555 Voltage Doubler Relay Driver
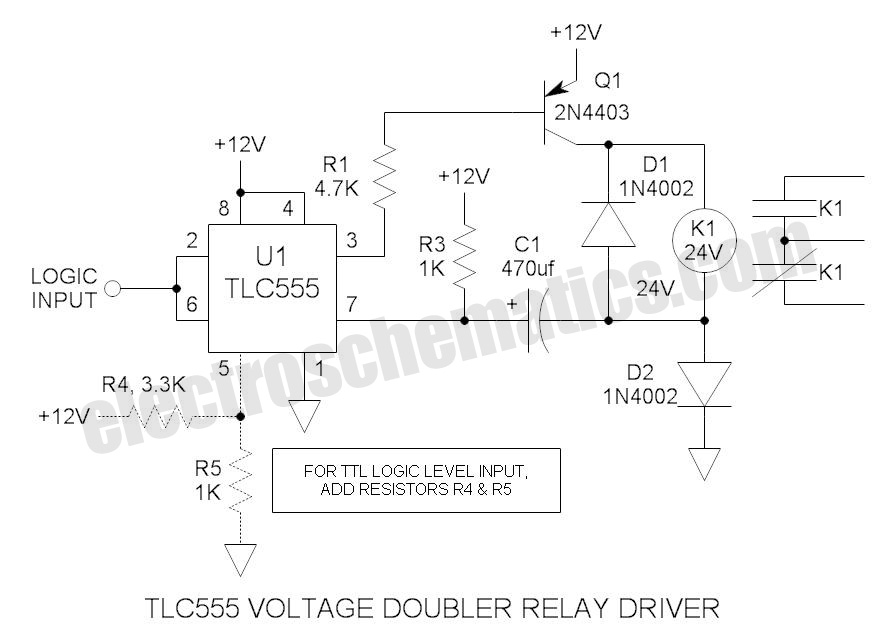
These novel relay driver circuits can activate a relay with a coil voltage rating that is double the Vcc. After activation, the relay armature is held in place.
The relay driver circuits described are designed for applications requiring the control of relays with higher coil voltage ratings than the supply voltage (Vcc) available in the circuit. These circuits employ innovative techniques to ensure reliable operation despite the increased voltage requirements.
The primary components of the relay driver circuit typically include a transistor or MOSFET that acts as a switch, a diode for flyback protection, and the relay itself. The circuit is powered by a voltage supply (Vcc), which is lower than the relay coil voltage rating. The transistor is used to amplify the control signal, allowing it to manage the higher voltage required to energize the relay coil.
When a control signal is applied to the base (for bipolar transistors) or gate (for MOSFETs) of the transistor, it turns on, creating a path for current to flow through the relay coil. This current generates a magnetic field strong enough to pull in the relay armature, connecting the normally open contacts and allowing current to flow through the load connected to the relay.
To safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is deactivated, a flyback diode is placed in parallel with the relay coil. This diode provides a path for the inductive kickback current, protecting the transistor from potential damage due to high voltage transients.
These relay driver circuits are particularly useful in applications where control signals are limited to low voltages, yet there is a need to control devices that operate on higher voltages. This capability enhances the versatility and reliability of relay-based control systems in various electronic applications.These novel relay driver circuits have the ability to pick up a relay with a coil voltage rating equal to double Vcc. After pickup, the relay armature is h.. 🔗 External reference
The relay driver circuits described are designed for applications requiring the control of relays with higher coil voltage ratings than the supply voltage (Vcc) available in the circuit. These circuits employ innovative techniques to ensure reliable operation despite the increased voltage requirements.
The primary components of the relay driver circuit typically include a transistor or MOSFET that acts as a switch, a diode for flyback protection, and the relay itself. The circuit is powered by a voltage supply (Vcc), which is lower than the relay coil voltage rating. The transistor is used to amplify the control signal, allowing it to manage the higher voltage required to energize the relay coil.
When a control signal is applied to the base (for bipolar transistors) or gate (for MOSFETs) of the transistor, it turns on, creating a path for current to flow through the relay coil. This current generates a magnetic field strong enough to pull in the relay armature, connecting the normally open contacts and allowing current to flow through the load connected to the relay.
To safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is deactivated, a flyback diode is placed in parallel with the relay coil. This diode provides a path for the inductive kickback current, protecting the transistor from potential damage due to high voltage transients.
These relay driver circuits are particularly useful in applications where control signals are limited to low voltages, yet there is a need to control devices that operate on higher voltages. This capability enhances the versatility and reliability of relay-based control systems in various electronic applications.These novel relay driver circuits have the ability to pick up a relay with a coil voltage rating equal to double Vcc. After pickup, the relay armature is h.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713