance characteristics of the circuit, including the stability of the output frequency and the precision of the duty cycle.
In summary, understanding the duty cycle and its calculation is essential for designing astable multivibrator circuits that meet specific timing requirements. The ability to manipulate R1, R2, and C allows for a wide range of applications, from simple LED blinkers to more complex timing circuits in digital electronics.In the following astable multivibrator circuit, in some books, it is mentioned that the duty cycle id d=( R1+R2)/(R1+2*R2) in some other books, it is.. 🔗 External reference
The astable multivibrator circuit is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. This circuit typically consists of two resistors (R1 and R2), a capacitor (C), and a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to operate in a feedback loop.
The duty cycle, defined as the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active, is crucial for determining the output waveform characteristics. In this context, the formula d = (R1 + R2) / (R1 + 2 * R2) calculates the duty cycle based on the resistors' values. The components' values influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform, which can be adjusted by changing R1, R2, or C.
In a typical astable multivibrator setup, the output frequency (f) can be derived from the formula f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C). This relationship indicates that both the resistor and capacitor values directly affect the frequency of oscillation. The output waveform will alternate between high and low states, with the duration of each state determined by the duty cycle.
The astable multivibrator can be implemented using various configurations, such as using a 555 timer IC or discrete components. The choice of components and their values will dictate the performance characteristics of the circuit, including the stability of the output frequency and the precision of the duty cycle.
In summary, understanding the duty cycle and its calculation is essential for designing astable multivibrator circuits that meet specific timing requirements. The ability to manipulate R1, R2, and C allows for a wide range of applications, from simple LED blinkers to more complex timing circuits in digital electronics.In the following astable multivibrator circuit, in some books, it is mentioned that the duty cycle id d=( R1+R2)/(R1+2*R2) in some other books, it is.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713